‘i’m 23 And Have Lived With Type 1 Diabetes All My Life This Is What I Wish People Knew’
Editor’s note: The opinions in this article are the author’s, as published by our content partner, and do not represent the views of MSN or Microsoft.
I was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at just 14 months old, so I’ve never known life without it.
I’ve also never known life without the love and support of parents who have never stopped encouraging me to live as normal a life as possible.
From a very young age, they instilled in me that all my dreams were achievable and nothing – certainly not my diabetes – would stop me.
“You live your life, and we’ll deal with the diabetes side of things,” is what they always told me.
Despite their reassurance, raising a toddler is tough enough, without the additional challenges of type 1 diabetes.
From waking up three times a night to test my blood glucose levels to all the extra planning that went into every single detail of my life, I didn’t know any different. This was my normal.
As I got older, I noticed I wasn’t the same as everyone else.
In primary school, my mum would come to school every lunchtime to administer my insulin, and I began wondering why my mum was the only one who came in to visit every single day.
The feeling of being different really manifested during my teen years.
Having type 1 diabetes as a high school student meant I had to be more organised than any teenager – thinking ahead about what foods I would eat and how activities like PE class would affect my blood sugar levels and insulin dosage.
Additional Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes In Babies And Toddlers
- Weight loss
- Failure to thrive, a condition involving weight loss or inability to gain weight combined with stunted growth
- Colic or fussiness that just won’t let up
- Poor-quality sleep that doesn’t improve no matter what you try
- Bedwetting, especially after successful potty-training
All of these symptoms are a result of hyperglycemia—too much glucose circulating in our bloodstream, also known as high blood sugar. Any person experiencing hyperglycemia, particularly after a viral illness, should seek immediate medical help.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Someone With Type 1 Diabetes
Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association reported that people with type 1 diabetes live about 11 years less than average; however, new research also suggests this differential can be reduced with good glycemic control. Most people with type 1 diabetes die from complications of type 1 diabetes such as heart disease or kidney disease. Thus, preventing complications and following a healthy lifestyle that prevents heart disease and controls blood sugar are the best things people with type 1 diabetes can do to live a long, healthy life.
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Type 1 Diabetes
Health care professionals usually test people for type 1 diabetes if they have clear-cut diabetes symptoms. Health care professionals most often use the random plasma glucose test to diagnose type 1 diabetes. This blood test measures your blood glucose level at a single point in time. Sometimes health professionals also use the A1C blood test to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose.
