How Insulin Pumps Work
Insulin pumps are worn externally and deliver a continuous amount of fast-acting insulin 24 hours a day.
There are three main components to insulin pump therapy:
- a pump , which pumps the insulin into your body
- a reservoir or a cartridge, where insulin is held
- an infusion set, which includes a thin tube that runs from the reservoir in the pump to the infusion site on your body, and a short cannula that is inserted under your skin
The main steps to using the pump include placing the insulin-filled reservoir inside the pump, and inserting the cannula under your skin using a needle. The cannula is held in place with an adhesive patch for 24 to 72 hours, after which time it should be replaced. A tube connects the cannula to the reservoir in the pump and delivers a set amount of insulin into your body.
Two types of insulin doses are delivered to your body by the pump:
- Basal insulin doses are delivered continuously over 24 hours and keep your blood sugar levels stable between meals and overnight.
- Bolus insulin doses are delivered when you push a button on the pump – you can use them when you eat to correct high blood sugar levels.
The pump can be worn in many places on your body. It can be attached to your waistband, pocket, bra, armband, or underwear. When you sleep, you can lay it next to you on your bed or nightstand. You can disconnect the pump for activities such as swimming or showering. Insulin pumps that are not waterproof should not be exposed to water.
Do Pumps Take Blood Glucose Readings
Traditionally, pumps have not taken blood glucose readings but it is now possible to get pumps that have sensors which measure sugar levels.
It should be noted that these sensors actually measure the level of sugar in interstitial fluid, a fluid which acts as a reservoir of nutrients, including glucose.
Some people may also wear a continuous glucose monitor in addition to an insulin pump.
A continuous glucose monitor also is worn on the body and provides regular interstitial fluid sugar level readings. The sugar level of our interstitial fluid is generally proportional to the sugar level of our blood
How Do I Choose An Insulin Pump
There are a variety of insulin pumps by different manufacturers on the market. All insulin pumps work in the same basic manner but will vary in their specific functions and features. Your diabetes educator can support you in the process of choosing an insulin pump and help you to work out which one is best for you.
Diabetes insulin pump technology is constantly changing. Be sure to thoroughly research the various insulin pumps you are interested in and make an informed choice. If you have any questions about insulin pump functions speak to your diabetes educator, or the relevant insulin pump company representatives who will be able to help you.
You May Like: Sideffects Of Metformin
What Does An Insulin Pump Do
An insulin pump is intended to act like a human pancreas outside the body. Your pancreas releases insulin in response to changes in your blood sugar level. But when you have diabetes, your body doesnt release insulin or use it properly. As a result, you have to find another way to get the insulin you need.
Insulin pumps work by delivering a basal, or set, rate of insulin through a tube called a cannula. The cannula is inserted just under the top layer of your skin. Your doctor will work with you to determine the amount of insulin you need each day.
Insulin pumps can also deliver an insulin bolus. This is an extra dose of insulin besides your basal rate. A pump wont automatically give you this extra dose of insulin, though. You need to tell the pump to administer the bolus dose.
Some insulin pumps will also monitor your blood sugar level. The pump will tell you in real time what your blood sugar is, so you can give yourself insulin.
Insulin pumps give you insulin according to how you program them. They dont adjust on their own to your changing insulin levels.
They require special training on your part to make sure you can use them safely and effectively.
An insulin pump is usually about the size of a deck of cards, although the size can vary depending on the model. You wear the pump outside your body.
