Diet Foods Are The Best Choices
MYTH. You might be paying more for “diet” food that you could find in the regular sections of the grocery store or make yourself.
Read the labels to find out if the ingredients and number of calories are good choices for you. When in doubt, ask your doctor, diabetes educator, or a dietitian for advice.
Eating A Healthy Balanced Diet
What you eat can make a difference to how you feel and how you manage your condition. Thats why weve got a huge range of tasty and nutritious recipes ready for you to try.
Whether youre cooking up a feast for dinner, or looking for something lighter for lunch, weve got you covered. Simply search by ingredient, meal type or dietary requirement and enjoy eating with diabetes.
Dr Tejal Lathia Answers This Common Diabetes Query
Written by Bhavyajyoti Chilukoti | Updated : February 14, 2018 3:57 PM IST
I do not consume sugar, why do I have diabetes? — It is a very common question most specialists hear while attending to patients who have been diagnosed with diabetes. However, this is one of the biggest misconceptions about diabetes mellitus. Consumption of excessive sugar does not directly cause diabetes. It is a metabolic disorder that is caused by the lack of insulin hormone in the body. Dr Tejal Lathia, Consultant Endocrinologist, Hiranandani Hospital, Vashi A Fortis Network Hospital explains in detail why a person can get diabetes even if he/she doesn’t eat sugar. Also read can a person with no family history of diabetes get diabetes?
Diabetes and glucose: What’s the connection?
Don’t Miss: Does Metformin Cause High Cholesterol
What If Not Under Control
When blood sugar levels go out of control, it can prompt short-term problems like hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, or diabetic ketoacidosis. Over the long term, not controlling diabetes can harm some important organs, including the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
The damage to important organs tells about how you get diabetes. This implies that several health problems such as heart diseases and stroke, kidney diseases, vision issues, and nerve issues can occur in people with diabetes.
These issues usually do not appear in children or teens that have had the infection for a couple of years. However, they can happen to adults with diabetes. Children and teens with diabetes who dont control their blood sugar levels can be late into adolescence and probably wont wind up as tall as they would otherwise.
Fortunately keeping your blood sugar levels in control can help you stay healthy. It also resists health problems from occurring later on. Many will tell about how you get diabetes but few will tell about its causes and types.
There are three types of diabetes:
Insulin In People With Type 1 Diabetes
A person with type 1 diabetes has dysfunctional beta cells because the “body’s immune system has attacked and destroyed them,” according to the NDIC, thus the body can’t produce insulin. When a type 1 diabetic forgets an insulin injection or doesn’t get enough insulin, eating a meal can raise the level of sugar significantly in the bloodstream, thereby inducing hyperglycemia.
You May Like: What Color Is The Diabetes Awareness Ribbon
Diabetes: 12 Warning Signs That Appear On Your Skin
Diabetes can affect many parts of your body, including your skin. When diabetes affects the skin, its often a sign that your blood sugar levels are too high. This could mean that:
-
You have undiagnosed diabetes, or pre-diabetes
-
Your treatment for diabetes needs to be adjusted
If you notice any of the following warning signs on your skin, its time to talk with your doctor.
Will I Need Medication Or Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
Some people take medication to manage diabetes, along with diet and exercise. Your healthcare provider may recommend oral diabetes medications. These are pills or liquids that you take by mouth. For example, a medicine called metformin helps control the amount of glucose your liver produces.
You can also take insulin to help your body use sugar more efficiently. Insulin comes in the following forms:
- Injectable insulin is a shot you give yourself. Most people inject insulin into a fleshy part of their body such as their belly. Injectable insulin is available in a vial or an insulin pen.
- Inhaled insulin is inhaled through your mouth. It is only available in a rapid-acting form.
- Insulin pumps deliver insulin continuously, similar to how a healthy pancreas would. Pumps release insulin into your body through a tiny cannula . Pumps connect to a computerized device that lets you control the dose and frequency of insulin.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Maximum Dosage Of Metformin
Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for more than 90% of all diabetes cases. Unlike type 1 diabetes which is an autoimmune disease, type 2 diabetes is mainly triggered by diet and lifestyle factors.
While sugar doesn’t directly cause type 2 diabetes, eating large amounts of added sugar may increase your risk of the disease. Excessive consumption of sugary foods and drinks may make you gain weight as they contain a lot of calories. And you are more likely to get type 2 diabetes if you are overweight.