Even though these tests can confirm that you have diabetes, they can’t identify what type you have. Treatment depends on the type of diabetes, so knowing whether you have type 1 or type 2 is important.
To find out if your diabetes is type 1, your health care professional may test your blood for certain autoantibodies. Autoantibodies are antibodies that attack your healthy tissues and cells by mistake. The presence of certain types of autoantibodies is common in type 1 but not in type 2 diabetes.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
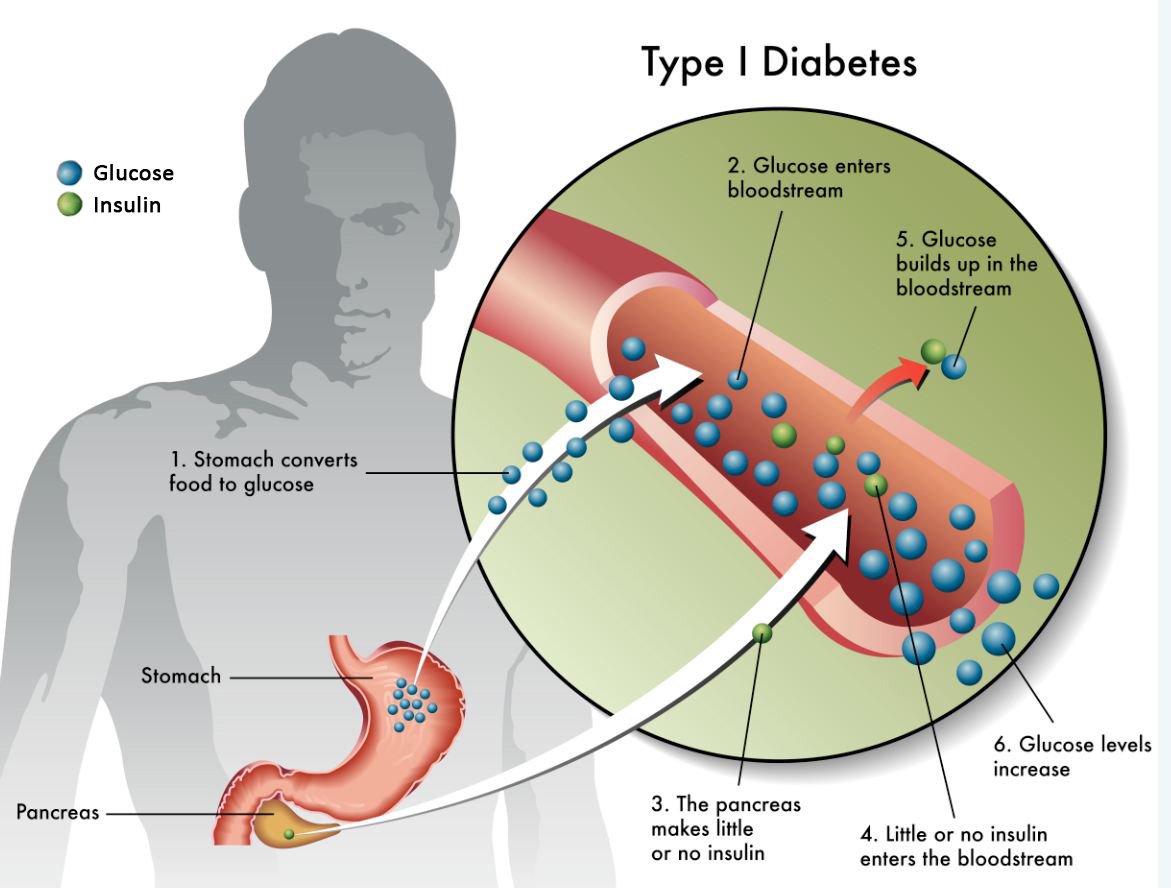
The major process that happens in type 1 diabetes is that the pancreas can no longer produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is more a result of insulin resistance , that is, it takes a large amount of insulin to move glucose out of the blood and into the cells. Over time, people with type 2 diabetes also may experience decreased insulin production in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, over time, the body can also develop insulin resistance — especially in people who gain a lot of weight while using insulin. This means there is some overlap in treatment and diet for people who have had diabetes of either type for a long time.
What Is The Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes Can It Be Cured
Currently, type 1 diabetes cannot be cured. People with type 1 diabetes require injectable insulin because their pancreas does not produce enough on its own. There are different types of insulin and different routes of administration. Most people with type 1 diabetes use both a long-acting insulin , and inject additional insulin before or after meals to match the carbohydrate content of the meal. An insulin pump may also be used to optimize insulin delivery to the body’s needs.
- Unfortunately, one of the major side effects of insulin is weight gain. People with type 1 diabetes can reduce weight gain by:
- Eating a healthy low-carbohydrate diet,
- Getting plenty of exercise, and
- Learning to use insulin correctly in order to use just the right amount
- Diet and level of activity.
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing “artificial pancreas” technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
What Happens If A Person With Type 1 Diabetes Gets Covid
COVID-19 has been controlling our lives since March of 2020. Over 2.7 million people worldwide are now dead from this virus. Many advisories have stated that people with type 1 diabetes and the elderly are both at high risks should they get COVID-19. It is therefore not surprising that many people are asking, what happens if a person with type 1 diabetes gets COVID-19?
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Think of insulin as a key that unlocks your cells, says Ilana Halperin MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto. In type 1 diabetes, there is simply no key. “There is a total absence of insulin coming from the cells in the pancreas,” she says. Essentially, the body destroys the cells in the pancreas that are responsible for making insulin.
