What To Do When Your Blood Sugar Is High Or Low
High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down. Here are some questions to ask yourself if your blood sugar is high.
- Are you eating too much or too little? Have you been following your diabetes meal plan?
- Are you taking your diabetes medicines correctly?
- Has your provider changed your medicines?
- Is your insulin expired? Check the date on your insulin.
- Has your insulin been exposed to very high or very low temperatures?
- If you take insulin, have you been taking the correct dose? Are you changing your syringes or pen needles?
- Are you afraid of having low blood sugar? Is that causing you to eat too much or take too little insulin or other diabetes medicine?
- Have you injected insulin into a firm, numb, bumpy, or overused area? Have you been rotating sites?
- Have you been less or more active than usual?
- Do you have a cold, flu, or another illness?
- Have you had more stress than usual?
- Have you been checking your blood sugar every day?
- Have you gained or lost weight?
How Much Is Metformin Without Insurance
Is metformin covered by insurance | How much does metformin cost without insurance?| How to get metformin without insurance
Metformin hydrochloride is a generic prescription drug used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar levels in people diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. It reduces blood glucose levels by increasing the uptake of blood sugar by the bodys cells. Metformin is typically prescribed not only as a first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes but is often used with other antidiabetic drugs when metformin alone cannot adequately control blood sugar.
Usually taken twice per day, doses will be determined based on blood sugar levels. The standard dose is 850 to 1000 mg per day, but this could rise to as much as 2,550 mg per day. Metformin is most commonly prescribed as a generic, but there are brand-name versions of metformin and extended-releasemetformin: Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Fortamet, Glumetza, Riomet, and Riomet ER. Note that several of the brand-name versions, including Glucophage, Glucophage XR, and Fortamet, have been discontinued in the U.S. There are no over-the-counter drugs or supplements that can be effectively or safely substituted for prescription metformin.
RELATED: Metforminside effects
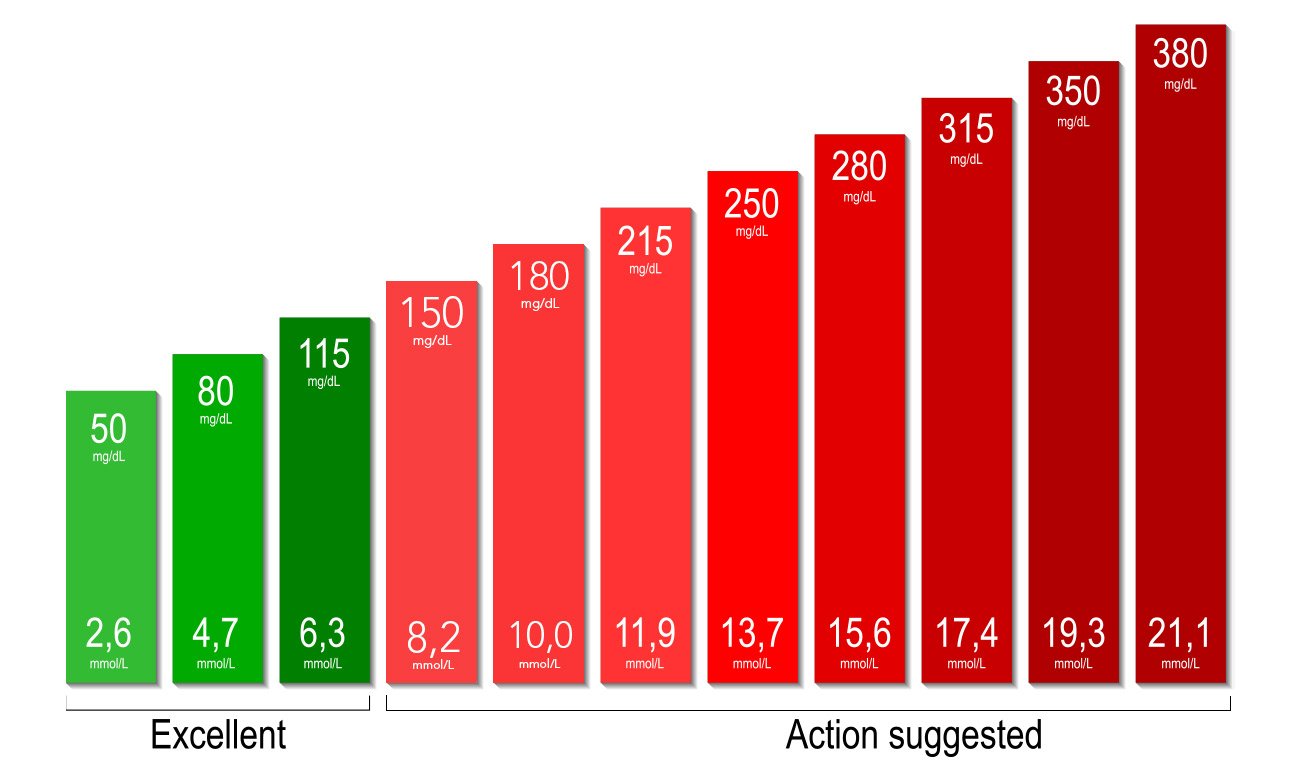
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose < 100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level < 140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Cholesterol
Change Your Life Today And Reduce Your Risk Of Diabetes
Diabetes can be a massive burden on both your health and your wallet. But, maintaining normal blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and staying physically active are great ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
If you are looking to improve your health and monitor your risk factors for disease, getting covered is a great way to relieve the financial pressures of looking after yourself.
