Choose The Right Insulin
The right insulin can make or break your ability to control those after-meal spikes.; In general, insulin that works quickly and for a short period of time will work better than those that work slowly over a long period of time.
For instance, rapid-acting insulin analogs will cover the post-meal blood sugar rise much better than regular insulin.; Newer ultra-rapid insulins, such as Fiasp, work even faster.
The way insulin is administered can dramatically affect its speed of action.; Afrezza is an inhaled insulin that can be used at mealtimes.; Because the dry powder is absorbed through the lungs, its onset and peak are much earlier than injected insulin.; For those who dont mind a twinge of pain, injecting insulin into muscle will also make it absorb and act much quicker than injecting it into the fat layer below the skin.
Research has also shown that injected insulin can work much faster when the injection site is warmed by rubbing the site, immersing in warm water, or exercising the muscle near the site.; Warming the site causes the blood vessels near the skin to dilate, which allows the insulin to absorb more quickly.; By the way, smoking causes the blood vessels to constrict, so quitting smoking might improve your post-meal blood sugar .
How High Should Your Blood Sugar Be After You Eat
How high should your blood sugar be after you eat? What levels are too high after a meal? Experts vary on what the number should be, but the ADA says a general goal is a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dL, 1 to 2 hours after a meal.
What is a normal blood sugar after eating?;What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels? Theyre less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least 8 hours. And theyre less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating. During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals.
Is 200 blood sugar normal after eating?;Less than 140 mg/dL is normal. 140 to 199 mg/dL is diagnosed as prediabetes. 200 mg/dL or higher after two hours suggests diabetes.
What should blood sugar be 1 hour after eating?;1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL. 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL. 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL.
How To Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
As Dr. Emanuele says, glucose monitoring can be an important tool to help you get your blood sugar under control. Typically, you would do it yourself using a glucose meter or glucometer, which analyzes a drop of blood that you draw by sticking your finger with a lancet and placing the blood on a disposable test strip that you insert into the meter. Your blood sugar goals are set by you and your doctor, but blood glucose for an adult without diabetes is below 100 mg/dl before meals and at fasting; and less than 140 mg/dl two hours after a meal, notes the;ADA.
Some people will check their blood sugar daily or multiple times a day, sometimes using a continuous monitor that is worn on the body particularly those who have;type 1 diabetes;or who have type 2 but take insulin. Yet how frequently a person should monitor their blood sugar is based on a number of factors, including but not limited to whether theyre on insulin, whether they’re taking;oral medication, and how well their blood sugar is controlled and how old they are.
Meanwhile, keep an eye out for these nine key warning signs and symptoms that blood sugar is too high and talk to your doctor about whether you need to adjust your management plan.
You May Like: Can Metformin Cause Low Blood Sugar
What To Know About High Blood Sugar When Living With Diabetes:
What is hyperglycemia?
After eating a meal, the body signals the release of insulin. Insulin is like a key that unlocks the cells in order to store glucose for later use. This process reduces the amount of glucose in your blood stream. In people with diabetes, this process does not work as well because either there isnt enough insulin being produced, or because the body is resistant to the effects of the insulin. As a result, levels of glucose in the blood stream can reach high levels, causing hyperglycemia or high blood sugar.
Scale of normal blood sugar range
- Hyperglycemia occurs when the blood sugar is above 130 mg/dL while fasting, or greater than 180 mg/dL after eating a meal.