In type 2 diabetes, you have a rusty key that can’t open the lock as well. In this form, a person develops an insulin resistance, so that insulin doesn’t perform correctly in their body.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes Onset In An Infant Or Child
The young child who is urinating frequently, drinking large quantities, losing weight, and becoming more and more tired and ill is the classic picture of a child with new-onset type 1 diabetes. If a child who is potty-trained and dry at night starts having accidents and wetting the bed again, diabetes might be the culprit.
Although it is easy to make the diagnosis diabetes in a child by checking blood sugar at the doctor’s office or emergency room, the tricky part is recognizing the symptoms and knowing to take the child to get checked. Raising the awareness that young children, including infants, can get type 1 diabetes can help parents know when to check for type 1 diabetes.
Sometimes children can be in diabetic ketoacidosis when they are diagnosed with diabetes. When there is a lack of insulin in the body, the body can build up high levels of an acid called ketones. DKA is a medical emergency that usually requires hospitalization and immediate care with insulin and IV fluids. After diagnosis and early in treatment, some children may go through a phase where they seem to be making enough insulin again. This is commonly called the “honeymoon phase”. It may seem like diabetes has been cured, but over time they will require appropriate doses of insulin to keep their blood sugar levels in the normal range.
What Medicines Do I Need To Treat My Type 1 Diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. Different types of insulin start to work at different speeds, and the effects of each last a different length of time. You may need to use more than one type. You can take insulin a number of ways. Common options include a needle and syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump.
Some people who have trouble reaching their blood glucose targets with insulin alone also might need to take another type of diabetes medicine that works with insulin, such as pramlintide. Pramlintide, given by injection, helps keep blood glucose levels from going too high after eating. Few people with type 1 diabetes take pramlintide, however. The NIH has recently funded a large research study to test use of pramlintide along with insulin and glucagon in people with type 1 diabetes. Another diabetes medicine, metformin, may help decrease the amount of insulin you need to take, but more studies are needed to confirm this. Reseachers are also studying other diabetes pills that people with type 1 diabetes might take along with insulin.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur if you take insulin but don’t match your dose with your food or physical activity. Severe hypoglycemia can be dangerous and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about hypoglycemia and how to prevent or treat it.
