Can Drinking Beer Lower Blood Glucose Level
Using beer monotherapy to control blood sugar has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. 🙂 Drinking beer can lower your blood sugar, especially if you drink a lot of it, but not in the way you want it too. If you really tie one on, not that Im recommending it, your blood sugar will definitely drop. The problem is that it will drop 6-10 hours downstream when you are sleeping it off. Depending on what other meds you are on for your diabetes, it might even drop you low enough to kill you. In the mean time, before your blood sugar drops so low that you die, your sugar will actually go up because beer has quite a few carbohydrates. Lets face it, a can of beer is just a fermented bowl of oatmeal, after all. But assuming you dont drink enough to kill yourself, drinking a lot of beer can actually make your diabetes worse because beer has a lot of calories, which can make you fat, which can make your insulin resistance worse, which will make your blood sugars higher, which will kill you very slowly instead. Dont get me wrong. Sorry wives of beer drinkers: your newly diabetic husband can still have his beer. But like anything else with diabetes, moderation is the key. So dont overdo it. Remember that too much alcohol is a recipe for too low blood sugar. Enjoy all that life has to offer, just enjoy it in moderation.Continue reading > >
Stick To Your Medication And Insulin Regimen
Skipping a dose of medication or insulin can be harmful to your body and increase your blood sugar levels.
Its important to stick to your treatment plan and follow your doctors instructions for taking your medication.
Summary
Healthful lifestyle habits can help people manage their blood sugar levels over the long term, such as eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting good sleep.
Recommended Reading: Smirnoff Ice Nutrition Sugar
What Level Of Blood Sugar Is Dangerous & How To Bring It Down Quickly
High blood sugar is a condition which occurs if the transport of the sugar from the blood to the cells is affected. And this condition if left unchecked can lead to a dangerous rise in the sugar level, which can further invite many other problems and complications. So what level of blood sugar is dangerous and how to bring it down quickly? It is important to know about this and the ways to deal with it.
Don’t Miss: Metformin / Sitagliptin Side Effects
Who Should Check The Level
Bloodtest to check blood sugar level is not always recommended for healthyindividuals. But you may need to take the test if you experience signs andsymptoms of diabetes.