- American Diabetes Association Glucose Goals for people with Diabetes:
- Before meals or fasting: 70 to 130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL
Hb A1C If blood glucose is regularly higher than the normal ranges, then this will reflect in the Hemoglobin A1C test that your doctor will run. The Hemoglobin A1C gives your care team an idea of what your blood sugar typically is at.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
- Illness, colds, infections, injuries, surgeries
- Emotional stress
- Not enough Diabetes Medication, or skipped doses of medication
- Too little exercise
How to treat hyperglycemia
When to call your doctor or seek emergency treatment:
REMEMBER: DO NOT DRIVE yourself if you think you may have very high blood Sugars or Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
FREE blood glucose level chart
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c Range
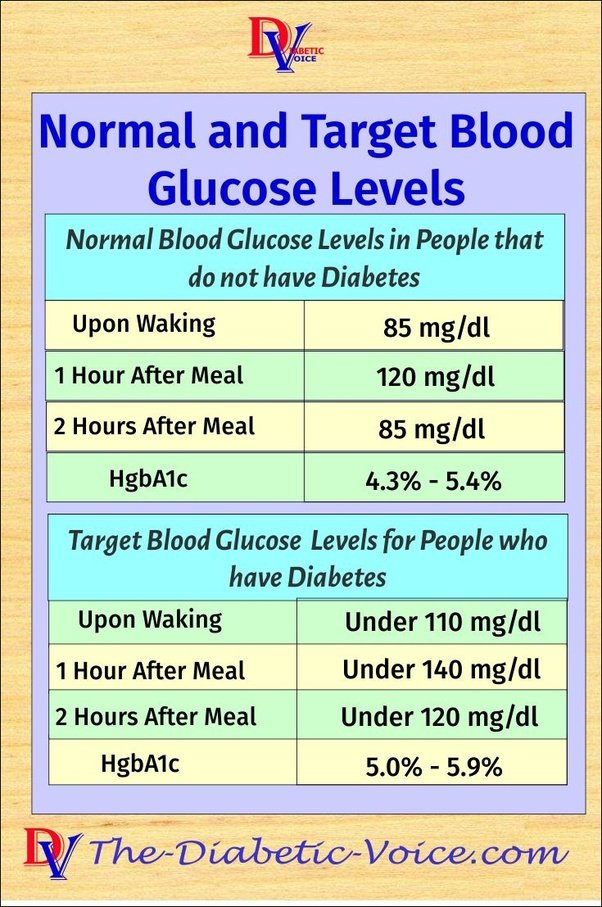
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person’s needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Don’t Miss: How To Mix Insulin
Why Is My Blood Sugar Level High
The clinical term for high blood sugar is hyperglycemia. The most common cause of high blood sugar is Diabetes Mellitus or DM. It is a condition where the body cannot absorb glucose due to any abnormality in the production or action of a hormone called Insulin. Diabetes is mainly of two types: Type 1 and Type 2. Majority of diabetics are suffering from type 2 diabetes, caused by reduced action of Insulin.
However, blood sugar can be high for various other reasons. Illness or injury, hormone disorders, overeating, obesity, some medications can increase blood sugar levels.
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level
Blood sugar level means the amount of glucose dissolved in the blood at any given time. It is an important indicator which shows the bodys overall metabolic condition. The normal range of blood sugar is from 3.5 mmol/L to 6.1 mmol/L during fasting and less than 7 mmol/L after having a meal.
If your blood sugar is higher than the normal range, it could be a sign of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes is the name of the condition where the body cannot properly process and absorb the glucose taken during eating, causing it to remain in the bloodstream. This can lead to many serious complications like nerve damage and loss of vision.
Recommended Reading: How To Mix Nph And Regular Insulin
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
Exercise Regularly Or Just Get Your Body Moving
Exercise is one of the gold standards when it comes to reducing blood sugar levels. This is because your body will be forced to utilize glucose when youâre working out. However, some exercises can temporarily raise your blood sugar level, so consult your doctor first to know which exercise program will work best for you.
Also, simply get moving. As they say, âAny exercise is better than no exercise.â If that exercise means taking more walks or becoming physically active by doing household chores such as mowing the lawn or mopping the floor, then thatâll be good for a start.
Don’t Miss: Can Type One Diabetics Donate Blood
Why Are Blood Sugar Spikes A Problem
Even though the spike is temporary, all of those spikes throughout the day can raise your HbA1c.; Research has shown that for those with an A1c below 7.5%, post-meal readings actually have a greater influence on A1c than fasting blood sugars.; In other words, managing pre-meal readings will only get you so far.; If you want tight control, you need to pay attention to the after-meal glucose as well.
The long-term effects of postprandial hyperglycemia have been studied extensively.; For those with type 1 diabetes, significant post-meal rises have been shown to produce earlier onset of kidney disease and accelerate the progression of existing eye problems .; And like a dagger through the heart, post-meal hyperglycemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular problems.; Recently, post-meal spikes and glucose variability have been associated with diminished brain function and an increased risk of dementia.
But the problems are not limited to long-term health issues.; Any time blood sugars rise particularly high, even temporarily, our quality of life suffers.; Energy decreases, cognitive ability falters, physical/athletic abilities become diminished, and moods become altered. ;And dont forget:; What goes up must come down.; The rapid blood sugar decline that usually follows a post-meal spike can cause false hypoglycemic symptoms.
What Does A1c Stand For
Hemoglobin A1C , commonly called A1C, stands for glycosylated hemoglobin. An A1C test provides information on how well-controlled a persons diabetes is. It does this by measuring the percentage of red blood cell hemoglobin protein that has sugar stuck to it and provides a three-month average of your blood glucose levels, explains , MD, a board-certified endocrinologist at the Center for Endocrinology at Mercy Medical in Baltimore. The higher blood sugar levels are, the more glucose attaches to hemoglobin. The results provide patients and their healthcare providers with information on how well their treatment, diet, and medication is working and whether adjustments are necessary.