What If My Child With Type 1 Diabetes Develops Covid
Children are heading back to school in most regions and there is a very real fear about them heading back to school during a global pandemic. Researchers at Diabetes Quebec feel that children and young adults living with type 1 diabetes are not likely to experience the extreme symptoms associated with COVID-19. This is most likely because children and adolescents usually do not have any complications yet. It seems that it is those comorbidities that increase the risk of complications from COVID-19.
More Severe Symptoms Of Untreated Type 1 Diabetes
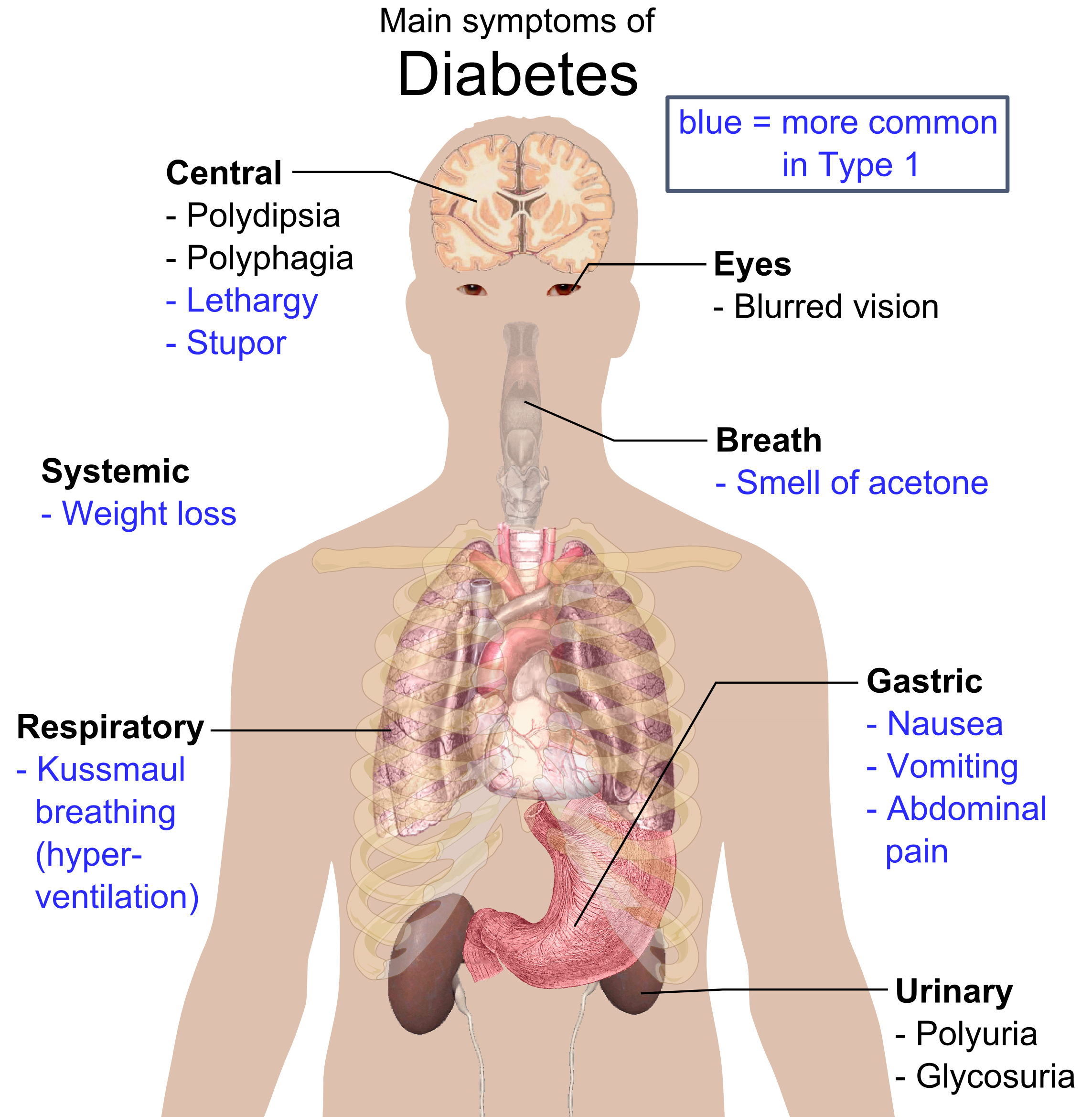
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
When type 1 diabetes goes untreated, it can lead to organ failure, coma, and even death. This happens because the body can no longer turn glucose into fuel, and it starts burning fat, which then produces ketones in the blood and urine.
A small amount of ketones aren’t dangerous and can usually be detected if a person has been fasting or is on a low-carbohydrate diet. But too many ketones can actually change the blood’s acidity and result in a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
If you have one or more of these symptoms contact your doctor.
Symptoms of type1 diabetes tend to look different in children than adults, according to Dr. Christofides.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
People can have diabetes without knowing it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Type 1 diabetes may come on gradually or suddenly.
When a person first has type 1 diabetes, he or she may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- eat a lot because the body is hungry for the energy it can’t get from sugar
- lose weight because the body starts to use fat and muscle for fuel
- feel tired all the time
Also, girls who have developed diabetes are more likely to get vaginal yeast infections before they’re diagnosed and treated.
If these early symptoms of diabetes aren’t recognized and treatment isn’t started, chemicals can build up in the blood and cause stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, breathing problems, and even loss of consciousness. Doctors call this diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
There’s good news, though — getting treatment can control or stop these diabetes symptoms from happening and reduce the risk of long-term problems.