Several studies have linked regular consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages to greater risk of type 2 diabetes.
Eating too much sugary foods may increase your risk of fatty liver, which may trigger abnormal insulin production and increase your risk of type 2 diabetes.
Having said so, sugar is not the only reason the condition develops. Your overall diet, lifestyle and genetics may also impact your risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
Treating Headaches From Hyperglycemia
Exercise can help relieve a headache from high blood glucose levels.
If a person with type 1 diabetes is concerned about their level of ketones, it is important to check their urine for ketones first, especially if blood sugar levels reach 240 mg/dl.
People with ketones in their urine should not exercise and must contact their doctor immediately. Exercise could have the unintentional effect of increasing blood sugar levels.
A person can also help prevent hyperglycemia headaches by maintaining a healthy weight, following a nutritious and balanced diet, and taking the correct medications.
Headaches can signal periods of either high or low blood glucose that can lead to life-threatening complications without treatment. People with diabetes who experience frequent headaches should, therefore, consult their doctor.
It is vital to contact a doctor immediately if the following becomes apparent:
- A headache is severe and impacts daily life.
- Blood sugar levels do not return to the necessary range.
- Other severe or persistent symptoms develop alongside headaches.
According to the International Classification of Headache Disorders that the International Headache Society publish, there are over 150 types of headache.
Broadly, headaches can be classified as either primary or secondary:
Other causes of secondary headaches include:
Recommended Reading: Severe Condition Of Deficient Sugar In The Blood
Problems Associated With Hyperglycemia
The ADA warns that a person with hyperglycemia who isn’t receiving proper treatment can develop serious health complications. When there isn’t enough insulin in the body, the cells can’t use glucose for energy, thus they use fat, then muscle, as a last resort. The breakdown of fats produces a byproduct, ketones, which the body will clear away through urination, but excess ketones will eventually build up in the tissues and bloodstream, thus leading to a condition called ketoacidosis, or diabetic coma. This condition can cause shortness of breath, extreme dry mouth, nausea and vomiting.
Sugars Diabetes And The Food Environment
Reducing intake of sugars is a healthy choice from many perspectives. From the societal perspective, it would have many health benefits, including preventing and reducing dental caries, reducing obesity, and preventing weight gain, with a favourable impact on other illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. From a diabetes perspective alone, reduction of free sugars, specifically SSBs, may have an independent influence on type 2 diabetes risk and gestational diabetes risk. All this said, dietary changes must occur within a societal context.
You May Like: Drug Classification For Metformin
Healthy Eating And Diabetes
Created on August 13th, 2018 · Last updated on April 6th, 2019 ·
Medically reviewed by Shahzadi Devje, Registered Dietitian & Certified Diabetes Educator
Oh my gosh nutrition and diet information – is everywhere!
And each expert tries to lead you in their direction because they know best and their advice is going to help you. Right?
And we seem to be accepting of self-proclaimed gurus, who dispense such advice.
Everyone has heard the intense focus on how much you eat. The calorie narrative has been beaten into our psyche, and we accept it without a second thought.
While how much you eat does affect blood sugars, weight, and energy level – it’s certainly not the holy grail of health and effective diabetes management.
Let’s focus a bit more on the often overlooked benefits of what you eat and drink and how you eat and drink it.
Make Physical Activity Part Of Your Daily Routine

Set a goal to be more physically active. Try to work up to 30 minutes or more of physical activity on most days of the week.
Brisk walking and swimming are good ways to move more. If you are not active now, ask your health care team about the types and amounts of physical activity that are right for you. Learn more about being physically active with diabetes.
Following your meal plan and being more active can help you stay at or get to a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan that is right for you.
Read Also: Moderate Weight Loss Can Reduce Or Eliminate Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes.
What Does A Diabetes Rash Look Like
Diabetes rashes look different depending on the type and cause.
Some diabetes rashes only affect people with diabetes. They usually go away when blood sugar is under control. These rashes include:
- Blisters : Painless blisters may form on the backs of hands and feet and on the legs and forearms. This rare condition most often affects people who have diabetic neuropathy.
- Diabetes dermopathy: Light-brown, round-shaped scaly patches, like age spots, appear on the shins. These harmless spots dont need treatment.