The pump usually consists of:
- a display screen
- a place for an insulin container
- a thin cannula, or tube, that attaches to your body
What Are The Advantages
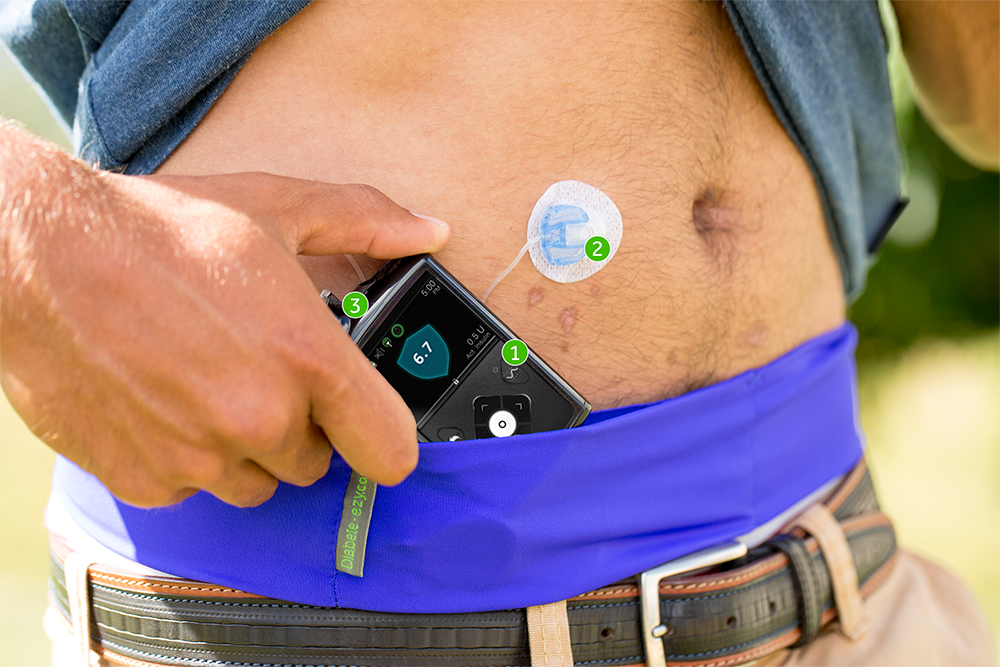

Insulin pump users like managing their type 1 diabetes this way for lots of different reasons. Some of the most common reasons are:
- feeling like you are more in control
- having the flexibility to have a lazy morning, skip a meal or eat late
- delivering food boluses in the most appropriate way, eg spreading it over 7 hours for pizza
- setting a temporary basal increase or decrease when ill, having your cycle, or stressed
- managing the dawn phenomenon
- only needing one needle every 2 or 3 days
Insulin pump users may also find the following things easier:
- managing blood glucose levels around planned or spontaneous exercise
- treating hypers with precise correction doses
- treating hypos with just fast-acting carbohydrate
- managing changing shift work patterns
- managing toddlers meal-time battles
- keeping good control through growth spurts and hormonal changes in adolescence
Don’t Miss: Average Lifespan Of A Type 1 Diabetic
Pump Safety Is A Commitment
The one requirement for using a pump is that you and/or your caregivers are ready and willing to do what it takes to use the pump safely. Checking blood sugar is important because it will warn you if your pump stops working right or your infusion set stops working. This can cause high blood sugar levels and cause diabetes ketoacidosis , which is very serious and dangerous. Checking blood sugar levels frequently will alert you to this possibility and will prevent the development of ketones.
Insulin Injections For Diabetics Just Once Monthly With New ‘jelly’ Substance Being Tested
Early stage tests suggest the new substance could dramatically cut the number of injections type 2 diabetics need, researchers at Duke University in America said. Traditional insulin needs to be injected frequently to keep blood sugar levels stable but even then it creates ‘peaks and troughs’ as the body processes it quickly which can cause complications. Scientists have been working to find a way to deliver the drug in an even way over time. Engineers have created a liquid that turns to jelly once injected under the skin and leaches out its active ingredient gradually. Tests on mice showed it kept blood sugar levels stable for five days, 120 times longer than normal. Related Articles Fizzy drinks linked to prostate cancer risk 28 Nov 2012 NHS care hit by more rationing, claims report 18 Nov 2012 Hundreds of patients subjected to NHS blunders 29 Oct 2012 Ashutosh Chilkoti, professor of biomedical engineering in Duke’s Pratt School of Engineering, and lead author of the study said: “For a patient with type 2 diabetes, it would be much more desirable to inject such a drug once a week or once a month rather than once or twice a day. “Additionally, this approach avoids the peaks and valleys of drug concentrations that these patients often experience.” Other drugs could be delivered in the same way. The findings were published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.Continue reading > >
Also Check: Can I Get A Tattoo With Diabetes
How To Use An Insulin Pump
Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely on how to use an insulin pump.