Will I Have To Go To The Hospital If I Get Covid
According to Diabetes Canada only one in every six people who get COVID-19 become seriously ill and develop difficulty breathing. For people with type 1 diabetes, the biggest risk when having COVID-19 seems to be developing Diabetic Ketoacidosis so make sure that you stay hydrated and check your blood glucose levels often.
You should contact your doctor if you …
- When you are not sure what to do.
- If you vomit repeatedly .
- If vomiting persists beyond 2 hours .
- If blood glucose stays high for more than 24 hours
- If you develop symptoms which could be indicative of their developing diabetic ketoacidosis .
- If blood ketones remain elevated > 1.5 mmol/L or urine ketones remain large despite extra insulin and hydration
Always keep your sick day protocol handy. You can get a copy of sick day management tips here.
Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatments And Support
With Ilana Halperin MD and Elena Christofides MD
Learning you or your child has type 1 diabetes means taking an active role in health 24/7. Luckily, there are more low-key ways to track blood sugar and administer insulin than ever. From glucose monitoring to meal planning, we’re here to empower you with clear answers to all your pressing questions.
| Frequently Asked Questions | Support
How Do I Keep My Blood Sugar Under Tight Control
Insulin helps people with type 1 diabetes keep the level of sugar in their blood at a normal level. Many people with type 1 diabetes take short-acting insulin before each meal. You can adjust the amount of insulin you take for each meal based on how many calories you eat and how physically active you plan to be in the next 3 to 4 hours. Most people with type 1 diabetes need to take about 8 to 10 units of insulin for every 500 calories they eat. You may need slightly less or slightly more insulin, depending on how your body reacts to insulin. Take enough insulin so your blood sugar level is usually between 80 and 120 mg and doesn’t go above 180 mg after meals.
To keep their blood sugar levels from rising during the night, most people with type 1 diabetes need to take 4 to 8 units of an intermediate-acting insulin before they go to sleep. If you carry a syringe of short-acting insulin wherever you go, you’ll always be ready if you need more insulin.
What Happens If You Don’t Treat Type 1 Diabetes
What happens if you don’t treat type 1 diabetes? If you dont keep your type 1 diabetes well controlled, you could set yourself up for serious or life-threatening problems: Retinopathy. This eye problem happens in about 80% of adults who have had type 1 diabetes for more than 15 years. Its rare before puberty no matter how long youve had the disease. To prevent it — and keep your eyesight — keep good control of blood sugar, blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. Kidney damage. About 20% to 30% of people with type 1 diabetes get a condition called nephropathy. The chances grow over time. Its most likely to show up 15 to 25 years after the onset of diabetes. It can lead to other serious problems like kidney failure and heart disease. Poor blood circulation and nerve damage. Damaged nerves and hardened arteries lead to a loss of sensation in and a lack of blood supply to your feet. This raises your chances of injury and makes it harder for open sores and wounds to heal. And when that happens, you could lose a limb. Nerve damage can also cause digestive problems like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.Continue reading >>
What Happens After A Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis
Once you—or your child—is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, treatment with insulin can begin to help regulate blood glucose levels. You will have a diabetes treatment team that will help you make the transition to this new world of type 1 diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes. Medline Plus. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000305.htm. Accessed January 30, 2015.
- What is Type 1 Diabetes? Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. http://jdrf.org/life-with-t1d/frequently-asked-questions/. Accessed January 30, 2015.
- American Diabetes Association. http://www.diabetes.org/are-you-at-risk/prediabetes/?loc=atrisk-slabnav. Accessed January 30, 2015.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment: Artificial Pancreas
Researchers are developing an artificial pancreas. This device is a combination of an insulin pump and continuous glucose monitoring system controlled by a computer program. The goal for the system is to have a device that mimics the function of a normal pancreas.
