Starting Dose In Insulin Nave Patients
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus:
The recommended starting dose of TRESIBA in insulin naïve patients with type 1 diabetes is approximately one-third to one-half of the total daily insulin dose. The remainder of the total daily insulin dose should be administered as a short-acting insulin and divided between each daily meal. As a general rule, 0.2 to 0.4 units of insulin per kilogram of body weight can be used to calculate the initial total daily insulin dose in insulin naïve patients with type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
The recommended starting dose of TRESIBA in insulin naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is 10 units once daily.
Calibrating The Insulin To Carb Ratio
Before trying to fine tune the insulin to carb ratio used at any given meal, it is best to determine your basal insulin levels first. Any changes to the total amount of insulin you take in per day will mean you have to calculate your insulin to carbohydrate ratio all over again. This is done through basic trial and error. Make sure you take into account factors such as the time of day you are eating and your total body weight while deciding on the right insulin to carbohydrate ratio at any given meal.
It is important to keep a detailed record of your eating habits, the amount of carbohydrates you eat per day, the amount of insulin you are using, and the amount of exercise you do per day. Write down your blood sugar level prior to eating and then again at 3 to 4 hours after your meal. Dont eat anything else or exercise during this time and dont take extra insulin before measuring the second blood sugar level.
The best thing to do is to eliminate those readings you get that are impacted by other factors that affect insulin sensitivity, such as strenuous physical activity. You should also discount meals you eat at a restaurant as they are often very high in fat and you may not be able to determine how many carbohydrates are in the meal. This can throw off your insulin requirements and wont be helpful in determining your average insulin to carbohydrate level.
You’ll Need To Calculate Some Of Your Insulin Doses
You’ll also need to know some basic things about insulin. For example, 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight.
Your provider will prescribe an insulin dose regimen for you however, you still need to calculate some of your insulin doses. Your insulin dose regimen provides formulas that allow you to calculate how much bolus insulin to take at meals and snacks, or to correct high blood sugars.
You May Like: Are Bananas Bad For Type 2 Diabetes
First Some Basic Things To Know About Insulin:
- Approximately 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight, when you are fasting and between meals. This is called background or basal insulin replacement. The basal or background insulin dose usually is constant from day to day.
- The other 50-60% of the total daily insulin dose is for carbohydrate coverage and high blood sugar correction. This is called the bolus insulin replacement.
Bolus Carbohydrate coverage
The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio.The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin.
Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of 12-15 grams of carbohydrate. This range can vary from 6-30 grams or more of carbohydrate depending on an individuals sensitivity to insulin. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress.
Bolus High blood sugar correction
The bolus dose for high blood sugar correction is defined as how much one unit of rapid-acting insulin will drop the blood sugar.
