Reduce Your Stress Levels Through Meditation
If you find your stress levels are high on a morning, you need to find a way to handle them. Stress is bad for you overall. Its known as a silent killer, as it raises your blood pressure and has no symptoms at all until you start to suffer from health problems seriously.
While exercise is a good way to reduce your stress levels, its not the only option. Nor is it the perfect option.
Meditation is a powerful way to keep your stress levels to a minimum. You can take in deep breaths, allowing your body to get all the oxygen it needs. Your mind focuses elsewhere, helping to release the tension and problems that are affecting your current levels of cortisol.
As your body can release more happy hormones, your stress hormones are suppressed. You can use breathing and meditation techniques regularly to keep your hormone levels balanced. Not only will you improve your morning glucose levels but youll find your overall health benefits considerably.
Read Also: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
Why Is My Blood Sugar High In The Morning
High blood sugar in the morning is mysterious to the extent that it may be a phenomenon. Specifically: the dawn phenomenon.
This is where hormones are released in the early hours of the morning. In turn, the hormones make the liver release its store of glycogen , thus raising blood sugar levels.
Its not exactly known why this happens, but these hormones are usually released to give extra energy. So, the theory is that the body releases extra glucose in order to give you extra energy to wake up and start the day.
Obviously, this extra glucose doesnt help those with diabetes, but at least the bodys trying. Its the thought that counts, right?
There may also be another potential reason for high blood sugar in the morning: the Somogyi phenomenon . This can occur as a result of insulin use.
Its theorised that taking insulin before bed can cause the body to have a rebound effect whilst sleeping. If insulin continues to lower blood sugar during sleep, and its not being treated, then the body responds in stress mode: it releases hormones to trigger a rise in blood sugar levels.
But for those with diabetes, this doesnt stabilise the blood sugar. That extra glucose cant be used without diabetes medication, and so, the blood sugar gets too high instead.
There could be other reasons for high blood sugar in the morning, such as too many carbs before bed or requiring a different level of insulin. We can look at what to do about that in a moment.
What Is Your Fasting Blood Sugar
Simply put, your fasting blood sugar is your blood sugar first thing in the morning before you eat breakfast. Since its been typically has been more than 8 hours since your last meal, the fasting blood sugar indicates how your body has managed its blood sugar levels when variables like food are not present.
You May Like: Metformin 1500 Mg Side Effects
What Is The Dawn Phenomenon
Your body uses glucose for energy and it is important to have enough extra energy to be able to wake up in the morning. So for a period of time in the early morning hours, usually between 3 a.m. and 8 a.m., your body starts churning out stored glucose to prepare for the upcoming day.
At the same time, your body releases hormones that reduce your sensitivity to insulin. In addition, these events may be happening while your diabetes medication doses taken the day before are wearing off.
These events cause your body’s blood sugar levels to rise in the morning .
What Is Low Blood Sugar

Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
- A pale face
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Metformin
Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
The NIDDK states that gestational diabetes is high blood sugar that occurs during pregnancy if you were not diabetic before getting pregnant. Healthy blood sugar during pregnancy can help lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. It can also lower the risk of your baby being born prematurely, at a high birth weight, and having respiratory problems.
Blood sugar and insulin levels during the first trimester of pregnancy tend to be lower than usual, but they rise during the late second and early third trimesters. You can be diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test .
These are the steps for the 2-step strategy.
- Drink a solution with 50 grams of glucose about the amount in 1 16-oz. bottle of a soft drink
- Get your blood drawn after 1 hour. IF the value is high, retest
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 100 grams of glucose about the amount in 12 peanut butter cups
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1, 2, and 3 hours
Or, your doctor might use the 1-step strategy with a 2-hour OGTT:
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 75 grams of glucose
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1 and 2 hours
These are some values to know from NIDKK related to gestational diabetes and healthy blood sugar in pregnancy.
| Time or Situation |
|---|
| Baseline: at least 105 mg/dl1 hour: at least 190 mg/dl2 hours: at least 165 mg/dl3 hours: at least 145 mg/dl |
How To Lower Your A1c: The Complete Guide
We are always told that having a low A1c is an important goal in our diabetes management, but do you know why? Do you know what a good A1c target is, how to lower your A1c, and how quickly you can lower your A1c safely?
These are the questions I will answer in this comprehensive guide on what A1c is, how to lower your A1c, and why achieving a low A1c isnt the only goal when it comes to diabetes management.
Read Also: Side Effects Of Diabetes Medication Metformin
Blood Sugar Level Chart By Age
Blood sugar levels tend to rise with age due to an increase in insulin resistance and decrease in insulin sensitivity. In one study by the National Health Institute , each extra decade of age was linked to a 2.7 mg/dl increase in fasting glucose, and a 4.5 mg/dl increase in 2-hour post-prandial glucose levels.
