What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of An Insulin Pump
An insulin pump is a small, computerized device that continuously delivers insulin. It attempts to mimic the normal release of insulin from the pancreas. A pump delivers a small amount of insulin continuously the basal rate. The basal rate helps keep blood sugars stable between meals and overnight, and replaces the need for your long acting insulin .
In addition to the basal rate you need insulin to COVER food and CORRECT high blood sugars which is called the bolus dose. You must tell the pump how many carbohydrates you are eating and what your blood sugar is following which your pump will calculate the appropriate bolus dose to be given.
Both the basal rate and bolus doses can be adjusted for certain situation, such as sick day management, hypoglycemia prevention, physical activity, etc.
Effective and safe use of the pump requires:
- Commitment to checking blood sugars at least 4-6 times/day and/or continuous glucose monitor.
- Ability and willingness to count carbohydrates
- Understanding of insulin dose adjustment based on physical activity or type of carbohydrates eaten
- Continued parental supervision
- Consistent improvement in HbA1c
- Basic understanding of diabetes, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia and problem solving provided in diabetes outpatient education class.
- Good communication with your diabetes team and if possible, the ability to download glucose data at home to share with your diabetes team.
The main advantages of pump therapy are:
- Increased flexibility
Access To Insulin Pumps
In Australia, insulin pump therapy is limited to people with type 1 diabetes who have private health insurance. There are some government subsidy programs and charitable organisations, such as the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation , that may assist with the cost of an insulin pump in special circumstances. Patients without private health insurance have to purchase the insulin pump themselves. The current commercial price of an insulin pump is approximately $10 000.
In 2017 a government subsidy for continuous glucose monitors was implemented for people under the age of 21 years. However, patients over 21 years receive no subsidy and must purchase continuous glucose monitors at the full price of approximately $300400 per month. Additional costs with pump use include consumables such as infusion sets and reservoirs, costing $2530 per month.
Benefits And Limitations Of Pump Therapy
It is undebatable that insulin pump users have lower A1c levels and fewer hypoglycemic events. In addition, the pump offers more accurate dosing, avoids the need for multiple daily injections, and thus provides convenience and a flexible lifestyle. Another potential benefit is that the pumps can store a plethora of data that can be transmitted to computer programs or bolus insulin calculators and further analyzed to make insulin dose adjustments.
Potential downsides of pump therapy are technical problems associated with the infusion set and higher acquisition costs. Patients often experienced skin irritations and infections at the insertion sites. Technical issues such as kinking, bending, or crimping of inserted cannulas and leakage of infusion sets have also been reported . Initial acquisition and total annual costs are high for pump therapy compared with MDI .
Also Check: Late Onset Diabetes Type 1
Disadvantages Of An Insulin Pump
- Youâll need to enter information into the pump all day and change out the infusion set every few days.
- Youâll need to commit to using it safely, including checking your blood sugar to make sure the pump is working right. Otherwise, you risk a life-threatening problem called diabetic ketoacidosis .
- Youâll need training to learn to use the pump, which means several visits with your health care team or a full day of outpatient training.
- Pump supplies can be expensive.
An insulin pump may not be right for you if:
- You donât want to wear a device that lets people know you have diabetes.
- You donât like the feeling of wearing a device.
- Youâre not comfortable operating the pump.
- You donât want to check your blood sugar at least four times a day.
- Youâre not sure you want to do the work to figure out insulin dosing, carbs, and physical activity.