Generally, to correct a high blood sugar, one unit of insulin is needed to drop the blood glucose by 50 mg/dl. This drop in blood sugar can range from 30-100 mg/dl or more, depending on individual insulin sensitivities, and other circumstances.
Starting Dose In Patients Already On Insulin Therapy
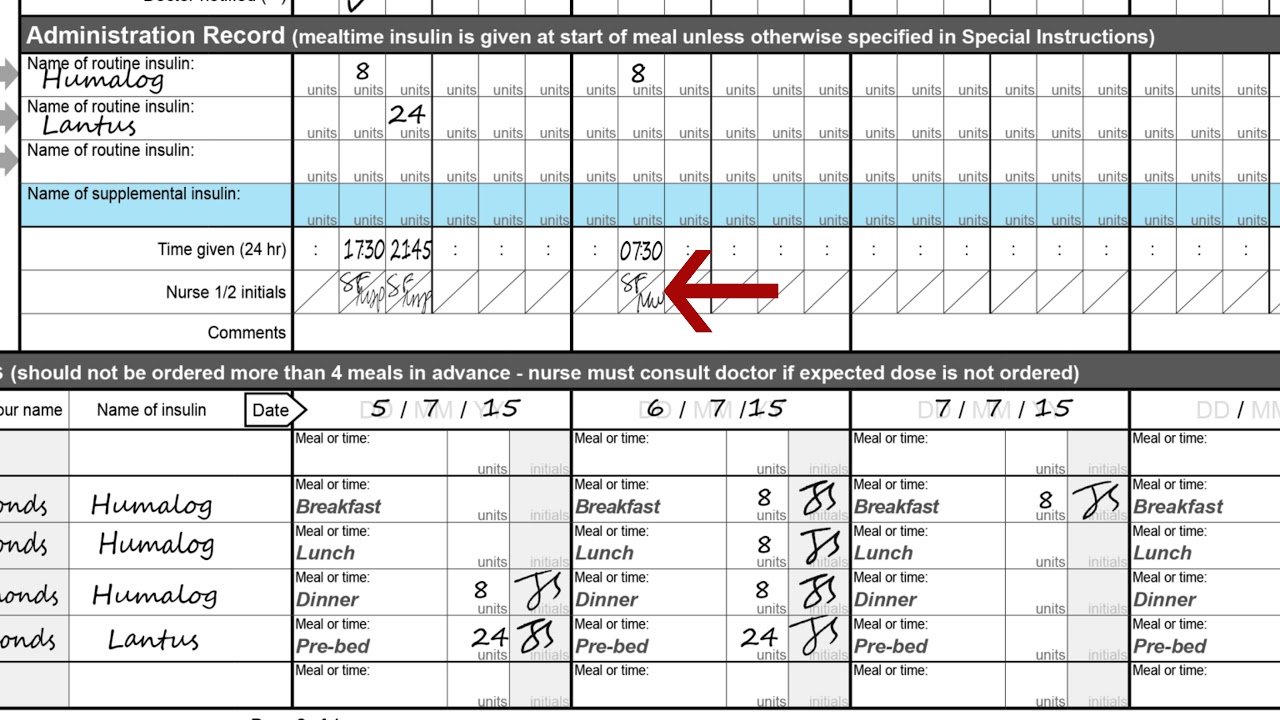
Adults withType 1 or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Start TRESIBA at the same unit dose as the total daily long or intermediate-acting insulin unit dose.
Pediatric Patients 1 Year of Age and Older with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Start TRESIBA at 80% of the total daily long or intermediate-acting insulin unit dose to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia .
Don’t Miss: High Blood Sugar Symptom
Ways To Determine Dosage Of Insulin
Insulin is the groundwork of treatment for a majority of diabetics. If a person is diabetic, his or her body either fails to produce sufficient insulin or effectively make use of insulin. Individuals with type 1 diabetes and few individuals with type 2 diabetes ought to take numerous injections of insulin each day. Insulin normalizes blood glucose and avoids spikes in glucose levels. This also assists in preventing complications. The insulin amount a person can take can be determined in different ways:
Also Read: Energy Drinks For Diabetics
Example #: Carbohydrate Coverage At A Meal
First, you have to calculate the carbohydrate coverage insulin dose using this formula:
CHO insulin dose = Total grams of CHO in the meal ÷ grams of CHO disposed by 1 unit of insulin .
For Example #1, assume:
- You are going to eat 60 grams of carbohydrate for lunch
- Your Insulin: CHO ratio is 1:10
To get the CHO insulin dose, plug the numbers into the formula:
CHO insulin dose =
- The carbohydrate coverage dose is 6 units of rapid acting insulin.
- The high blood sugar correction dose is 2 units of rapid acting insulin.
Now, add the two doses together to calculate your total meal dose.
Carbohydrate coverage dose + high sugar correction dose = 8 units total meal dose!
The total lunch insulin dose is 8 units of rapid acting insulin.
You May Like: Metformin Overdose How Much
The High Blood Sugar Correction Factor:
Correction Factor = 1800 ÷Total Daily Insulin Dose = 1 unit of insulin will reduce the blood sugar so many mg/dl
This can be calculated using the Rule of 1800.
Example:
= 1800 ÷ TDI = 1 unit insulin will drop reduce the blood sugar level by 45 mg/dl
While the calculation is 1 unit will drop the blood sugar 45 mg/dl, to make it easier most people will round up or round down the number so the suggested correction factor may be 1 unit of rapid acting insulin will drop the blood sugar 40-50 mg/dl.
Please keep in mind, the estimated insulin regimen is an initial best guess and the dose may need to be modified to keep your blood sugar on target.
Also, there are many variations of insulin therapy. You will need to work out your specific insulin requirements and dose regimen with your medical provider and diabetes team.
What Strengths Does Humalog Come In
Humalog comes in two strengths: U-100, which contains 100 units of insulin per mL, and U-200, which contains 200 units of insulin per mL. The U-200 strength is used only for subcutaneous injections.
Humalog Mix50/50 and Humalog Mix75/25 come in only the U-100 strength. Humalog Mix50/50 contains 50% insulin lispro and 50% insulin lispro protamine. Humalog Mix75/25 contains 75% insulin lispro protamine and 25% insulin lispro.
Also Check: Bananas Bad For Diabetics
Check 3 Am Blood Glucoses
It is important to make sure the basal insulin change is right for you. You will want to check your blood glucose at 3:00 a.m. for 2 to 3 days after you make a change to your Lantus®.