Isaacs says there are a few other guidelines to keep in mind:
- Change insulin regularly. Knowing how often to add insulin can help ensure you don’t waste it. Most pumps hold 200 to 300 units of insulin and should be changed out every two to three days.
- Carry extra batteries and supplies as needed.
- Make sure to check your glucose regularly or wear a continuous glucose monitoring device. You may have to check your glucose as often as 8 to 12 times a day when you first get adjusted to your pump.
- Work with your diabetes care team to learn how to use your insulin pump. Insulin pumps can be more difficult to use than injections at times, so you want to feel comfortable with using one.
Benefits Of Using An Insulin Pump
Studies have shown that an insulin pump can improve diabetes control and lessen the risk of hypoglycemia. Many people find increased flexibility in the timing of meals and exercise when wearing an insulin pump.
Sharing insulin pump datawith your care team between office visits helps to make the most of the time you spend with them during your appointments. Uploading your pump reports allows the care team to track patterns and make adjustments to your care plan if needed.
Don’t Miss: Does Metformin Cause Rashes
Benefits Of Pump Therapy
Unlike insulin pens or injections, data can be uploaded from most insulin pumps via web-based software. The data relating to glucose concentrations and insulin delivery can be reviewed by the health professional in conjunction with the patient. The GP should instruct the patient to download PDFs of these reports and bring them to their appointment.
Meta-analyses and randomised controlled trials have reported improvements in glycaemic control using insulin pump therapy compared to multiple daily injections. These include reductions in blood glucose, reduced hypoglycaemia , lower glycated haemoglobin , lower insulin requirements, and improved quality of life. The greatest motivating factor for Australians with type 1 diabetes to use an insulin pump is to improve their diabetes control.
There are numerous benefits in using insulin pump therapy rather than multiple daily injections. However, it is important to recognise that there may also be some disadvantages .
When Pumps Are Funded By The Nhs
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends an insulin pump if:
- you’re having frequent hypos or hypers without warning
- your HbA1c is 69mmol/mol or above even though you have tried to manage your blood glucose levels
Your consultant may recommend a pump if this is happening and you can show you’re:
- regularly injecting insulin
- checking your blood glucose at least 4 times a day
- carb counting
Read Also: Can You Take Too Much Metformin
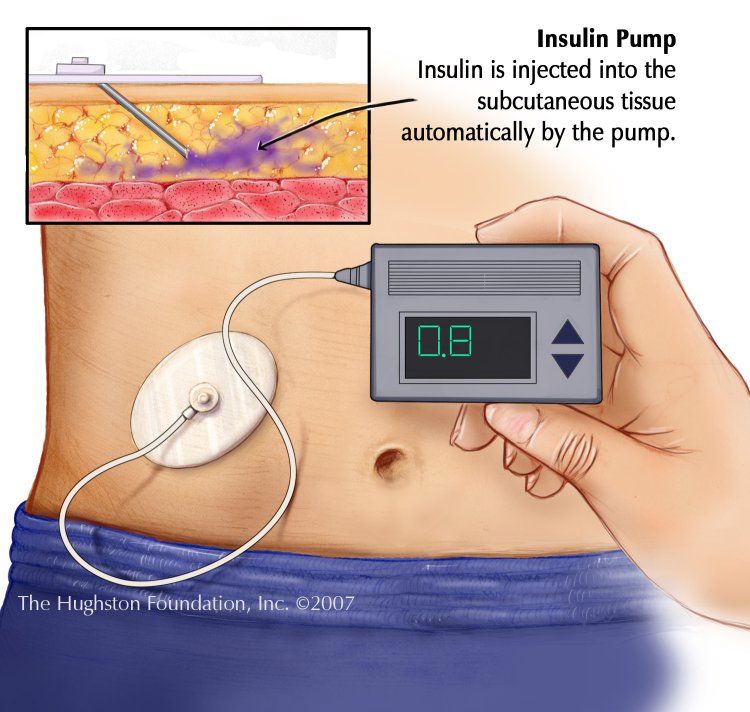
How An Insulin Pump Works
The device releases insulin almost the way your body naturally would: a steady flow throughout the day and night, called basal insulin, and an extra dose at mealtime, called a bolus, to handle rising blood sugar from the food you eat. You program the pump for both basal and bolus doses. If you eat more than normal, you can program a larger bolus to cover the carbs in your food. A bolus can bring down high blood sugar at other times, too.