Why not contact us today at Insurdinary for a free, personalized, no-obligation quote from some of the best health care providers in Canada!
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Read Also: Mac And Cheese Diabetes
Things To Do If You Have Diabetes
Common things that people with diabetes should avoid include eating lots of simple sugars, eating too much food for the activity theyve performed recently, and not following medication or exercise plans.
Some things that can be harmful to people with diabetes are smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol in excess, and eating large portions of unhealthy foods.
The person should maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly. The doctor may also recommend taking insulin or other medications to manage their blood sugar levels.
Different Levels And What They Mean
The ranges of safe levels of blood glucose depend on factors such as what time of day it is and when you last ate. Safe levels of blood sugar are high enough to supply your organs with the sugar they need, but low enough to prevent symptoms of hyperglycemia or complications of diabetes which follow the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases guides. Dangerous levels of blood glucose are outside of this range.
The target levels can also vary if you have diabetes. For example, if you are diabetic and are monitoring your blood sugar, you might get a reading of 65 mg/dl. That is considered to be mild hypoglycemia, and you would be wise to eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and retest your blood sugar in 15 minutes.
If you were not diabetic, you probably would not know that your sugar was low because you would not test and because you would not symptoms, and you would not act.
That is fine because your body is capable, under normal circumstances, of raising your blood glucose to healthy levels when needed, even if you have not eaten. It is important to keep them in control to help prevent issues like heart disease or nerve damage.
Looking for the best prediabetes diet? Learn what foods are best to help you manage your prediabetes.
You May Like: Metformin Uses And Side Effects
What Is The Normal Range For Blood Sugar Levels And What Blood Sugar Level Constitutes A True Emergency
Dr. Horton answers the question: ‘Normal Range For Blood Sugar Levels?’
— Question:What is the normal range for blood sugar levels, and what blood sugar level constitutes a true emergency?
Answer:Now, in a normal individual we measure blood sugar under different circumstances. What we call fasting blood sugar or blood glucose levels is usually done six to eight hours after the last meal. So it’s most commonly done before breakfast in the morning and the normal range there is 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter.
Now when you eat a meal, blood sugar generally rises and in a normal individual it usually does not get above a 135 to 140 milligrams per deciliter. So there is a fairly narrow range of blood sugar throughout the entire day.
Now in our diabetic patients we see both low blood sugar levels that we call hypoglycemia, or elevated blood sugars, hyperglycemia. Now, if the blood sugar drops below about 60 or 65 milligrams per deciliter, people will generally get symptoms, which are some shakiness, feeling of hunger, maybe a little racing of the heart and they will usually be trenchant or if they eat something, it goes away right away. But if blood sugar drops below 50 and can get down as low as 40 or 30 or even 20, then there is a progressive loss of mental function and eventually unconsciousness and seizures. And of course that is very dangerous and a medical emergency.
Broccoli And Broccoli Sprouts
Sulforaphane is a type of isothiocyanate that has blood-sugar-reducing properties.
This plant chemical is produced when broccoli is chopped or chewed due to a reaction between a glucosinolate compound called glucoraphanin and the enzyme myrosinase, both of which are concentrated in broccoli .