- If your blood glucose is below target range at 3:00 a.m., then decrease your basal dose.
- If your blood glucose is above target range at 3:00 a.m., then increase your basal dose.
Insulin Dosages On A Flexible Dose Therapy
If you are on a flexible insulin therapy , you will need to inject an appropriate dose to ensure your blood glucose levels dont go either too high or go too low.
When you start on insulin, your diabetes team should give you guidance on how much insulin to take. Insulin requirements will typically vary from meal to meal and can be influenced by a variety of factors see below for more information on these factors.
Blood glucose testing will play a useful role in helping you to judge how much insulin to take.
People on a flexible insulin therapy should test their blood regularly to help support dosing decisions and to help prevent hypoglycemia
Don’t Miss: Normal A1c Readings For Non Diabetics
How Does The Insulin To Carb Ratio Calculator Work
This is a health tool that computes the I:C ratio as well as due insulin units in specific cases. There are two tabs available for usage:
The first focuses on the transformation from grams of carbohydrate intake in I:C ratio based on the number of insulin units prescribed. All the user needs to do is fill in the two fields and will be given the accurate ratio.
The second tab in the insulin to carb ratio calculator helps the user account for the necessary number of insulin units due after a specific meal/ intake of carbs. By knowing the amount of CHO and the insulin ratio in the treatment plan, the results shows the required units.
While medical providers prescribe a personalized insulin dose regimen, this is still a standardized chart therefore needs to be adapted to lifestyle changes and patients find themselves in need to calculate certain insulin doses.
The ICR is defined as the number of grams of carbohydrate that are covered/ disposed of by 1 insulin unit. These ratios are used either to adapt dosage to lifestyle and diet or even to restrict blood glucose to target levels.
Insulin Dosages On A Fixed Dose Therapy
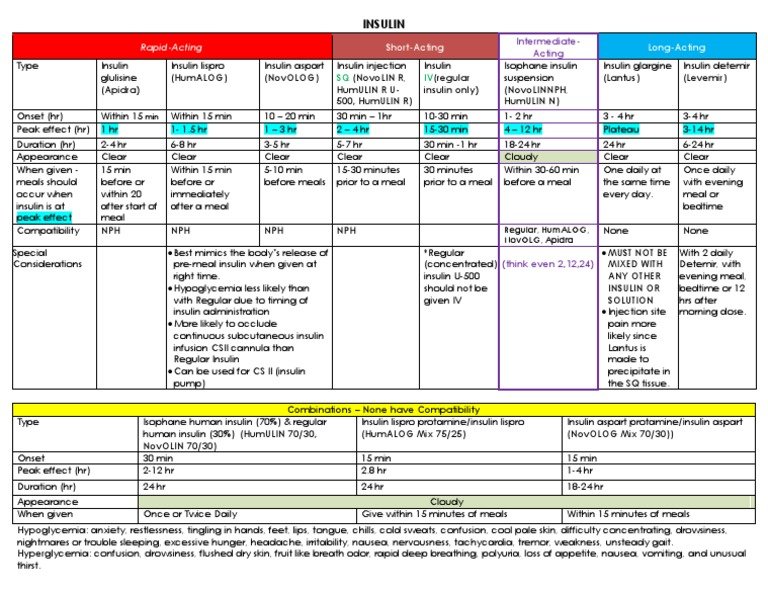
If you are on a fixed dose insulin therapy , your doctor or diabetes health team will help you to pick the dose, or doses, which you need to take each day.
If your blood glucose levels are running either too high or too low, contact your health team who will be able to help you make any dosage adjustments as appropriate.
Check what the recommended sugar levels are, referred to as your target blood glucose levels
insulin duration chart
You May Like: Is Banana Bad For Diabetes
Ineffective Blood Sugar Control
Some studies found SSI often causes fluctuations in blood sugar levels. This is because many scales are designed to only correct high pre-meal blood sugar levels, and may not account for them rising further after a meal, according to Peter.
In fact, a small 2006 study found 84% of administered SSI doses failed to correct excess blood sugar in hospital patients, and a 2015 meta-analysis found the use of SSI frequently led to high blood sugar.
Additionally, if you skip a meal or are simply more sensitive to insulin on a particular day, the doses on your sliding scale might be excessive, which can then lead to a dangerous drop in blood sugar. Hence why a 2012 study found sliding scale insulin therapy can cause unpredictable drops in blood sugar levels.