The pump is about the size of a smartphone. You attach it to your body using an infusion set: thin plastic tubing and either a needle or a small tapered tube called a cannula you put under the skin. The place where you put it in — your belly, buttock, or sometimes thigh — is called the infusion site. Some pumps come with inserters for easier placement even in hard-to-reach areas.
Insulin pumps use short-acting and rapid-acting insulin, but not long-acting, since the pump is programmed to deliver a small amount continuously to keep your blood sugar levels even.
How Often Insulin Pumps Need To Be Replaced
Infusion sets can be expensive, so some patients may try to extend the use of it for as long as possible. This can be dangerous, though, as you run the risk of infection or of having high blood sugar levels.
Therefore, it is recommended that infusion sets that have metal needles be replaced every one to two days. Infusion sets with a soft cannula should be replaced every two to three days.
Patch pumps are a little different since they do not have infusion sets. The battery on the Omnipod insulin pump will last no more than 80 hours. However, it will start reminding you to replace the insulin pump at hour 70 or so.
It is important to replace your insulin pump regularly and rotate application sites. Not taking these steps can lead to skin irritation and infections.
Don’t Miss: Average A1c Non Diabetic
Good Insulin Pump Habits
It may take several months to get comfortable with the insulin pump. During those first months is the time to adopt some good habits. Here are some tips to help you adjust:
Places to wear the insulin pump
Some people are comfortable with wearing the insulin pump on their belt. The pump may come with a leather carry case or clip, which holds the device and gives the appearance of a pager or small mobile phone.
Others simply carry the pump in a pocket. Some women prefer to wear the pump in their bra or attached to a garter on the leg. Each of the pump suppliers has accessories and there are now also many websites selling pump accessories.
The cannula, which is inserted under the skin, is often placed in the abdominal area but can also be placed in the upper buttock, upper and outer thigh, hip or upper arm.
Swimming
Swimming is a very healthy activity for people with diabetes including those using a pump. Some pumps are waterproof and tested to an international standard while others are watertight. This means it is possible to swim, shower and surf without taking your pump off if you so choose. If you participate regularly in water sports it is advisable to check the individual product specifications regarding waterproof status before choosing your pump.
Sleeping
One of the questions most commonly asked about pump therapy is Where do I put the pump when I go to sleep?
Some common places people leave their pumps are:
Exercise
Pregnancy
Sick days
School
Travel
Diabetes Insulin Pump Features To Consider
Calculating insulin
Insulin pumps calculate the amount of insulin required to cover the carbohydrate eaten . Insulin pumps also calculate the insulin dose required to correct any high blood glucose level that you enter in the insulin pump that is outside your target range.
Tracking active insulin
Insulin pumps have a feature that prevents you from stacking or giving too much insulin. When you enter your blood glucose level and carbohydrate intake, the pump will calculate the dose required after considering the insulin still active or on board from a previous bolus. This may assist with avoiding hypos.
