Biopharmaceuticals: Reference Biosimilars And Biobetters
Additionally, while the first biopharmaceuticals were predominantly delivered by injections, biobetters adopt different approaches to drug delivery administration as oral, dermatological and inhaled formulations which are related with different encapsulation approaches aiming to minimize the biologic instability caused by protein aggregation and denaturation as consequence of physicochemical modifications processes of the biodrug as deamination, hydrolysis, oxidation, among others.1515 Mitragotri S, Burke PA, Langer R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 13:655-672. Protein engineering and rational modification is also a very promising area in new biopharmaceuticals and some aspects will be discussed later.
Animal Insulin Vs Synthetic Insulin: Similar Genes Different Origins
Humans with diabetes started using insulin extracted from the pancreas of cows or pigs in 1922. Some people developed allergies to animal insulin, but its use saved countless lives. Today, most people who need it use synthetic or human insulin, first manufactured in the early 1980s.
Though many individuals complained of side effects after switching from animal to synthetic insulin, the synthetic type is now prescribed almost exclusively in many parts of the world.
Whether natural or synthetic, the therapeutic use of insulin by humans depends on our similarity to nonhuman creatures.
Our Genetic Cousins
Proteins are similar to a string of beads, and the beads are called amino acids. The amino acids that make up our human insulin protein are nearly identical to the string of amino acids in cow and pig insulin. Pork insulin is different by one amino acid, and bovine insulin by three similar enough for most humans to use.
In the 1950s, when the complete protein structure of insulin was deciphered, some companies began modifying animal insulin. They removed the different amino acid from pig insulin, replacing it with the human counterpart. So, other than its origin, the pig insulin was made human.
Although insulin was being modified before the creation of the synthetics, the production of synthetic insulin has nothing to do with altering the proteins of other mammals. It involves life forms much smaller.
Synthetic Soup
Synthetic Pros and Animal Insulin Advocates
Can Synthetic Biology Make Insulin Faster Better And Cheaper
Rising insulin prices have become a dangerous norm for diabetics. Whether on Twitter, TV, or public … radio, the insulin market has the worlds attention and for all the wrong reasons.
Getty
He lost his insurance and turned to a cheaper form of insulin. It was a fatal decision.
Rising insulin prices have become a dangerous norm for diabetics. Whether on Twitter, TV, or public radio, the insulin market has the worlds attention and for all the wrong reasons.
Insulin prices are not only skyrocketing lack of access is killing Americans. People with Type 1, Type 2, and even gestational diabetes need to take insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. Insulin is the signal that tells our cells to take in glucose and convert it to energy. Without this molecule, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and can cause serious complications, including cardiovascular disease.
We are at the precipice of a profound public health crisis. If insulin has been around for nearly fifty years, and production has become cheaper over time, how did we get here? And what can synthetic biology do about these circumstances?
The cost burden of insulin
NBC News
In the early 1900s, Frederick Banting and Charles Best, two scientists at the University of Toronto, found that insulin extracted from dogs pancreases could effectively regulate blood glucose levels. The discovery was earth-shattering, marking the first hope of a feasible treatment for diabetics.
GettySynBioBeta
Read Also: How Does High Blood Sugar Make You Feel
E Coli Expression System For Production Of Insulin
E. coli is a preferred microorganism for large-scale production of recombinant proteins. However, several disadvantages limit its use for production of recombinant biopharmaceuticals. Various post-translational modifications such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, proteolytic processing and formations of disulfide bonds which are very crucial for biological activity, do not occur in E. coli . N-linked glycosylation is the most common posttranslational modification of proteins in eukaryotes. It has been discovered that the bacterium Campylobacter jejuni possess the capability to glycosylate the proteins and it was also shown that a functionally active N-glycosylation pathway could be transferred to E. coli . Although the structure of bacterial N-glycan is different from that observed in eukaryotes, engineering of Campylobacter N-linked glycosylation pathway into E. coli, provides an opportunity to express heterologous proteins in glycosylated form in E. coli. Expression of Pglb oligosaccharyltransferase or from C. jejuni in E. coli showed a significant increase in glycopepetide yield . Recently efforts has been made to produce glycosylated proteins with substrates other than native and non-native to E. coli and C.jejuni .