- Digital sclerosis: Some people with Type 1 diabetes develop hardened, thick, waxy skin on the backs of their hands. The finger joints stiffen, making movement difficult. A related rash is scleredema adultorum of Bushke which is tightness, thickening, and hardening of the back, neck, shoulders and face. There are various treatments that dermatologists can provide for this.
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum : This lower leg rash is more common in women. NLD causes raised, red, shiny patches with a yellow center. Blood vessels may be more noticeable. The rash may be itchy and painful. You should see a dermatologist for treatment options.
- Diabetes Foot Syndrome: These are ulcers that develop from trauma to the skin. The ulcers can take a long time to heal and there is an increased risk for infection.
Other conditions can affect anyone, but are particularly common among people with diabetes. These rash-causing conditions can also be a warning sign of pre-diabetes:
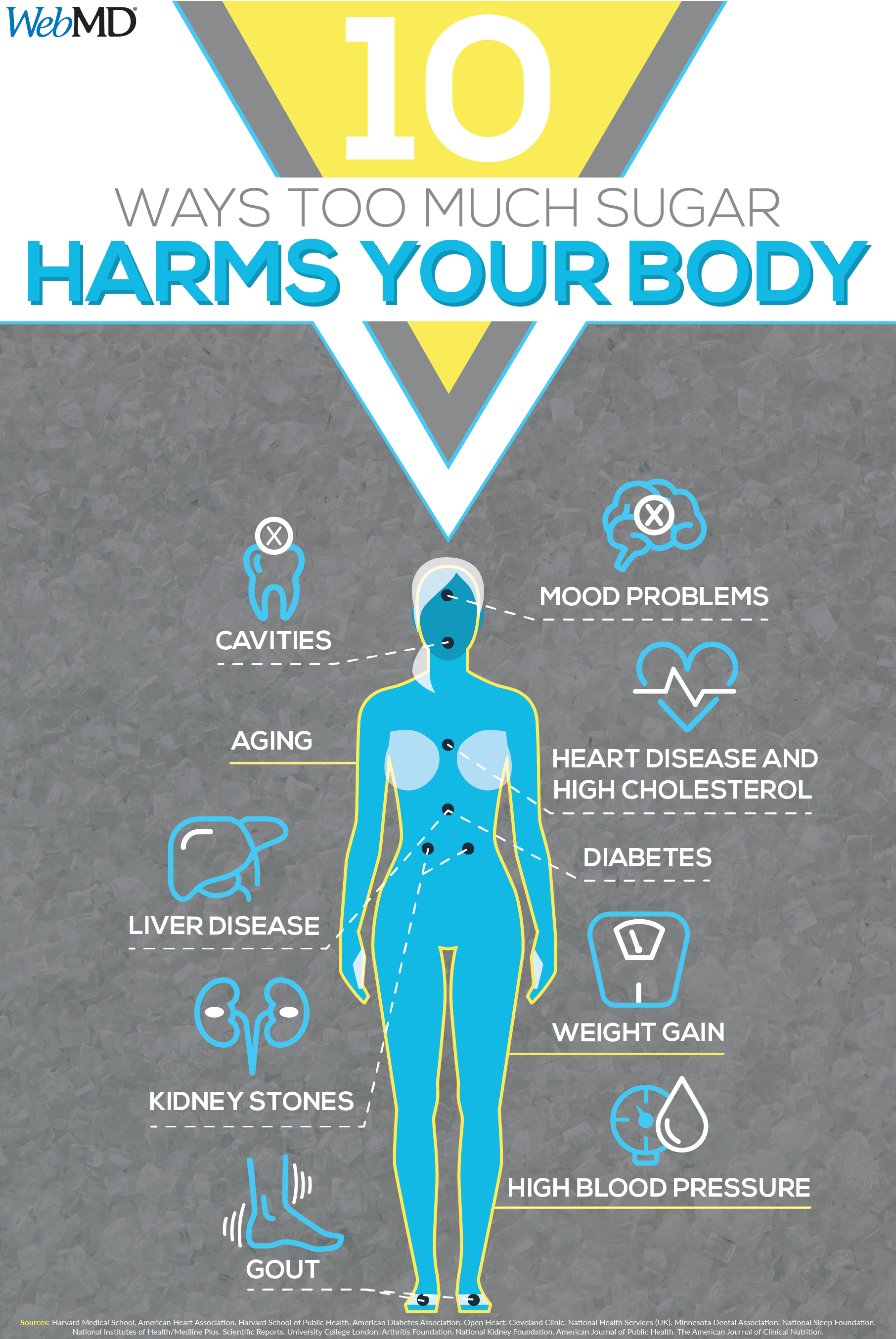
How Does Too Much Sugar Affect Your Body
Chances are you already know that eating too much sugar isnât good for you. Yet youâre probably still overdoing it. Americans average about 270 calories of sugar each day, thatâs about 17 teaspoons a day, compared to the recommended limits of about 12 teaspoon per day or 200 calories.