Test-tube, animal, and human studies have shown that sulforaphane-rich broccoli extract has powerful antidiabetic effects, helping enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar and markers of oxidative stress .
Broccoli sprouts are concentrated sources of glucosinolates like glucoraphanin, and theyve been shown to help promote insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes when supplemented as a powder or extract (
11 ).
Keep in mind that the best way to enhance the availability of sulforaphane is to enjoy broccoli and broccoli sprouts raw or lightly steamed, or to add active sources of myrosinase like mustard seed powder to cooked broccoli (
Recommended Reading: Cheese Diabetics Can Eat
Causes Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst the liver and muscles produce some glucose, most comes from the foods we eat. Food and drinks that are high in carbohydrates are most impactful on blood sugar level. What we eat provides us most of the nutrients our body needs and sometimes, does not need. That is not to say that food is a major cause of blood sugar level increasing or decreasing too dramatically.
Typically, if a person has health conditions or poor nutrition, this will lead to a spike or decline in blood sugar level. The causes differ from high to low blood sugar levels and are as follows:
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
What Causes High Blood Sugar
A variety of things can trigger an increase in blood sugar level in people with diabetes, including:
- stress
- missing a dose of your diabetes medicine or taking an incorrect dose
- overtreating an episode of low blood sugar
- taking certain medicines, such as steroids
Occasional episodes of hyperglycaemia can also occur in children and young adults during growth spurts.
How To Lower Morning Blood Sugar
Matthew Garza
Trying to learn how to lower morning blood sugar? Heres why your glucose levels rise in the morning and a few things you can try to keep them in range.
Waking up with high glucose levels may feel like it doesn’t make sense. You spend several hours asleep, not consuming any carbs, and yet somehow your glucose levels are still high when you wake up in the morning.
Why does this happen? What can you do to make sure your glucose levels are safely in range in the morning? Learn more about some tips on avoiding high morning blood sugar levels so you can start your day off right.
Don’t Miss: Adverse Effects Of Metformin
How To Get Mail Order Metformin Hcl
SingleCare partners with GeniusRx to deliver mail order Metformin Hcl to your front door. With the SingleCare and GeniusRx home delivery program, when you mail order Metformin Hcl online, you save on your Metformin Hcl prescription and get Metformin Hcl delivered to your home. To get started with your Metformin Hcl mail order and start saving, click the button below.
Random Blood Sugar Test
This measures your blood sugar at the time youre tested. You can take this test at any time and dont need to fast first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
| 140 mg/dL or below | N/A |
*Results for gestational diabetes can differ. Ask your health care provider what your results mean if youre being tested for gestational diabetes.Source: American Diabetes Association
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Also Check: Is Pasta Good For Diabetics
Is 120 Fasting Blood Sugar High
A fasting blood glucose level less than 100 is considered to be normal. Fasting glucose between 100 and 120 is referred to as impaired fasting glucose or pre-diabetes. A diabetic is defined as someone who has a fasting blood sugar greater than 120 or a non-fasting blood sugar greater than 200. When fasting glucose levels are low, it should be seen as a warning sign.
Levels After Youve Eaten
Many foods have types of carbohydrates called starches and sugars. When you eat foods with these types of carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is a type of simple sugar, and releases the glucose into your bloodstream. Aside from glucose produced by your liver, food is the main source of plasma glucose.
Two hours after eating, your blood sugar levels rise. They rise more when you eat more carbohydrates, when you do not eat fiber, fat, or protein with your carbs, and when you eat certain types of carbohydrates, such as refined sugars and starches.
These are target values from The Joslin Diabetes Center, which include levels for people with diabetes:
| When Measured |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Bad Side Effects Of Metformin
How Can One Tell If I Have Diabetes By Examining My Blood
Your body converts sugar, also called glucose, into energy so your body can function. The sugar comes from the foods you eat and is released from storage from your bodys own tissues.
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. Its job is to move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of tissues. After you eat, the level of glucose in the blood rises sharply. The pancreas responds by releasing enough insulin to handle the increased level of glucose moving the glucose out of the blood and into cells. This helps return the blood glucose level to its former, lower level.
If a person has diabetes, two situations may cause the blood sugar to increase:
- The pancreas does not make enough insulin
- The insulin does not work properly
As a result of either of these situations, the blood sugar level remains high, a condition called hyperglycemia or diabetes mellitus. If left undiagnosed and untreated, the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, blood vessels and other organs can be damaged. Measuring your blood glucose levels allows you and your doctor to know if you have, or are at risk for, developing diabetes.