Upstream Processing On Biopharmaceuticals Production
The manufacturing technology for biopharmaceuticals can be divided into up- and downstream processes . Upstream process is defined as the microbial growth required to produce biopharmaceuticals or other biomolecules and involves a series of events including the selection of cell line, culture media, growth parameters, and process optimization to achieve optimal conditions for cell growth and biopharmaceutical production. The main goal of the upstream process is the transformation of substrates into the desired metabolic products.2929 Gronemeyer P, Ditz R, Strube J. Trends in upstream and downstream process development for antibody manufacturing. Bioengineering. 2014 1:188-212. This requires well-controlled conditions and involves the use of large-scale bioreactors. Several factors should be considered such as the type of process temperature, pH, and oxygen supply control, sterilization of materials and equipment employed, and maintenance of the environment to ensure it is free of contaminating microorganisms.3030 Schmidell W, Lima U de A, Aquarone E, Borzani W. Biotecnologia Industrial. v.2.1a ed. Engenharia Bioquímica São Paulo, Brasil: Blucher 2001.
Fig. 2
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Structure Of Human Insulin:
- Chemically Human insulin is small, simple protein composed of 51 amino acids sequences and has a molecular weight of 5808 Da.
- Insulin hormone is a dimer of a A- chain and a B-chain which are linked together by a disulphide bond.
- Fredrick Sanger et al gave the first complete description of insulin. Insulin consists of two polypeptide chain,o Chain A- 21 amino acids longo Chain B-30 amino acids longo Both chains are joined together by disulphide bond between two cysteine residue
Scientists Report Using Bacteria To Produce The Gene For Insulin
- Read in app
- May 24, 1977
WASHINGTON, May 23Scientists in California reported today that bacteria bred in laboratories have been engineered to make the gene for insulin, a developmeat that could provide a virtually limitless supply of the vital hormone and have an important impact on the treatment and understanding of diabetes.
Giving bacteria the ability to make insulin has been one of the most discussed goals of recombinant. DNA research, controversial realm of genetic experimentation known popularly as gene splicing.
What the scientists at the University of California at San Francisco did was to transplant into bacteria the genes from rat cells that carry the genetic instructions for making insulin. It is believed to he the first time this was accomplished with the gene for making insulin, or any other important animal hormone.
Now, the scientists said there should be no major. scientific obstacles to doing the same with the genes for human insulin.
What diabetics use today is a purified mixture of insulin from the pancreas glands of cows and pigs slaughtered for food.
But the worldwide demand for insulin is believed to be putting some strain on these supplies. And some diabetics develop allergic reactions to the animal insulin or its chemical precursors. It is conservatively estimated that there are more than two million diabetics in this country.
In order to live, mammals and humans need insulin, a protein hormone secreted
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Humulin N Nph Human Insulin Isophane Suspension
- Description
- Humulin is human insulin used for treating diabetes. Prior to its development, diabetics used insulin isolated from pig and cow pancreases. Developed by Genentech, the first American biotechnology company, Humulin was licensed to Eli Lilly and became the first marketable product created through recombinant DNA technology. Its licensing by the FDA in October 1982 also made it the first recombinant pharmaceutical approved for use in the United States.
- Recombinant pharmaceuticals are created by inserting genes from one species into a host species, often yeast or bacteria, where they do not naturally occur. The genes code for a desired product, and therefore the genetically modified host organisms can be grown and used as a kind of living factory to produce the product. In this case, genes coding for human insulin are inserted into bacteria. Bacteria produce insulin, which is harvested and used as the active ingredient in Humulin.
- Humulin N is formulated to have a slower onset of action than regular insulin and a longer duration of activity .
- Object consists of a white cardboard box with black and red printing. Box contains two product inserts and one clear round glass bottle with an orange plastic cap and a white label. Bottle contains a pinkish substance suspended in a clear solution.
- Location
Working With Human Insulin
- 1 The insulin gene is a protein consisting of two separate chains of amino acids, an A above a B chain, that are held together with bonds. Amino acids are the basic units that build all proteins. The insulin A chain consists of 21 amino acids and the B chain has 30.
- 2 Before becoming an active insulin protein, insulin is first produced as preproinsulin. This is one single long protein chain with the A and B chains not yet separated, a section in the middle linking the chains together and a signal sequence at one end telling the protein when to start secreting outside the cell. After preproinsulin, the chain evolves into proinsulin, still a single chain but without the signaling sequence. Then comes the active protein insulin, the protein without the section linking the A and B chains. At each step, the protein needs specific enzymes to produce the next form of insulin.
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Blood Sugar From Dropping
Application Of Recombinant Dna Technology To The Advancement Of Agriculture Medicine Bioremediation And Biotechnology Industries
Taylor Robinson AW,1
Verify Captcha
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers. Please type the correct Captcha word to see email ID.