Sugary drinks, candy, baked goods, and sweetened dairy are the main sources of added sugar. But even savory foods, like breads, tomato sauce, and protein bars, can have sugar, making it all too easy to end up with a surplus of the sweet stuff. To complicate it further, added sugars can be hard to spot on nutrition labels since they can be listed under a number of names, such as corn syrup, agave nectar, palm sugar, cane juice, or sucrose.
No matter what itâs called, sugar is sugar, and in excess, it can negatively affect your body in many ways. Hereâs a closer look at how sugar can mess with your health, from head to toe.
You May Like: Insulin Secreted By Beta Cells
Take Your Insulin As Prescribed
High blood sugar occurs when your body has too little insulin, or your body cant use insulin properly. Administering insulin can bring your blood sugar levels down.
Talk to your doctor about how much rapid-acting insulin you should administer when your blood sugar is high.
You may want to check your blood sugar about 1530 minutes after taking insulin to make sure your blood sugar is going down and that its not dropping too low.
Healthy Foods And Beverages In Public Places
Improving the nutritional quality of foods and beverages in public places is a low-cost public health strategy that can help to change social norms and create healthier food and beverage environments. This can help to model and reinforce healthy eating in other spaces and at home. Most public spaces have health promoting services that are undermined and contradicted by the sale of unhealthy foods.
You May Like: Regular Insulin Adverse Effects
What We Mean When We Talk About Sugar
What most people understand to be sugar is sucrose: a mix of glucose and fructose. A common misunderstanding is that blood glucose is derived solely from dietary sugar. Almost all of the sugar in the body, including the blood, is in the form of glucose one of many sugars belonging to the family of carbohydrates.
Sugars typically form a small part of the diet, not all of them are equally effective at increasing blood glucose levels, and other carbohydrates, as well as fats and protein, influence glucose levels, too.
Animal studies show that high sugar diets lead to rapid weight gain and impair the bodys ability to effectively regulate blood glucose. But these effects are mainly due to the fructose component of sucrose and not glucose.
In people, diets high in sugar have also been shown to increase weight as well as risk factors for cardiovascular disease. But these effects only seem to occur when calories are not being controlled simply exchanging extra sugar with calories from another source wont prevent these negative effects. Also, observational studies have failed to show a harmful association between dietary sugar and type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes has arisen through rising body weights. Fatter people eat more of many things not only sugar and extra calories from any nutrient will lead to weight gain. Most sugary processed foods, such cakes and chocolate, contain large amounts of fat which contribute heavily to the calorie content.
Calculating Your Daily Allowance
If you don’t have diabetes, the AHA recommends limiting calories from sugar to 10% of your total calories. One gram of sugar equals 4 calories.
For a 2,000-calorie diet, that means you can have up to 50 grams of sugar from all sources per day. It’s worth noting that the World Health Organization recommends an even lower percentage: no more than 5% of total calories from sugar.
If you have diabetes, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to figure out what’s right for you. Ask what percentage of your total daily calories should come from sugar. This will help you to make adjustments if you are obese and need to cut calories or if you are underweight and need to increase calories.
You May Like: What Kind Of Candy Can A Diabetic Eat
Nighttime Low Blood Sugar
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think youre at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldnt rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while youre sleeping.
What Are Blood Sugar Targets

A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
Read Also: Too Much Sugar Diabetic
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes may include feeling tired, increased hunger or thirst, losing weight without trying, urinating often, or having trouble with blurred vision. You may also get skin infections or heal slowly from cuts and bruises. Some people with type 2 diabetes may not realize they have it because symptoms often develop slowly and go unnoticed. Sometimes older adults dismiss these symptoms as getting old, but they can be signs of a serious problem. Talk with your doctor if you have any of these symptoms.

