Communicating With Your Veterinarian
IMPORTANT: Make sure that you communicate with your veterinarian prior to any changes. It is important that he or she knows exactly how much insulin your dog or cat is getting. Because of the âconversion,â you need to be sure to tell them the type of insulin and strength , the type of insulin syringe , and the amount, so that they can determine the actual amount of insulin your pet is getting.
A U-100 insulin syringe and a 1 ml regular syringe .
Throw Away Insulin And Use A New Vial Pen Or Cartridge If:
-
Insulin has been left where it is very hot or very cold.
-
Insulin is cloudy or contains particles.
-
It is later than the expiration date on the vial, pen, or cartridge.
-
It has been more than 28 days since you began using the vial, pen, or cartridge.
-
Put a label on your pen, vial, or cartridge with date opened.
- Insulin vials have U-100 insulin. That means there are 100 units of insulin in each milliliter of insulin.
- Humalog® insulin comes in 3 mL vials or 10 mL vials.
- All other types of insulin come in 10 mL vials. Insulin pens or cartridges come in boxes of five 3 mL pens or cartridges.
History Or How This Came About
The history of the insulin Unit has been well reviewed elsewhere,, but it is, in short, a history of change. Originally defined as the amount of insulin required to cause convulsive hypoglycemia in a fasted 2kg rabbit, standards for potency have changed with improvements in the preparation and stabilization of insulin in solution. Where potency was defined in the 1920s as 8IU/mg of insulin, this definition was revised upward in 1959 by the World Health Organization Expert Committee on Biological Standardizations Fourth International Standard to 24IU/mg. It was revised upward again by the same committee in the 1986 to 26IU/mg., This value remains the standard to date, with the latest updates made in 2010.
However, as the 1986 standard contains some water and salts, amino acid analysis gives a corrected potency of 6 nmol per 1IU., If instead, anhydrous insulin is considered, the 6 nmol per 1IU potency is equivalent to 28.8IU/mg, or 0.0347mg/IU. This latter potency is more common and has been referred to as the established standard.
As a result, there is one standard, but two human insulin potencies due to improvements in the quality of insulin preparation. The conversion factors arising from these different potencies are given in . The conversion factor resulting from the Fourth International Standard was calculated as per, and can still be occasionally found .
Also Check: Metformin Maximum Dose
You Are Leaving A Sanofi Us Website
Sanofi US does not review the information contained in this website and/or database for content, accuracy, or completeness. Use of and access to this information is subject to the terms, limitations, and conditions set by the website and/or database producer.
Sanofi US makes no representation as to the accuracy or any other aspect of the information contained on such website and/or database, nor does Sanofi US necessarily endorse such website and/or database.
How Many Ml Are In A Unit Of Insulin
| Number of units the syringe holds | |
|---|---|
| 1/4 mL or 0.25 mL | 25 |
| 1/3 mL or 0.33 mL | 30 |
| 1/2 mL or 0.50 mL | 50 |
100 units
Likewise, how many mL is 30 units of insulin? How to Know What Syringe Size to Choose
| Syringe Size | Number of Units the Syringe Holds |
|---|---|
| 0.25 ml | |
| 100 |
Keeping this in consideration, how much is a unit of insulin?
That 1 mg. of this standard contains eight units of insulin
How many units are in a 3ml vial of insulin?
Each vial contains 1000 units insulin lispro in 10 ml solution. Each cartridge contains 300 units of insulin lispro in 3 ml solution. Each pre-filled pen contains 300 units of insulin lispro in 3 ml solution. Each KwikPen delivers 1- 60 units in steps of 1 unit.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Interaction Of Levemir With Other Drugs:
Levemir can be used with other drugs like metformin to control blood sugar levels. It can also be taken with mealtime insulins to control blood sugar quickly. However, with certain other drugs, it can cause serious consequences.