There are a few reasons a doctor might suggest an A1C test:
- To make a diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes
- To test for prediabetes
- To monitor blood sugar levels
- To determine if treatment adjustments are needed
The A1C blood test is not for diagnosing Type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, or cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . ;
Don’t Miss: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes;you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Before a meal.
- Two hours after a meal.
- At bedtime.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes;and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose <100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level <140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends;and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
Also Check: How Long Does Someone With Diabetes Live
Can You Have High A1c And Not Be Diabetic
According to one 2009 study, 3.8% of people without a history of diabetes have an elevated A1C level . This group is more likely to have other risk factors for Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Researchers found that the following groups were more likely to have an elevated A1C without having a diagnosis of diabetes:
- Older
- Obesity
- Higher C-reactive protein levels
A high A1C result might signal that there is a problem. Even a modest increase in your blood sugar, above normal levels, can increase your risk of heart disease, even when you dont have full-blown diabetes, says Dr. Bellatoni. A physician can review test results and talk to patients about risk factors and lifestyle changes to improve blood sugar levels.;
Glipizide Contraindications & Warnings
Glipizide is a great medication for treating Type 2 diabetes, but it isnt right for everyone. Here are some contraindications and warnings about glipizide to be aware of:
- Abuse and dependence: Glipizide isnt a habit-forming drug, but it is important to talk with your healthcare provider about any concerns you may have while taking it.
- Overdose: The maximum daily dose of glipizide for adults is 40 mg for regular tablets and 20 mg for extended-release tablets. That dose may be lower for people with certain health conditions. Overdosing on glipizide can potentially cause life-threatening hypoglycemia and symptoms like seizures, tremors, confusion, and blurred vision. The maximum daily dose of glipizide shouldnt be exceeded unless approved by a medical professional. If you or someone you know has overdosed on glipizide, seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.;
- Restrictions: The risks and benefits of glipizide while pregnant or breastfeeding should be discussed with your doctor. Glipizide shouldnt be taken by pregnant women who are near-term. It also shouldnt be taken by people who have an allergy to the medication or diabetic ketoacidosis. It should be used with caution in people who have:;
- A G6PD deficiency
- Are allergic to sulfonamide medications
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
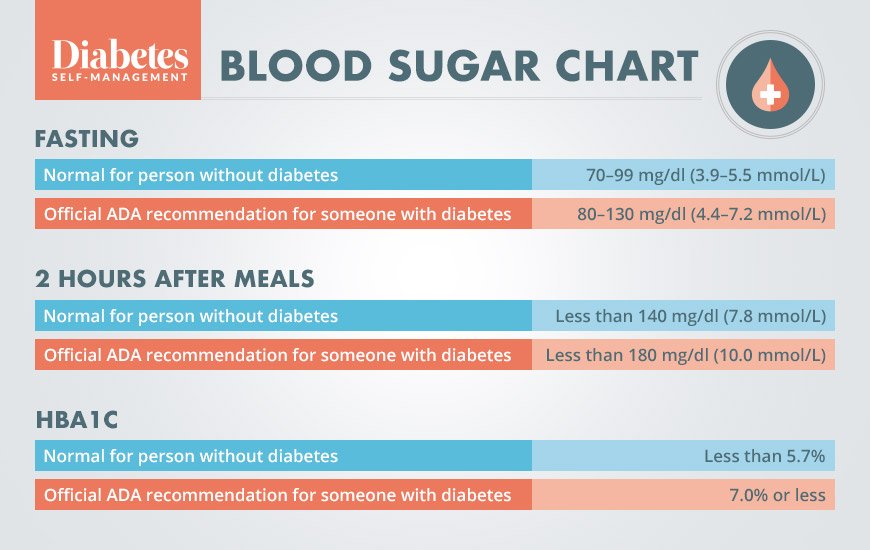
Blood Sugar Chart: Summary
The fasting blood sugar, 2-hour post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1C tests are important ways to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, as well as indicate how well a persons diabetes is being managed. If you think you have diabetes, its important to not try and diagnose yourself by doing a finger-stick with a home blood glucose meter. There are strict standards and procedures that laboratories use for diagnosing diabetes; therefore, you should get tested at your doctors office or at a laboratory.
Its also important to talk with your doctor to make sure you understand a) how often you should have certain tests, such as a fasting blood glucose or HbA1C test; b) what your results mean; and c) what your blood sugar and HbA1C targets are.
If you have not been previously diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes but your results are above normal, your doctor may recommend other tests and should discuss a plan of treatment with you. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, a healthy eating plan, and regular physical activity. You may need to start taking diabetes medications, including insulin. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, its recommended that you learn how to check your blood sugars with a meter so that you and your healthcare team can determine how your treatment plan is working for you.