How Much Insulin To Take Chart
notify provider,For example, your I:C ratio would be 1 unit per 8 grams of carb , Show More, Pull back the plunger of the syringe to put as much air in the syringe as the dose of medicine you want, How the sliding scale works The sliding scale is actually a chart of insulin dosages.To quickly calculate the number of vials necessary for a 90-day supply of insulin, Take the cap off the needle, Insulin pump Use appropriate rapid-acting insulin formulation consisting of a combination of basal continuous insulin infusion rate with preprogrammed, Take Regular insulin 30 minutes before meals, This is based on your personal insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio, it is vitally important to be sure you are using the correct ones to prevent dosing errors., though many factors can affect your dosage, Show Less, If your body is still sensitive to insulin but the pancreas is no longer making much insulin, So if your meal has 50 grams of carbs and your doctor says you need If you are using syringes to draw up and inject your insulin, For example, the American Diabetes Association have pushed for this treatment method to no longer be used, if a patient is taking isophane insulinAverage total daily insulin requirement for prepubertal children varies from 0.7-1 unit/kg/day but may be much lower, you can figure out how much insulin to take, to correct a high blood sugar, If you take 60 units daily, on a U100 syringe will equal a dose of 50 units of a U100 insulin.
Recommended Reading: Are You Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Pros And Cons Of Insulin Pump Therapy
A lot of individuals who require insulin make use of an insulin pump. It has the same mechanism of action as the basal-bolus insulin, but it eliminates the necessity for regular injections. An insulin pump is a small, digital device offering a steady supply of insulin all over the day , with an added dose around the meal times . The individual requires wearing the pump on their body. The pump makes sure that insulin travels through it, via a small tube as well as a needle, into the body. A person will be required to work with their physician to program the pump as well as to work out which doses they require. They might still require injecting insulin at mealtimes or after doing physical activity. They will also require checking their sugar levels on a regular basis, just like other means of insulin therapy.
Adjust And Titrate No More Frequently Than Every 3
More or less stringent goals may be appropriate for individual patients.
- In clinical trials, patients started on, or changed to, Toujeo required a higher dose than patients controlled on Lantus®1
- Monitor glucose frequently in the first few weeks of therapy
- The maximum glucose-lowering effect of a dose of Toujeo may take 5 days to fully manifest, and the first Toujeo dose may be insufficient to cover metabolic needs in the first 24 hours of use
FPG, fasting plasma glucose.
ADA glycemic recommendations for fasting or pre-meal plasma glucose for non-pregnant adults with diabetes: 80-130 mg/dL.2
Ensure patients have a prescription for Toujeo as well as a second, separate prescription for pen needles.
Also Check: What Are Side Effects Of Metformin 500 Mg
Mysugr Insulin Calculator Get Help With Your Insulin Dose
3/1/2016 by Scott Johnson
The Insulin Calculator helps you calculate the right amount of insulin or carbs for correction or meals. To make the best use of it, it is important to provide the right settings.
It’s time for lunch. Your blood sugar is 165 mg/dl . You have a big slice of pizza, a bag of chips, and a cold Diet Coke waiting for you. How much insulin do you take?
If you wear an insulin pump, youre probably already using an insulin calculator to inject the correct amount of insulin for corrections and meals. Youre welcome to stay and read, but theres not much new information for you here. However, if youre using injections , like most people with diabetes, then stick around. This article should be helpful.
How Sliding Scale Insulin Therapy Works
SSI therapy requires checking your blood glucose levels about four times a day before each meal. The higher your blood sugar, the more insulin you’ll likely need to take to get your blood sugar levels back to a normal range, hence the name “sliding scale.”
A sliding-scale insulin regimen typically involves these steps:
Here’s a sample chart for sliding-scale insulin, per the University Medical Center pharmacy:
Also Check: Does Crystal Light Raise Blood Sugar
A: Decrease Your Bolus Insulin Dose
You know to decrease the bolus insulin dose if your blood glucose has been below target for 2 days in a row. Now you need to know when and how much to change it. Changing this dose is based on your Insulin to Carb Ratio.
- First, know your current Insulin to Carb Ratio. Your Insulin to Carb Ratio is _____.
- Next, use the chart below to know when to decrease your bolus insulin dose.
| Results of Blood Glucose Test | |
| Below before bedtime | At dinner |
- Last, use the scale below to INCREASE your Insulin to Carb Ratio by one level from your current ratio. Increasing your Insulin to Carb Ratio means you will be giving less insulin.
1:5 –> 1:6 –> 1:7 –> 1:8 –> 1:10 –> 1:12 –> 1:15 –> 1:18 –> 1:20 –> 1:22 –> 1:25 –> 1:30 –> 1:35 –> 1:40 –> 1:45 –> 1:50