For example, Levemir with thiazolidinedione can affect your heart and cause a heart attack. Similarly, taking Levemir with certain other diabetic drugs may cause hypoglycemia. These include Glucotrol and Symlin etc.
Also Check: Glucophage Dosage For Weight Loss
Factors That Speed Insulin Absorption
Variation in insulin absorption can cause changes in blood glucose levels. Insulin absorption is increased by:
- injecting into an exercised area such as the thighs or arms
- high temperatures due to a hot shower, bath, hot water bottle, spa or sauna
- massaging the area around the injection site
- injecting into muscle this causes the insulin to be absorbed more quickly and could cause blood glucose levels to drop too low.
You May Like: Does Squeezing Finger Affect Blood Sugar Reading
How Do I Store Insulin
| Insulin | |
| Store in refrigerator. Good until expiration date on insulin pen or cartrige. | Store at room temperature. Throw away 28 days after first use. |
*Source: These are the manufacturers recommendations.
- When storing insulin in the refrigerator, the temperature should be between 36 degrees F and 46 degrees F.
- When storing insulin at room temperature, temperature should be between 36 degrees F and 86 degrees F.
Adjust And Titrate No More Frequently Than Every 3
More or less stringent goals may be appropriate for individual patients.
- In clinical trials, patients started on, or changed to, Toujeo required a higher dose than patients controlled on Lantus®1
- Monitor glucose frequently in the first few weeks of therapy
- The maximum glucose-lowering effect of a dose of Toujeo may take 5 days to fully manifest, and the first Toujeo dose may be insufficient to cover metabolic needs in the first 24 hours of use
FPG, fasting plasma glucose.
ADA glycemic recommendations for fasting or pre-meal plasma glucose for non-pregnant adults with diabetes: 80-130 mg/dL.2
Ensure patients have a prescription for Toujeo as well as a second, separate prescription for pen needles.
You May Like: Medications To Lower A1c
More About How Many Units Are In A Ml Recipes
VOLUME CONVERSIONS FOR RECIPE INGREDIENTS
RECIPE CONVERSION BASICS | ALLRECIPES
UNITS OF MEASURE – HOW TO COOKING TIPS – RECIPETIPS.COM
MEASUREMENT CONVERSION CHARTS FOR RECIPES
LIQUID & AMP DRY MEASUREMENT CONVERSION CHART
IMPERIAL TO METRIC CONVERSIONS FOR COOKING
HOW TO CONVERT METRIC UNITS TO US CUSTOMARY UNITS
GOOD COCKTAILS – BAR MEASUREMENTS AND BAR UNIT CONVERTER
HOW TO MEASURE COCKTAIL INGREDIENTS – DIFFORD’S GUIDE
COOKING CONVERSIONS AND MEASURES – MY PARISIAN KITCHEN
BAKING 101 – BAKING MEASUREMENTS | EGGLESS COOKING
HOW TO MEASURE FLOUR AND BAKING CONVERSION CHART – PASTRY …
THE EASIEST WAY TO COUNT A STANDARD DRINK | CHATELAINE
COOKING WEIGHTS AND MEASURES – WIKIPEDIA
COOKING RECIPE CONVERTER – THE CALCULATOR SITE
1000 MG EQUALS HOW MANY TEASPOONS RECIPES
750 ML TO CUPS | ABCADDA.COM
IMPERIAL AND U.S. SYSTEMS OF MEASUREMENT BASIC KITCHEN …
MEASUREMENT CONVERSION CHART
RECIPE CONVERSION CHARTS – FOODGEEKS
COOKING EQUIVALENTS AND MEASURES – SCIENCE OF FOOD …
HOW MANY CUPS IN MILLILITERS RECIPES
CHAPTER 7 RECIPE AND MENU COSTING INTRODUCTION TO FOOD …
COCKTAIL CALCULATOR RETHINKING DRINKING – NIAAA
BEST HOW MUCH IS 80 ML IN CUPS YOU CAN PLAY RIGHT NOW
VOLUME TO WEIGHT CONVERTER FOR RECIPES – HOW MANY WIKI …
DRINK SIZE CALCULATOR RETHINKING DRINKING – NIAAA
TABLESPOONS AND CUP SIZES AROUND THE WORLD
PHARMACY CALCULATIONS REVIEW
CONVERTING UNITS OF INSULIN TO MILLIGRAMS AND MILLILITERS
CONVERT ML TO OZ – CONVERSION OF MEASUREMENT UNITS
How Is It Given
Insulin is given by injection because it cannot be taken orally – the stomach will break it down so that is is no longer effective in breaking down blood sugar.