Bolus types
Insulin pumps can be programmed to deliver a meal bolus in different ways. A meal bolus may be delivered, for example, over a period of two hours rather than all at once. These different bolus types can make eating a variety of foods and eating out much easier.
Insulin delivery
Pumps vary in the increments of the basal rate and bolus dose that can be delivered. If you have a very small total daily dose of insulin or are very insulin sensitive then small delivery doses will be important.
Insulin reservoir/cartridge size
The reservoir/cartridge size varies between pumps, so depending on your daily dose of insulin some pumps will be more suitable than others.
Infusion sets
Insertion devices
Computer software
Food database
Water resistance
Continuous glucose monitoring systems
Insulin pump cost
Who pays?
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetic Can T Get Blood Sugar Up
Medtronic Minimed 630g System
For an integrated CGM
This model from Medtronic comes with an optional CGM so a person can also monitor their blood sugar levels using the same device. It is also compatible with the Contour Next Link 2.4 blood glucose meter.
Medtronic claims that this system makes a person four times more likely to reach their target A1C level, which is their average blood glucose level over about 3 months.
Other stand out features include:
- alarms if a person goes below their preset glucose levels the device will stop issuing insulin if a person does not respond
- a bolus calculator, which automatically calculates doses and tells a person if they set them too close together
- predictive alerts
- compatible app for smartphones, which displays all readings and allows for notifications and alarms
- suitable for those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
Many insurance companies cover the Omnipod Dash. It is also available through pharmacies with a prescription.
How Do You Manage Patients Using Subcutaneous Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are now commonly used and can ensure good glucose control. The pumps use one of the newer analog insulins and deliver both basal and bolus insulin doses. Since the basal rate is set to deliver necessary insulin for the fasting state, the pump can be used for insulin delivery during the perioperative and intraoperative periods, continuing the established basal rates. Check blood sugars at regular intervals, every 1 to 2 hours, to ensure that the patient’s blood sugar stays between 80 and 180 mg/dl. If the stress of a long surgery raises glucose levels, the basal infusion rate can be safely raised in increments of 0.1 unit per hour. If glucose levels fall, the rate can be safely reduced in increments of 0.1 unit per hour, or the pump can be suspended until glucose levels rise. When the patient is fully recovered, return to normal routines for pump use. The patients may consume a regular diet, as appropriate, when fully alert, awake, and with good bowel sounds.
Elizabeth A. Stephens, Terri Ryan, in, 2009
Read Also: What To Do If Blood Sugar Is Over 400
Have You Ever Wondered How Does The Omnipod Work So Have We We Scoured The Internet And Talked To Some Of Our Favourite Podders To Learn As Much As We Could About How The Omnipod Works And Wanted To Share What We Learned With You
Disclaimer: Please check out CIMs Partners Page to learn more about the companies we work with. Its important for CIM to recognize and to disclose that our writing may be biased based on the fact that the Omnipod provides sponsorship and support to CIM. We work hard to get information into the hands of the diabetes community whenever we feel it may help people live life without limits.
What is different about the Omnipod Insulin Management System? If you are brand new to Omnipod , we suggest checking out Connected in Motions Tech Update blog about the Omnipod Insulin Management System. In short, Omnipod is a tubeless insulin pump made by Insulet, a company whose mission is to make the lives of people with diabetes easier. Insulet was founded in Massachusetts back in 2000 and officially brought to Canada in 2011. Interested in learning more about how the Omnipod came to be? Read more about what inspired Insulets co-founder to create the product one that is now used by 140,000 adults and youth around the world today.
There are two parts of the Omnipod System: The Pod and the PDM .
The Pod and Personal Diabetes Manager communicate wirelessly to deliver continuous insulin based on your personal settingsgiving you what you ask for, when you ask for it. Youll need to keep the PDM within 5 feet of the Pod to program a bolus or make a change to your settings, otherwise, you dont need the PDM with you at all times.