Advantages Of An Insulin Pump
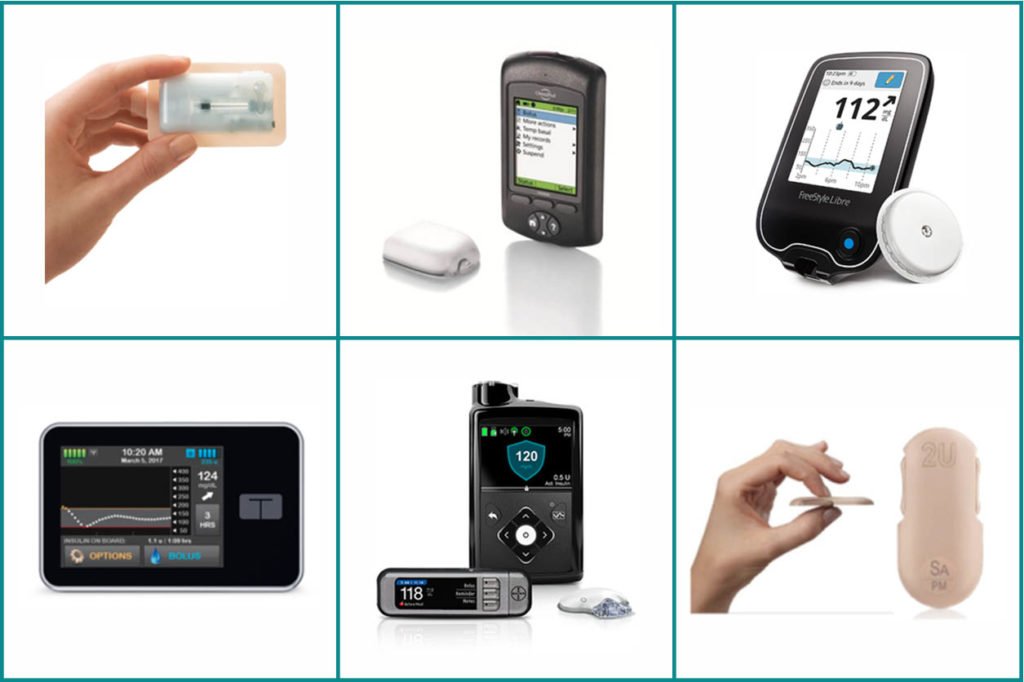

The biggest advantage is you dont need to give yourself daily injections. You can match your insulin to your lifestyle rather than planning your life around insulin injections.
Other advantages:
-
Insulin pumps deliver insulin more accurately than insulin injections, in a manner more like your body normally releases insulin.
-
Insulin pumps do a better job of improving your A1Ca test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the last 3 months.
-
Insulin pumps avoid the unpredictability of intermediate or long-acting injectable insulin. The result is fewer highs and lows, and better diabetes management.
-
You can adjust an insulin pump around your diet. This lets you be more flexible about what and when you eat.
-
You can adjust an insulin pump to your level of exercise. You wont need to load up on carbohydrates before you exercise.
You May Like: Black Coffee And Blood Sugar
Whats The Best Insulin Pump
This really depends on many factors, both personal and institutional. So many different things go into ones choice on a big diabetes device purchase like this, ranging from the specific features you prefer, to how it works with other technology and smartphones, and whether it includes tubing or is a tubeless patch pump.
Access and affordability are also huge factors that make this decision for many people, because insurance plans dont always like to cover expensive medical devices like these or they have specific criteria that must be met in order to buy a particular insulin pump.
Talking to your healthcare professional about the different options and what might work best for your diabetes management is always advisable, as well as reviewing credible and reliable information online about how the various technologies work.
User reviews can also make a big difference in deciding on which insulin pump may be right for you. You can start by checking out our product reviews here at DiabetesMine on Medtronic, Omnipod and Tandem pumps.
As the saying goes, it all depends on you and whats important for your life with diabetes.
Who Should Use A Pump
Individuals across all age groups can use a pump. You can replace multiple insulin injections by using a pump. The pump is functional whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. An insulin pump is more suitable for people who like the pumps operation and features. It is also more ideal to:
The insulin pumps suitability relies on its efficiency to deliver the required amounts of insulin. If you decide to use a pump, you should learn how to operate it for effectiveness. It would be best also to understand the advantages and disadvantages of using the pumps.
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
The Pumps Substitute Multiple Injections And Involve Fewer Jabs
With diabetes, you can be required to inject insulin numerous times a day to manage your blood sugar levels. However, technology has enabled the delivery of insulin to the body using pumps as alternatives to injections. The use of pumps involves fewer jabs as it only requires a change of the catheter after 2-3 days.
Why Waitget Started On Insulin Pump Therapy Today
References* Assumes 4 injections per day for 30 days and one infusion set change every two to three days.1 Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HAW. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008 359:1577-1589.2 U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complication in patients with type 2 diabetes . The Lancet. 1998 352:837-853.3 Reznik Y, Cohen O, Aronson R, et al, Insulin pump treatment compared with multiple daily injections for treatment of type 2 diabetes : a randomized open-label controlled trial. The Lancet. 2014 2014 384:1265-1272.4 Lauritzen T, Pramming S, Deckert T, Binder C, Pharmacokinetics of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetologia. 1983 24:326-329.5 Doyle EA, Weinzimer, Steffen AT, et al. A randomized, prospective trial comparing the efficacy of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with multiple daily injections using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care. 2014 271554-1558.
** MiniMed 630G 6-Week Evaluation Program Terms:
See www.medtronicdiabetes.com/importantsafetyinformation and the appropriate user guides for additional important details.