Theearly warning signs could be vogue or so mild, making you unaware to theexistence of the disease . Some people may not have any noticeable symptom until thedisease causes long-term damage.
But ingeneral, here are a few common signs and symptoms of diabetes :
Additionally,type 2 diabetes is likely to cause yeasts infections, slow healing wounds/sores /cuts, and pain in the legs. Type 1 diabetes might also causeunintentional weight loss, nausea, and vomiting .
Checkingblood sugar regularly is usually important for people with the followingsituations:
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
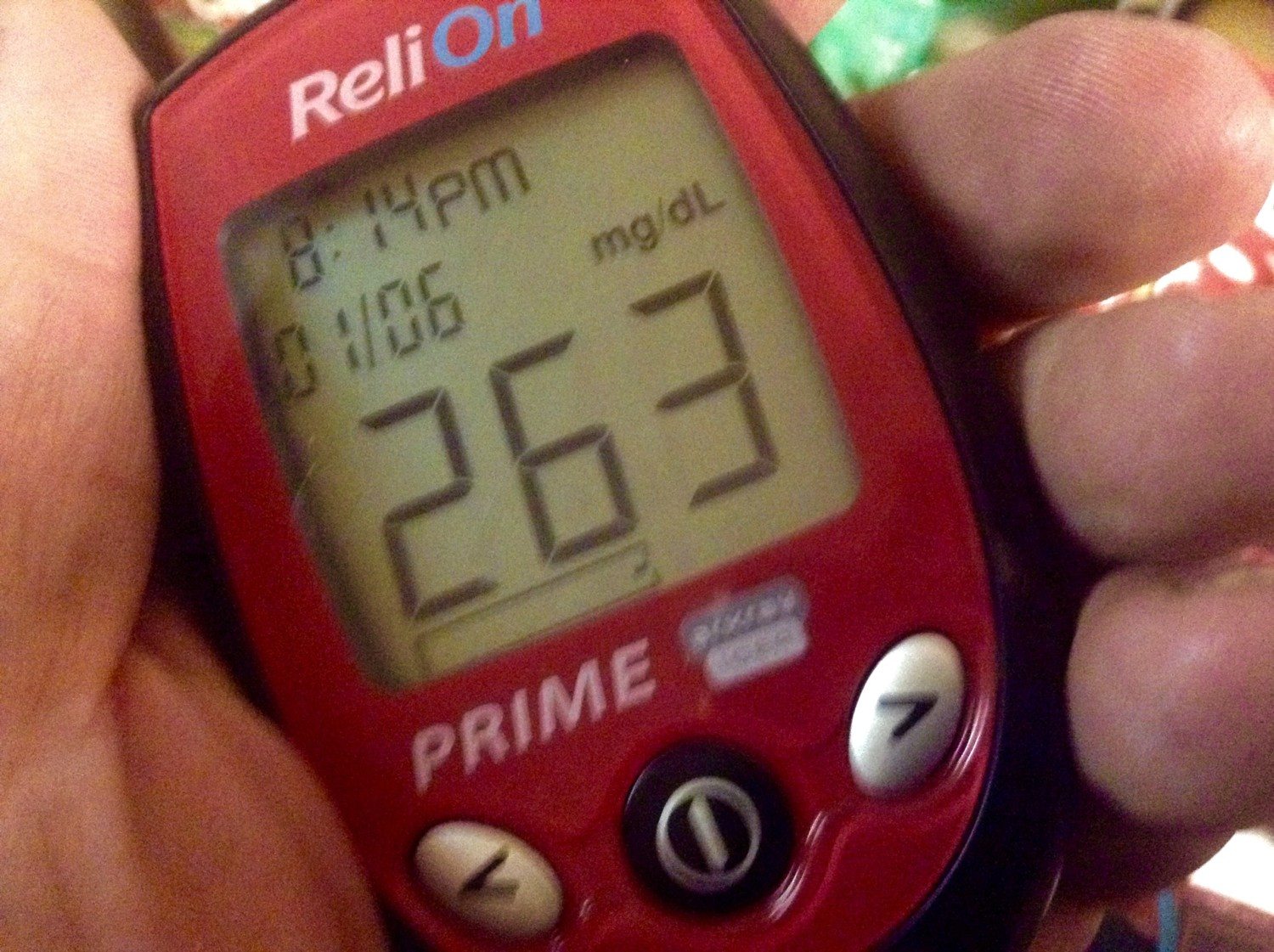
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
Also Check: What A1c Requires Insulin
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.
How High Can Blood Sugar Go Before Death You Need To Know This
High Blood Sugar or Hyperglycemia is a disease that is the cause of most deaths worldwide. Yet, mostly ignored. We used to take diabetes casually. But should we? The answer is NO. High blood sugar is a fatal disease. We must be attentive to how high can blood sugar go before death? What happens to your body when your sugar level inclines? What are the risks associated and ways to prevent them? Read this article to increase your awareness.
Hyperglycemia is the condition when the body has insufficient insulin or when the body cannot utilize insulin appropriately.
Blood glucose is said to be excessively high when it is higher than 130 mg/dl before a meal or higher than 180 mg/dl two hours after the primary nibble of a dinner. We have to take note that majority of the symptoms of high blood glucose will only show up if your blood sugar is more than 250mg/dl. But thats not always the case.
Don’t Miss: Can I Get A Tattoo If I Have Diabetes
Fruit Juice And Smoothies
Dr Roxburgh said it can be easy to over indulge when it comes to fruit juices and smoothies – meaning you are packing in extra sugar and calories which can lead to both glucose spikes and weight gain.
She explained: “Fruit juice and smoothies should be avoided as they can put blood sugar up very quickly.
“Fruit in general can be consumed and I would never recommend excluding any fruit totally because of the nutritional value that fruit contains, however, there are certain fruits that I would recommend over others for someone with type 2 diabetes.
“For example, berries or an apple rather than pineapple, oranges or bananas. Tinned fruit, however, I would avoid as it is kept in a high-sugar syrup.”
Healthy smoothies can sometimes have just as much sugar as fizzy drinks in them – even though the sugars are natural these can contribute to weight gain.