Additional Information on Diabetes
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 1 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to take insulin, think about how they eat, and control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, helpless, or that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your doctor or diabetes health care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
What Should I Do If I Test Positive For Covid
As we have said, everyone will experience COVID-19 differently and for varying lengths of time. This is the best advice that we came across for people living with type 1 diabetes…
I would say that each and everyone’s COVID-19 experience is different just like their diabetes. Please reach out to your Endocrinologist and let them know you are currently positive. They can help you best with blood sugar control. Wash and clean as much as you can. Most of all rest and be kind to yourself during this time.
L. Ellingson
Whether you develop COVID-19 or come down with any other bug, make sure that you stay hydrated, check your blood glucose levels often, and follow the sick day guidelines provided by your diabetes care team.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes And Why Does It Occur
There are two main types of diabetes, known as “Type 1 Diabetes” and “Type 2 Diabetes”.
These two conditions are generally considered to be 2 different and separate conditions, so it is important to understand the differences between the two.
Some old names for Type 1 Diabetes include: “Juvenile Diabetes”, “Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus” and “IDDM”. These old names should not be used, as they are no longer considered correct.
Important Stuff to Know
In our bodies, an organ known as the pancreas produces insulin, which is a very important hormone. Insulin is vital because it enables the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. We need insulin to survive.
In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks the insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas. This usually happens in younger people, but it can happen at any age. When this happens, the pancreas no longer produces insulin.
So what happens if there is no insulin in your body?
The main effect is high blood sugar . Insulin normally moves blood sugar into body tissues where it is used for energy. When there is no insulin, sugar builds up in the blood.
High blood sugar is dangerous, with many side effects. It also causes damage to the body.
What are the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes?
The symptoms of Type 1 diabetes are all based on the fact that there is high blood sugar. The symptoms include:
- Extreme thirst
When the blood sugar is stabilised by treatment, these symptoms go away.
How Will I Know If My Blood Sugar Is Too High
Even with treatment, people with type 1 diabetes sometimes have blood sugar levels that are too high. The best way to check your blood sugar level and to see how sensitive you are to insulin is to test your blood sugar level at least three times each day, including at bedtime. If it’s too high, take some extra short-acting insulin. If your level is too low, eat some food.
Diabetes: Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus , also known as type 1 diabetes, usually starts before 15 years of age, but can occur in adults also. Diabetes involves the pancreas gland, which is located behind the stomach . The special cells of the pancreas produce a hormone called insulin.
The body is made up of millions of cells. All cells need glucose from the food we eat for energy. Just as a car can’t run without gasoline, the body can’t work without glucose. Insulin is the “key” that allows glucose to enter the cells. Without this key, glucose stays in the bloodstream and the cells can’t use it for energy. Instead, the glucose builds up in the blood and spills over into the urine. When a person develops type 1 diabetes, the pancreas stops making insulin. To help the body’s cells use the glucose, a child with type 1 diabetes mellitus must receive insulin by injection .
Type 1 Diabetes And What Happens In The Body
Type 1 diabetes is what happens when the beta cells in the pancreas die and there is little or no insulin in the body. Children and teens are more frequently diagnosed with type 1 much more frequently than adults. Symptoms may not show themselves until an emergency occurs when the body can no longer handle the impact of extremely high blood sugar levels. This is when a condition called ketoacidosis occurs.
Type 1 diabetes is also an autoimmune disease. It results usually from the failure of the body’s failure to fight infections naturally, commonly such as strep infections.
Though scientists never have been clear about what causes Type 1, there are several known factors about this complex disease.
Ketoacidosis is an medical emergency. The symptoms are extreme thirst/dehydration, fruity breath, vomiting, and if the sugars get over 500, trouble breathing. It is important to seek medical attention right away when this happens.
Early on, signs of type 1 may show in extreme weight loss even with eating a lot and a ravenous appetite. There is usually extreme thirst and frequent urination, sometimes with bedwetting. A simple blood sugar test by fasting determines whether type 1 is present or is in the process.
Type 1 can lead to other serious complications if not treated properly. A close relationship with your doctor and healthcare team is very important when diagnosed with Type 1 or 2 diabetes.