Much less commonly, the opposite can happen too. Too low a level of blood sugar, a condition called hypoglycemia, can be caused by the presence of too much insulin or by other hormone disorders or liver disease.
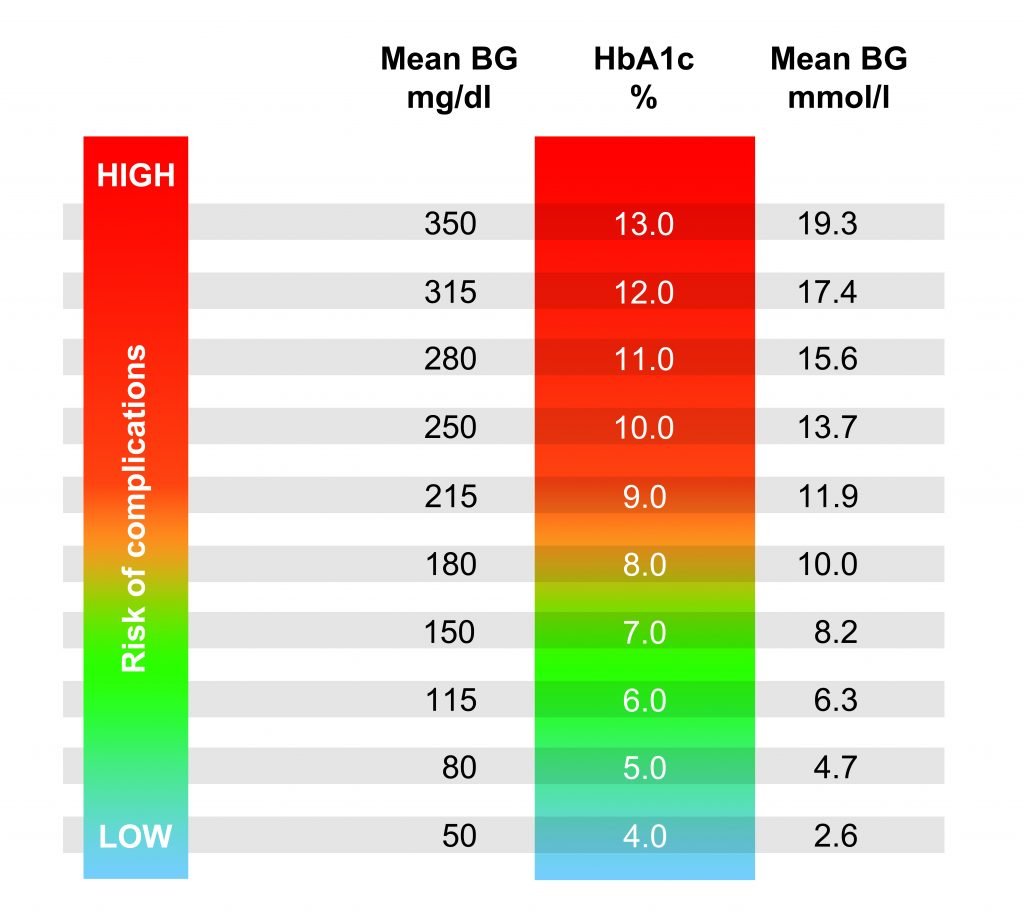
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
You May Like: What Are The Side Effects Of Metformin
How To Do A Finger
Your healthcare team will show you how to do it the first time, but these are the key steps:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water. Dont use wet wipes as the glycerine in them can affect the test result. Make sure your hands are warm so its easier to get blood and wont hurt as much.
- Take a test strip and slot it into the meter to turn it on. Some meters will have tests strips built in.
- Remove the cap from your finger prick device and put in a new lancet. Then put the cap back on and set the device by pulling or clicking the plunger.
- Choose which finger to prick but avoid your thumb or index finger . And dont prick the middle, or too close to a nail. Place the device against the side of your finger and press the plunger. Use a different finger each time and a different area.
- Take your meter with the test strip and hold it against the drop of blood. Itll tell you if the test strip is filled, usually by beeping.
- Before you look at your reading, check your finger. Use a tissue to stop bleeding, then use it to take out the lancet and throw it away in your sharps bin.
- You can use the same tissue to take out the test strip and throw that away too. Taking out the strip will usually turn the meter off.