What Is High Blood Sugar
If your blood sugar levels are chronically higher than normal, then this is referred to as hyperglycaemia. This is a common issue for those suffering from diabetes. The condition can also affect pregnant women who have gestational diabetes and occasionally those who are severely ill .
Some of the symptoms of hyperglycaemia include:
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Issues with concentration and/or thinking
If severe hyperglycaemia is left untreated the condition can lead to organ and tissue damage as the excess glucose present in the body can make it difficult for the organs and cells to function correctly. The disorder can also impair the immune system response in the healing of wounds and cuts.
Also Check: Does Glipizide Lower Blood Sugar Immediately
How To Prevent High Blood Glucose In The Morning
We have explored why your morning glucose level might be high. Now, letâs explore how we can take action to address it.
Our team has analyzed thousands of usersâ CGM data, and there are several strategies that consistently improve morning blood glucose levels. The ones that tend to produce the biggest ROI include:
Is Diabetes Diagnosed The Same Way In Every Country
There are four methods of diagnosing diabetes, which are used around the world. They are:
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Nondiabetic Person
What If I Have Trouble Getting To My Blood Sugar Goals
There may be times when you have trouble reaching your blood sugar goals. This does not mean that you have failed. It means that you and your health care team should see if changes are needed. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is often too high or too low. Taking action will help you be healthy today and in the future.
What Causes High Morning Blood Sugars
Two main culprits prompt morning highs: the dawn phenomenon and waning insulin. A third, much rarer cause, known as the Somogyi effect, may also be to blame.
The occasional morning high will have little impact on your A1C, a measure of your average blood sugar levels over time that indicates how well managed your diabetes is. But if those highs become consistent, they could push your A1C up into dangerous territory.
Recommended Reading: Normal Dosage Of Metformin
What Is A Normal A1c
Now that you have your A1c number, lets look at what that number actually tells you. The American Diabetes Association has established the following guidelines:
This does NOT mean that you need an A1c of less than 5.7% if youre living with diabetes. It means that if you do NOT live with diabetes, your A1c is expected to be below 5.7%. There are different recommendations for what an appropriate A1c is for people living with diabetes.
I had a chance to asked Dr. Anne Peters, MD, Director, USC Clinical Diabetes Program and Professor of Clinical Medicine Keck School of Medicine of USC as well as Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, owner and Clinical Director of Integrated Diabetes Services and author of Think Like a Pancreas, what their perspectives are on a good A1c target:
Dr. Peters:
The A1c target should be whatever is best given the persons clinical situation. For athletes, too many lows can limit performance, for someone who is pregnant it should be < 6%, for an older person the target should be higher. I generally think an A1c target of 6.0 7.0% is ideal and data shows that going below 7% has fairly little impact on complications. Basically, Id rather see someone with an A1c of 6.9% and low blood sugar variability than an A1c of 6.2% with lots of variability
Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE:
To learn more about blood sugar levels, please read What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels.
How To Test Your Blood Sugar
What should my blood sugar be when I wake up? You already know the answer, but you should also know the correct way to test your blood sugar. To get an accurate reading, check your blood sugar level in 10-15 minutes of waking up in the morning. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before you test any contaminant can cause inaccuracies. Avoid any caffeinated beverages before you test because it can lead to a spike in blood sugar.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Candy Can A Diabetic Eat
Can Prediabetes Be Reversed
For some, prediabetes is reversible if it is the simple result of weight gain and unhealthy habits. For many, however, prediabetes is the result of the bodys gradual destruction of beta-cells.
Beta-cells play a critical role in insulin production. More and more research today regarding type 2 diabetes demonstrates that approximately 60 percent of people with type 2 diabetes are experiencing a lack of insulin production through beta cell dysfunction and destruction.
It is now well recognized that 2 factors are involved: impaired function and insulin resistance, explains John E. Gerich, MD, in a study published by the Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Prospective studies of high-risk populations have shown insulin-resistance and/or insulin-secretory defects before the onset of impaired glucose tolerance.
This means that while you should absolutely still pursue healthier habits around nutrition, exercise, weight-loss, sleep, quitting smoking, the gradual progression of your disease means your diagnosis is here to stay.
That being said, making any changes you can in your habits can play a tremendous role in whether or not you need to start taking diabetes medications or if you need to start insulin injections to help bring your blood sugars down to a healthy level.
Read more on reversing diabetes: Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversible?
Prediabetes is diabetes. The sooner you take action, the sooner you improve your health.