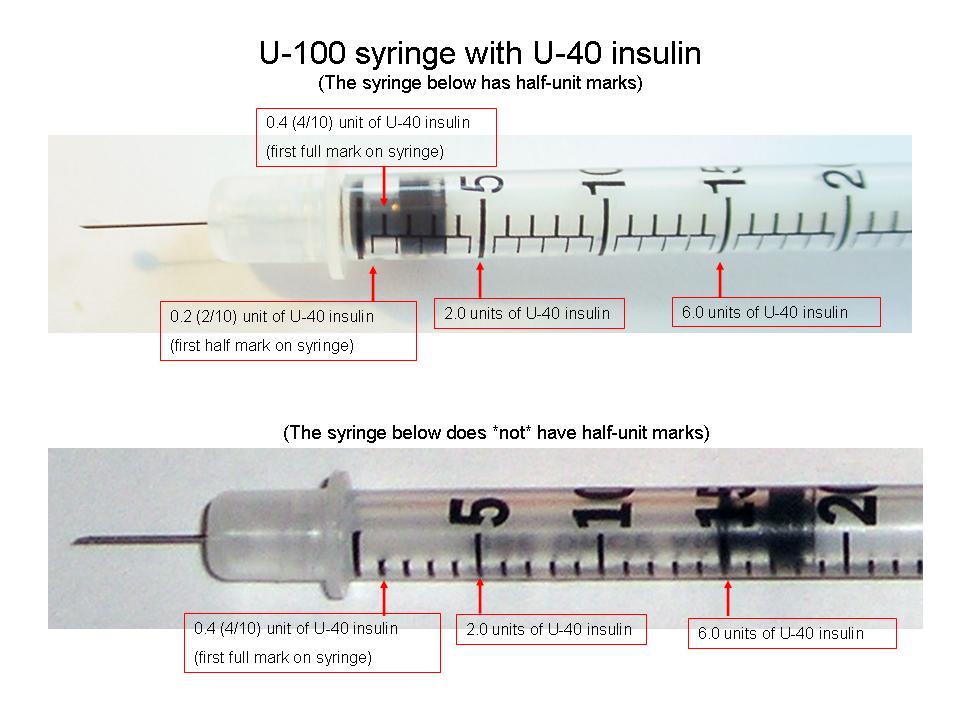
Insulin should always be dosed using special insulin syringes marked with insulin units. Common insulin U-100 syringes can hold 100 units there are also Lo-dose syringes, which are syringes that can hold a total of 30 units or 50 units.
The above picture shows the syringes themselves but they are so small that they can be hard to read, so often we flatten out the measurement on the side of the syringes, so that each syringe label looks something like the pictures below:
| Lo-Dose insulin syringe for measuring up to 50 units Each mark is 1 unit apart. | Insulin syringe for measuring up to 100 units Each mark is 2 units apart. | Insulin syringe for measuring up to 100 units Each mark is 2 units apart. Even numbers are marked on the scale on the rightand odd numbers are marked on the scale on the left. |
You May Like: Can You Die From Diabetes Type 1
How Much Insulin Do You Need
In type 1 diabetes, most people need a total of 0.5 – 0.8 units of insulin per kilogram of body weight each day. Roughly half this insulin is needed for food intake, and half is the basal rate. In DAFNE half is therefore taken as long-acting insulin and this is divided into two injections of Levemir insulin. One injection when you get up in the morning, and the other in the evening at bedtime. For most people, this is about 24 units in 24 hours.