1Department of Botany, Open University of Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka2Department of Medical & Applied Sciences, Central Queensland University, Australia
Correspondence: Andrew W Taylor-Robinson, Infectious Diseases Research Group, School of Medical & Applied Sciences, Central Queensland University, 160 Ann Street, Brisbane, QLD 4000, Australia, Tel 61 7 3295 1185
Received: November 07, 2016 | Published: December 29, 2016
Citation: Rajakaruna SS, Taylor-Robinson AW. Application of recombinant DNA technology to the advancement of agriculture, medicine, bioremediation and biotechnology industries. J Appl Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016 1:78-80. DOI: 10.15406/jabb.2016.01.00013
How Does Genetic Engineering Work
To help explain the process of genetic engineering we have taken the example of insulin, a protein that helps regulate the sugar levels in our blood.
- Normally insulin is produced in the pancreas, but in people with type 1 diabetes there is a problem with insulin production.
- People with diabetes therefore have to inject insulin to control their blood sugar levels.
- Genetic engineering has been used to produce a type of insulin, very similar to our own, from yeast and bacteria like E. coli.
- This genetically modified insulin, Humulin was licensed for human use in 1982.
The genetic engineering process
Recommended Reading: How Much Will 15 Grams Of Carbs Raise Blood Sugar
Global Consumer Market Of Microbial Biopharmaceuticals
In 1982, human insulin was the first recombinant protein that was FDA approved for use in humans as a biopharmaceutical product.1010 Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 7:21-39.,3939 Rosenfeld L. Insulin: discovery and controversy. Clin Chem. 2002 48:2270-2288. In the 1980s, the biopharmaceutical industry experienced a significant growth in the production and approval of recombinant proteins including interferons and growth hormones. In the 1990s, the first monoclonal antibodies and related products experienced an extraordinary growth, and in 2015, these products represented two-thirds of the products approved for commercial use in the world according to the Biotrack database7676 bioTRAK database. Available from: http://bptc.com .
Table 5S. cerevisiae.
What Is Genetic Engineering
- Genetic engineering, sometimes called genetic modification, is the process of altering the DNA in an organisms genome.
- This may mean changing one base pair , deleting a whole region of DNA, or introducing an additional copy of a gene.
- It may also mean extracting DNA from another organisms genome and combining it with the DNA of that individual.
- Genetic engineering is used by scientists to enhance or modify the characteristics of an individual organism.
- Genetic engineering can be applied to any organism, from a virus to a sheep.
- For example, genetic engineering can be used to produce plants that have a higher nutritional value or can tolerate exposure to herbicides.
Also Check: Why Does My Blood Sugar Go Up Overnight
Downstream Process: Isolation And Purification Of Biophamaceuticals
Downstream processing includes all steps required to purify a biological product from cell culture broth to final purified product. It involves multiple steps to capture the target biomolecule and to remove host cell related impurities , process related impurities and product related impurities . Each purification step is capable of removing one or more classes of impurities.5353 Azevedo AM, Rosa PAJ, Ferreira IF, Aires-Barros MR. Chromatography-free recovery of biopharmaceuticals through aqueous two-phase processing. Trends Biotechnol. 2009 27:240-247.,5454 Rathore AS, Kapoor G. Application of process analytical technology for downstream purification of biotherapeutics. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2015 90:228-236. Downstream processing usually encompasses three main stages, namely initial recovery , purification , and polishing .5353 Azevedo AM, Rosa PAJ, Ferreira IF, Aires-Barros MR. Chromatography-free recovery of biopharmaceuticals through aqueous two-phase processing. Trends Biotechnol. 2009 27:240-247.,5555 Rosa PAJ, Ferreira IF, Azevedo AM, Aires-Barros MR. Aqueous two-phase systems: a viable platform in the manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals. J Chromatogr A. 2010 1217:2296-2305.,5656 Fields C, Li P, OMahony JJ, Lee GU. Advances in affinity ligand-functionalized nanomaterials for biomagnetic separation. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016 113:11-25.