The CONTOUR®NEXT LINK 2.4 Meter is used with the MiniMed 630G system.
Ascensia, the Ascensia Diabetes Care logo, and Contour are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Ascensia Diabetes Care.
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Disadvantages Of Insulin Pumps
It may take some time to learn how to use your insulin pump. Here are other possible negatives to consider:
- Some people gain weight while using an insulin pump.
-
You can get into trouble if your pump stops working or your catheter comes out. If you dont get any insulin for several hours, you can develop a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis.
- You might find you dont like wearing your pump all the time.
-
You’re more likely to develop a skin infection at the pump insertion site than you are with insulin injections.
-
Insulin pumps and infusion set supplies can be expensive. Check with your insurance carrier to find out what it covers.
If you decide to try an insulin pump, you may need to spend a day in the hospital getting started. With time, you will find the best site to place your needle and the best way to wear your pump. You will also learn what to do with the pump when you sleep and when you bathe, swim or shower. Once you get started, you should be able to use your pump and lead an active lifestyle without much difficulty. Most pump users find the advantages outweigh the disadvantages. Talk with your team to make the right decision for you.
Adverse Event Reporting After Market Approval
Once insulin pumps and other medical devices are marketed, associated adverse events or concerns can be reported either to the manufacturers or directly to the regulators: the FDA in the US or the National Competent Authorities in the EU . The FDA requires that manufacturers report and analyze spontaneously reported AEs associated with all medical devices. It has the authority to impose additional postmarketing surveillance requirements on the manufacturer. In the EU, postmarketing and premarketing evaluation is delegated to the individual national authorities.
AE reports from insulin pump users provide a potentially rich source of information for quality assurance and improving safety . In the EU, AEs are compiled in the EU-wide database known as the European Databank on Medical Devices . This database is accessible to notified bodies and NCAs , but cannot be accessed by the public. We have therefore focused on the FDAs adverse reporting system and relied primarily on the Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience database as a source of data .
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Registries: Sources Of Real
A US survey from the 1980s stated that 25% of CSII pumps malfunctioned: 29% of these malfunctions were due to drive failure and 14% due to battery issues . It is likely that these proportions are lower with modern pumps, but the available information is insufficient for this to be concluded with certainty.
In the US, the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry includes over 26,000 individuals with type 1 diabetes from over 70 centers across the US on MDI or CSII . It represents a variety of demographic settings and approaches to diabetes management, but covers the more skilled and experienced centers with a relatively large volume of pump usage. In a report from this registry, individuals with the best HbA1c levels were more likely to be using CSII. In children, 69% in excellent glycemic control used pumps compared with 41% of those in poor control . Of the 627 adults in excellent control , 54% were using an insulin pump compared with 46% in the fair/poor control group P = 0.001 . Of 6,500 pump users who provided baseline and 1-year follow-up data, 4.4% had discontinued pump use in the past year, with a variety of reasons noted, most commonly relating to user comfort. Reported rates of ketoacidosis were similar between MDI and CSII users . The T1D Exchange Clinic Registry is closely allied to Glu, a US patient networking site that collects data on insulin pump use: this could also be a useful source of safety information if the data were made available for these purposes .
Increased Blood Glucose Control
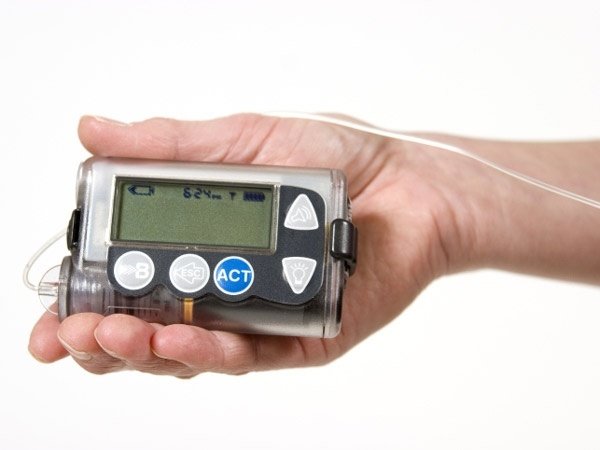
All this extra flexibility adds up to mean a better chance of controlling blood sugar levels and research shows that insulin pump therapy is generally linked with better blood glucose numbers
NICE reviewed 18 adult and mixed age group studies and in each study, insulin pump therapy showed reduced Hba1c values. In studies of teenagers and children, 20 out of 23 studies showed an improvement in HbA1c results as a result of starting insulin pump therapy.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy Of Person With Type 1 Diabetes
Continuous Intraperitoneal Insulin Infusion
The intraperitoneal route of insulin delivery has been investigated since the 1970s. Continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion is intended to enable the infusion of insulin into the peritoneal cavity. The advantage of this method is that it more closely resembles the physiology than the other conventional therapies . Two different technologies have been developed in CIPII: implanted intraperitoneal pumps such as MiniMed MIP2007C and a percutaneous port attached to an external pump such as the Accu-Chek® Diaport system . The MIP 2007C is implanted beneath the subcutaneous tissue in the lower abdomen, and from this subcutaneous pocket, the peritoneum is opened, and the tip of the catheter is carefully inserted and directed toward the liver. After implantation, the pump reservoir is refilled in the outpatient clinic with concentrated insulin transcutaneously at least every 3 months. The Accu-Chek® Diaport system enables infusion of insulin into the peritoneal cavity through an Accu-Chek insulin pump and an infusion set. CIPII has been proven as a viable option for T1D patients with skin problems and unable to securely or efficiently control their diabetes with subcutaneous insulin . The limitations of this route of insulin administration include the invasive nature, cannula blockage, higher cost, portal-vein thrombosis, and peritoneal infection.