The amount of background insulin does not depend on what you eat, and the dose should be low enough to allow you to miss meals without the risk of low glucose , whilst still keeping the glucose levels within the target range.
The remainder of the total daily dose is taken at meal times, as a quick acting insulin. Sometimes these are given as insulin mixtures, but not in the DAFNE program.
How Many Units Is 10 Ml Of Insulin
4.1/5mlunitsinsulinunits insulin10 ml
100 units
Beside above, how much insulin do I inject? Generally, to correct a high blood sugar, one unit of insulin is needed to drop the blood glucose by 50 mg/dl. This drop in blood sugar can range from 30-100 mg/dl or more, depending on individual insulin sensitivities, and other circumstances.
Thereof, how many units of insulin is normal?
Eventually, many people with Type 2 diabetes will require 12 units of insulin for every kilogram of body weight that is, an 80-kilogram person will require at least 80 units of insulin each day. To start, however, your doctor may begin by prescribing 0.15 units of insulin per kilogram.
How do you measure units of insulin in a syringe?
When measuring the amount of insulin, read from the top ring , and not the bottom ring or the raised section in the middle of the plunger. For example, Figure 1 shows a 100 unit insulin syringe. Each line represents two units of insulin. Therefore the syringe contains 32 units of insulin.
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Much Does A Month Of Insulin Cost
Everyone has different insulin needs. There isnt a one size fits all approach to determining how much insulin you need. Those taking analog insulin take a background or basal dose once or twice a day. In contrast, those taking regular human insulin take it three to four times a day.
This cadence is the only insulin some people with type 2 diabetes need. But for type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2, additional insulin is needed at mealtime. Depending on which insulin you are using, it should be taken 10 to 30 minutes before your meal. The amount of insulin depends on what you plan to eat. For example, you might need 1-3 units per carbohydrate portion .
People with type 1 diabetes generally use two different types of insulin per day. They start with two injections per day and progress to three to four doses per day, according to the American Diabetes Association . People with type 2 diabetes might start with 0.5-0.8 units per kilogram of body weight per day and eventually take 1-2 units per kilogram of weight. For a person weighing 150 pounds, this would be 68 to 136 units per day. For a person weighing 175 pounds, this would be 80-160 units per day.
One vial of insulin contains 1000 units, and pens contain 300 units.
| Insulin Prices |
|---|
* Based on three vials or 10 pens
In addition to the above costs, you might also require additional supplies, such as:
How Is It Used
U-500 is 5 times more concentrated than U-100 insulin. This means that every 1 unit of U-500 is the same as 5 units of your usual insulin. This makes it a more powerful medicine.
-
It also means that you need to be careful about giving yourself the right amount of U-500. If you are using a regular insulin syringe like the kind used for U-100 insulin, the markings each correspond to one-fifth of a U-500 unit. So, if you are taking 100 units of U-500 in an insulin syringe, you would draw insulin from the vial up to the 20 mark . Your health care provider might want you to use a different kind of syringe, called a tuberculin syringe. This kind of syringe is marked in milliliters . If you are taking 100 units of U-500 in a tuberculin syringe, you would draw insulin from the vial up to the 0.2-ml mark.
-
Check your insulin before you leave the pharmacy to be sure you have the right kind. U-500 insulin comes in 20-ml vials and has orange stripes on the box and label. Make sure you are also using the correct syringes. Your health care provider will tell you whether to use the usual insulin syringes or to switch to tuberculin syringes.