What Is The Dawn Phenomenon
Another reason for high nighttime blood sugar levels is the dawn phenomenon. The dawn phenomenon occurs early in the morning when the body naturally signals your liver to produce glucose, giving your body the energy it needs to wake up.
The hormonal changes associated with the dawn phenomenon happen to people with or without diabetes, though those without diabetes do not experience hyperglycemia. If you take insulin, you may need to try a new basal insulin or adjust the timing and amount of your basal dose or your nighttime basal rates to cover an early morning rise.
Also Check: A Severe Diabetic Emergency Is Characterized By
How To Lower Your A1c Levels
Its important to get your hemoglobin A1C levels as close to normal as possible, says Dr. Bellatoni, Decreasing your hemoglobin A1C decreases your risk of having complications from diabetes. Even if you cannot get your A1C back to the normal range, any improvement lowers your risk of diabetes complications.
What Is High Blood Glucose
People who do not have diabetes typically have fasting plasma blood glucose levels that run under 100 mg/dl.
Your physician will define for you what your target blood glucose should be identifying a blood glucose target that is as close to normal as possible that you can safely achieve given your overall medical health. In general, high blood glucose, also called ‘hyperglycemia’, is considered “high” when it is 160 mg/dl or above your individual blood glucose target. Be sure to ask your healthcare provider what he or she thinks is a safe target for you for blood glucose before and after meals.
If your blood glucose runs high for long periods of time, this can pose significant problems for your long-term increased risk of complications, such as eye disease, kidney disease, heart attacks and strokes and more. High blood glucose can pose health problems in the short-term as well. Your treatment plan may need adjustment if the blood glucose stays over 180 mg/dl for 3 days in a row. It is important to aim to keep your blood glucose under control and treat hyperglycemia when it occurs.
- Increased thirst
- Slow healing cuts and sores
- Unexplained weight loss
- Too much food
- Too little exercise or physical activity
- Skipped or not enough diabetes pills or insulin
- Insulin that has spoiled after being exposed to extreme heat or freezing cold
- Stress, illness, infection, injury or surgery
- A blood glucose meter that is not reading accurately
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Reaction To Too Much Sugar
Slow Healing Of Cuts And Wounds
High blood sugar greatly slows the healing of skin and soft-tissue infections because neutrophils, the most common type of leukocyte in the immune systems arsenal, are particularly vulnerable to high levels of glucose. High blood sugar keeps the neutrophils from sticking to the endothelium, the inner lining of the blood vessels disrupts chemotaxis, the bodys chemical signaling control system that directs neutrophils to the site of injuries or infections and, as noted above, makes phagocytosis sluggish.
Another critical element of wound healing is a sufficient supply of oxygen, and the delivery of oxygen can be reduced by either peripheral neuropathy or peripheral vascular disease both common conditions caused by or made worse by high blood glucose.
The slow healing of wounds sets the stage for some of the grimmest diabetes complications. Minor wounds can advance to cellulitis, which is a serious infection. Cellulitis can advance to tissue necrosis, or tissue death. Tissue necrosis can then extend from the soft tissue into the bone, which is what often leads to amputation: Roughly 73,000 amputations are performed on people with diabetes in the United States each year.
Great Bedtime Snacks For People Living With Diabetes
For some people, a healthy bedtime snack helps to prevent glucose swings during the night. By eating a small snack that is full of protein and healthy fats , your body may be better able to avoid an overnight high but if you take insulin, be sure to cover the carbohydrates in your snack even if it only requires a small dose of insulin.
Here are some snack ideas:
-
Plain nuts or seeds try eating a small handful
-
Raw vegetables, such as carrots, celery, cucumbers, or tomatoes, with a small amount of hummus or peanut butter
-
Plain yogurt, and you can add berries or cinnamon
You May Like: Normal Dosage For Metformin
When To Get Urgent Medical Attention
Contact your diabetes care team immediately if you have a high blood sugar level and experience the following symptoms:
- feeling or being sick
- a fever for more than 24 hours
- signs of dehydration, such as a headache, dry skin and a weak, rapid heartbeat
- difficulty staying awake
These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious complication of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital.