What If Your Morning Blood Sugar Level Is High
Due to certain hormonal changes, it is quite natural to have a relatively higher blood sugar levels in the morning. If you do not have diabetes, your body will produce enough insulin to bring your blood sugar back to normal again. It may not happen though if you have diabetes.
Your blood glucose levels may stay elevated because of insulin resistance, which refers to a condition in which your body’s fat cells and muscles fail to use insulin effectively. The condition also affects the function of your liver and changes the way it processes and releases sugar, especially at night.
The situation is different when you have type-2 diabetes because the liver starts releasing more glucose than is needed into your blood. It means that your hormones are causing your blood sugar to go up and your liver is also making things worse by releasing more sugar into your system. This leads to a spike in blood sugar levels that stay elevated unless you pay attention to your diet and exercise. You may also have to take medications to manage your blood sugar better.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects From Taking Metformin And Glipizide
Normal After Meal Blood Sugar
The chart below compares post-meal blood sugars in a typical person with diabetes and someone without diabetes. Most diabetes organizations recommend trying to keep your post-meal rise below 180 mg/dL .
It was not until recent years, and the advent of continuous glucose monitoring technology, that scientists began to look in detail at the blood glucose patterns of individuals without diabetes.
Heres some of the best data from studies looking at glucose profiles in healthy individuals using CGM technology:
- A 2008 study on 32 patients who wore a CGM for ~30 days, all of whom had normal results on an oral glucose tolerance test, showed that the average glucose level was 102 mg/dL +/- 7 mg/dL.
- A 2010 analysis of 80 patients without diabetes who wore a CGM for 12 weeks showed that while 93% of study participants reached 140 mg/dL, they spent only a median of 26 minutes per day at this level.
- A 2020 study of 153 participants aged 7 to 80 found that mean average glucose was 98 to 99 mg/dL for all age groups except those over 60 years, in whom mean average glucose was 104 mg/dL . Participants spent 96% of their day within the range of 70-140 mg/dL, and very little time above or below.
Overall, this research indicates that individuals identified as non-diabetic only exceed ~140 mg/dL rarely and briefly.
If you would like to reduce your blood sugars after meals, consider exploring this article: How to Start a Low-Carb Diabetes Diet.
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Before a meal.
- Two hours after a meal.
- At bedtime.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Recommended Reading: Can Diabetics Have Mac And Cheese
What Is Normal Blood Sugar
ByElizabeth Palermopublished 31 March 14
Blood sugar, or glucose, is an important source of energy and provides nutrients to your body’s organs, muscles and nervous system. The body gets glucose from the food you eat, and the absorption, storage and production of glucose is regulated constantly by complex processes involving the small intestine, liver and pancreas.
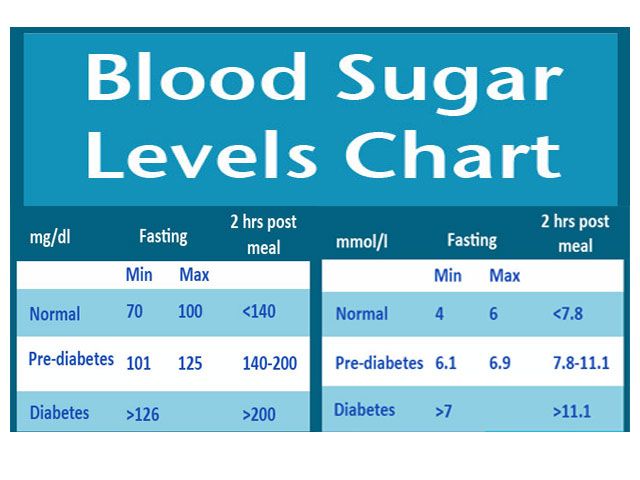
Normal blood sugar varies from person to person, but a normal range for fasting blood sugar is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter. For most individuals, the level of glucose in the blood rises after meals. A normal blood-sugar range after eating is between 135 and 140 milligrams per deciliter.
These variations in blood-sugar levels, both before and after meals, are normal and reflect the way that glucose is absorbed and stored in the body. After you eat, your body breaks down the carbohydrates in food into smaller parts, including glucose, which can be absorbed by the small intestine.
As the small intestine absorbs glucose, the pancreas releases insulin, which stimulates body tissues and causes them to absorb this glucose and metabolize it . This stored glucose is used to maintain healthy blood-sugar levels between meals.
When there isn’t enough glucose stored up to maintain normal blood-sugar levels, the body will even produce its own glucose from noncarbohydrate sources . This process, known as gluconeogenesis, occurs most often during intense exercise and instances of starvation.