In 2007, Medtronic announced the worldwide termination of the implantable insulin pump.
Managing Insulin Pumps In General Practice
The management of a patient on an insulin pump requires the involvement of a specialist diabetes team including an endocrinologist, diabetes nurse educator and dietitian. The GP is an essential member of this team and it is therefore important GPs understand the terminology related to insulin pump therapy .
You May Like: Normal A1c For Diabetic
Clinically Suitable Insulin Pump Candidates
The 2010 AACE statement proposed the following patients as clinically suitable insulin pump candidates.
Class 1
Patients are classified as class 1 if they have type 1 diabetes mellitus and do not reach glycemic goals despite adherence to a maximum multiple daily injection and are on a non-CSII program , especially if they have the following:
-
Very labile DM
-
Frequent severe hypoglycemia and/or hypoglycemia unawareness
-
Significant dawn phenomenon
-
Extreme insulin sensitivity
-
Special circumstance
Class 2
Patients are classified as class 2 if they have type 1 DM and are on a maximized basal-bolus MDI insulin regimen, defined as more than 3 daily injections, regardless of their level of glycemic control and who, after investigation and careful consideration, feel that CSII would be helpful or more suitable for lifestyle reasons.
Class 3
Patients are classified as class 3 if they have insulin-requiring type 2 DM and satisfy any or all of the following:
-
Positive C-peptide results but with suboptimal control on a maximal program of basal/bolus injections
-
Substantial dawn phenomenon
-
Erratic lifestyle
-
Severe insulin resistance, candidate for U500 insulin via CSII
-
Selected patients with other DM types
Introducing The Minimed 630g Insulin Pump System
Ask your doctor about insulin pump therapy at your next visit! Print out the below brochure to take with you to your next office visit.
The testimonial above relates an account of an individual’s experience using a Medtronic device. The account is genuine, typical and documented. However, this individual’s experience does not provide any indication, guide, warranty or guarantee as to the response or experience other people may have using the device. The experience other individuals have with the device could be different. Experiences can and do vary. Please talk to your doctor about your condition and the risks and benefits of Medtronic devices.
Read Also: Side Effects Of High A1c
Reducing Episodes Of Severe Hypoglycaemia
Possibly because insulin pumps require less need to plan hours into the future than with injections, pumps are also linked with a lower risk of having a severe hypo
NICE reviewed 10 studies looking at adult and mixed age groups and found 80% of these studies showed reduced incidence of severe hypoglycemia associated with CSII. Out of 11 studies of teenagers and children, all had reduced incidence of severe hypoglycemia.
Benefits And Disadvantages Of Insulin Pump Therapy
Benefits and disadvantages of insulin pump therapy
Since 1963 when Dr. Arnold Kadish developed the first prototype for a pump that had the ability to deliver insulin and glucagon injections, pumps have come a long long way. This original pump was about the size of a microwave and was designed to be worn like a backpack!
More recently, some of our members have found the following benefits and disadvantages of insulin pump therapy, however as everyone is different these will vary from person to person.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Survival Rate
Insulin Pump Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes
When a person is newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, their healthcare professionals may offer various treatment options such as oral medication, insulin shots, or insulin pump therapy. People living with type 2 diabetes may choose insulin pump therapy as it requires fewer insulin injections or insulin shots.*