-
Don’t hesitiate to ask your prescriber or pharmacist any questions you may have about U-500. It can be confusing at first to make the switch, but your health care team is there to help you.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Too Much Metformin
Cost Of Insulin By Country 2021
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows the body to use sugar in the food that you consume for energy. Insulin regulates the blood sugar levels in the body. Type 1 diabetics do not produce insulin naturally and must take insulin when they eat to help their bodies properly process glucose. Some type 2 diabetics need insulin as well, especially as the condition progresses if diet and exercise do not help.
Of the 30.3 million people in the United States with diabetes, about 5% are type 1 diabetics and need insulin to survive.
In the United States, insulin prices are extremely high and are continuing to rise. In 2012, the average annual cost of insulin per patient was $2,864 per year. In 2016, the prices nearly doubled to $5,705 per year. The cost of one insulin vial varies depending on the type of insulin and how the patient pays for it.
In addition to insulin vial, diabetics also pay for glucose monitors, test strips, lancets, and other supplies. Even with insurance, the cost of insulin can cost more than what most can afford. Insulin can range anywhere from $25 per vial to $300 per vial. Some people may need up to six vials per month.
In addition to vials, diabetics can choose to use insulin pens, which are prefilled and easier to use and travel with. Insulin pens, however, can cost more than vials per month because they typically contain fewer units of insulin.
How Should I Store Soliqua 100/33
Store your unused Soliqua 100/33 pen in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F . Protect the pen from light. Do not use past the expiration date. Do not freeze Soliqua 100/33 pens and do not use Soliqua 100/33 if it has been frozen.
After your first use, you can store your Soliqua 100/33 pen at room temperature no higher than 77°F for up to 28 days. After 28 days, throw it away, even if there is some medicine left in the pen.
Replace the pen cap after each use to protect from light. Do not store the Soliqua 100/33 pen with the needle attached.Keep your Soliqua 100/33 pen, pen needles, and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Example #: Carbohydrate Coverage At A Meal
First, you have to calculate the carbohydrate coverage insulin dose using this formula:
CHO insulin dose = Total grams of CHO in the meal ÷ grams of CHO disposed by 1 unit of insulin .
For Example #1, assume:
- You are going to eat 60 grams of carbohydrate for lunch
- Your Insulin: CHO ratio is 1:10
To get the CHO insulin dose, plug the numbers into the formula:
CHO insulin dose =
- The carbohydrate coverage dose is 6 units of rapid acting insulin.
- The high blood sugar correction dose is 2 units of rapid acting insulin.
Now, add the two doses together to calculate your total meal dose.
Carbohydrate coverage dose + high sugar correction dose = 8 units total meal dose!
The total lunch insulin dose is 8 units of rapid acting insulin.
To Figure Out How Long A Pen/vial Of Insulin Will Last:
Take your total daily dose, add any extra insulin waste such as priming pens/infusion sets, then use that number to divide the number of units in the pen or vial that you use. – 3 ml pen/cartridge contains 300 units of insulin – 5 ml vial contains 500 units of insulin – 10 ml vial contains 1000 units of insulin.
Did you catch that? ) No problem.
Don’t Miss: Are Pork Rinds Good For Diabetics
First Some Basic Things To Know About Insulin:
- Approximately 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight, when you are fasting and between meals. This is called background or basal insulin replacement. The basal or background insulin dose usually is constant from day to day.
- The other 50-60% of the total daily insulin dose is for carbohydrate coverage and high blood sugar correction. This is called the bolus insulin replacement.
Bolus Carbohydrate coverage
The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio.The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin.
Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of 12-15 grams of carbohydrate. This range can vary from 6-30 grams or more of carbohydrate depending on an individuals sensitivity to insulin. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress.
Bolus High blood sugar correction
The bolus dose for high blood sugar correction is defined as how much one unit of rapid-acting insulin will drop the blood sugar.
Generally, to correct a high blood sugar, one unit of insulin is needed to drop the blood glucose by 50 mg/dl. This drop in blood sugar can range from 30-100 mg/dl or more, depending on individual insulin sensitivities, and other circumstances.