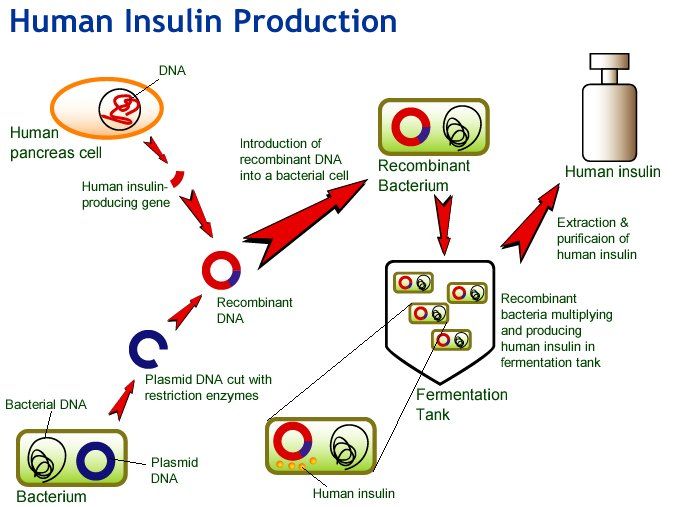
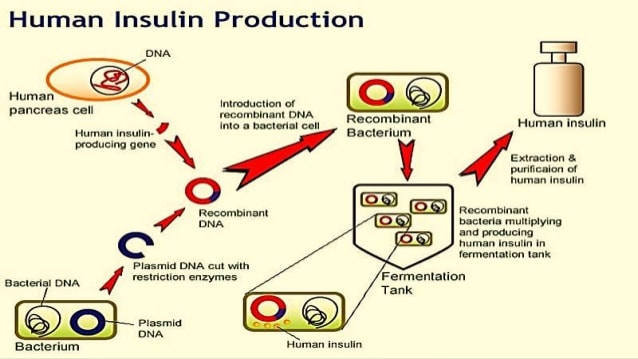
Human Insulin Production By Genetic Engineering
- Insulin is a hormone produced by -cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas. It was discovered by sir Edward Sharpey Schafer while studying Islets of Langerhans.
- Pancreas is a mixed gland situated transversely across the upper abdomen behind stomach and spleen.
- Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by pancreas and is a central regulator of carbohydrates and fat metabolism in the body.
Read Also: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Biobetters Based In Protein Structure Engineering
One of the most promising areas of the biobetters relies in protein structure engineering aiming the development of biodrugs with better pharmacological properties including higher activity, fewer side effects, and lower immunogenicity. The breakthrough in the determination of protein structures and their use as medicines dates from 1980s as a consequence of the advances in recombinant DNA technology. In turn, structural biochemistry has revolutionized our understanding of protein biology and afforded the beginning of protein engineering processes that can create protein drugs that are more effective than wild type proteins. Protein engineering may increase catalytic activity, stability, lower immunogenicity, and susceptibility to proteolytic processes.1111 Zawaira A, Pooran A, Barichievy S, Chopera D. A discussion of molecular biology methods for protein engineering. Mol Biotechnol. 2012 51:67-102.,1919 Carter PJ. Introduction to current and future protein therapeutics: a protein engineering perspective. Exp Cell Res. 2011 317:1261-1269.20 Courtois F, Schneider CP, Agrawal NJ, Trout BL. Rational design of biobetters with enhanced stability. J Pharm Sci. 2015 104:2433-2440.-2121 Chirino AJ, Ary ML, Marshall S. Minimizing the immunogenicity of protein therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2004 9:82-90.
Fig. 1
Production Of Processed Insulin In Bacteria
Genetically-engineered bacteria are used to produce insulin in industry, but as far as I know, the bacteria can produce only proinsulin. Why is that? What happens in the human body in order to make functional insulin, that can’t happen in some microorganisms? In the body proteases cut some at amino acids, and cleave the polypeptide while other enzymes create disulfide bonds. Why is there no bacteria in the industry that can do the same? It’s not possible for some reason or in other words can such a bacterial strain not be engineered?
- $\begingroup$Have you read the Wikipedia article on Proinsulin? This has an explanation, can you say, which part of it you don’t understand?$\endgroup$ ChrisJan 1 ’15 at 14:57
- 4$\begingroup$Because insulin is held together by disulfide bonds, which are a pain the ass to properly form in a bacterial expression system. We tried to make bee venom PLA2, which has 5 disulfides, in e coli, and even following a published protocol for recovering the misfolded protein from inclusion bodies, unfolding it, refolding it with glutathione, our yield was terrible. Trying to mutate any of the cysteines ruined the refolding and all enzyme was inactive. Producing proinsulin is just easier at industrial scale.$\endgroup$ user137Jan 1 ’15 at 18:17
Also please note that I am not fully aware of how insulin is made on the industrial scale and I could be wrong. That’s why this was originally a comment.
You May Like: Which Organ Produces Glucagon