How Often Should I Check My Blood Sugar
The number of times that you check your blood sugar will depend on the type of diabetes that you have and the type of medicine you take to treat your diabetes. For example, people who take insulin may need to check more often than people who do not take insulin. Talk with your health care team about how often to check your blood sugar.
The common times for checking your blood sugar are when you first wake up , before a meal, 2 hours after a meal, and at bedtime. Talk with your health care team about what times are best for you to check your blood sugar.
Also Check: Diabetes Thing On Stomach
What Are The Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia
Its especially important to know the early signs of hyperglycemia if you have type 1 diabetes. If hyperglycemia is left untreated in people with type 1 diabetes, it can develop into ketoacidosis, where ketones, which are toxic acids, build up in the blood. This condition is an emergency situation that can lead to coma or death.
Early symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- High blood sugar.
- Unusual fruity smell on the breath.
- Deep labored breathing or hyperventilation.
- Rapid heartbeat.
Manage Your Carb Intake
Your carb intake strongly influences your blood sugar levels .
Your body breaks carbs down into sugars, mainly glucose. Then, insulin helps your body use and store it for energy.
When you eat too many carbs or have insulin-function problems, this process fails, and blood glucose levels can rise.
Thats why the American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes manage their carb intake by counting carbs and being aware of how many they need .
Some studies find that this can help you plan your meals appropriately, further improving blood sugar management (
Foods that are high in fiber include:
- vegetables
- legumes
- whole grains
The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women and 35 grams for men. Thats about 14 grams for every 1,000 calories .
Summary
Eating plenty of fiber can aid blood sugar management. Soluble dietary fiber appears to be more effective than insoluble fiber for this purpose.
Also Check: Does Metformin Make You Tired
High Blood Sugar Symptoms: Causes Signs And Taking Control
If youve had diabetes for any length of time at all, youve probably seen lists of the signs and symptoms of high blood sugar dozens of times. Doctors and diabetes educators hand them out. Hundreds of websites reprint them. Most diabetes books list them. You likely know some of the items on the list by heart: thirst, frequent urination, blurry vision, slow healing of cuts, and more.
But have you ever stopped to wonder why these symptoms occur? How does high blood sugar cause frequent urination, make your vision go blurry, or cause all of those other things to happen? Here are some answers to explain whats going on in your body when you have high blood sugar.
Only Diabetics Get High Glucose Values
While a high glucose value can indicate diabetes, nondiabetics can also have higher values than normal. When researchers studied people wearing a continuous glucose monitor who did not have a diabetes diagnosis, they found 93% of individuals reached glucose levels that are considered dangerous, with 10% spending over 2 hours per day in these dangerous levels. Traditional glucose measurements, like a single point in time blood glucose value, are unable to capture these abnormalities.
There are actually several causes of high blood sugar unrelated to diabetes that the CDC recognizes. These include certain foods, like artificial sweeteners and coffee. Other factors like stress can do it, too. If you live with an endocrine or pancreatic condition, had surgery recently, or are experiencing intense physical stress , you may also see your glucose value rise.
You May Like: Abnormal Glucose Levels Are Associated With Which Condition
What Are High Blood Sugar Levels
It is essential to address glucose levels in general. In persons without type 1 or type 2 diabetes, blood sugar levels generally range between 70 to 130 mg/dl.
It depends on the last time they ate a meal and the time of day. Normal blood glucose ranges in persons without any type of diabetes are:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning before eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
- One hour after a meal 90 to 130 mg/dl
- Two hours after a meal 90 to 110 mg/dl
- Five or more hours after eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
In pregnant women, blood sugar levels tend to be lower. Harvard Health also confirms that a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 mg/dl after an eight-hour fast. Also, a person has diabetes if their blood sugar is 126 mg/dl or higher.
When it comes to hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, there are two kinds of the problem. The first kind is fasting hyperglycemia, which is blood sugar higher than 130 mg/dl after not eating or drinking for eight hours.
The other kind is postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia, where blood sugar is higher than 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. People without diabetes rarely have blood sugar higher than 140 mg/dl after a meal unless its a big one.

