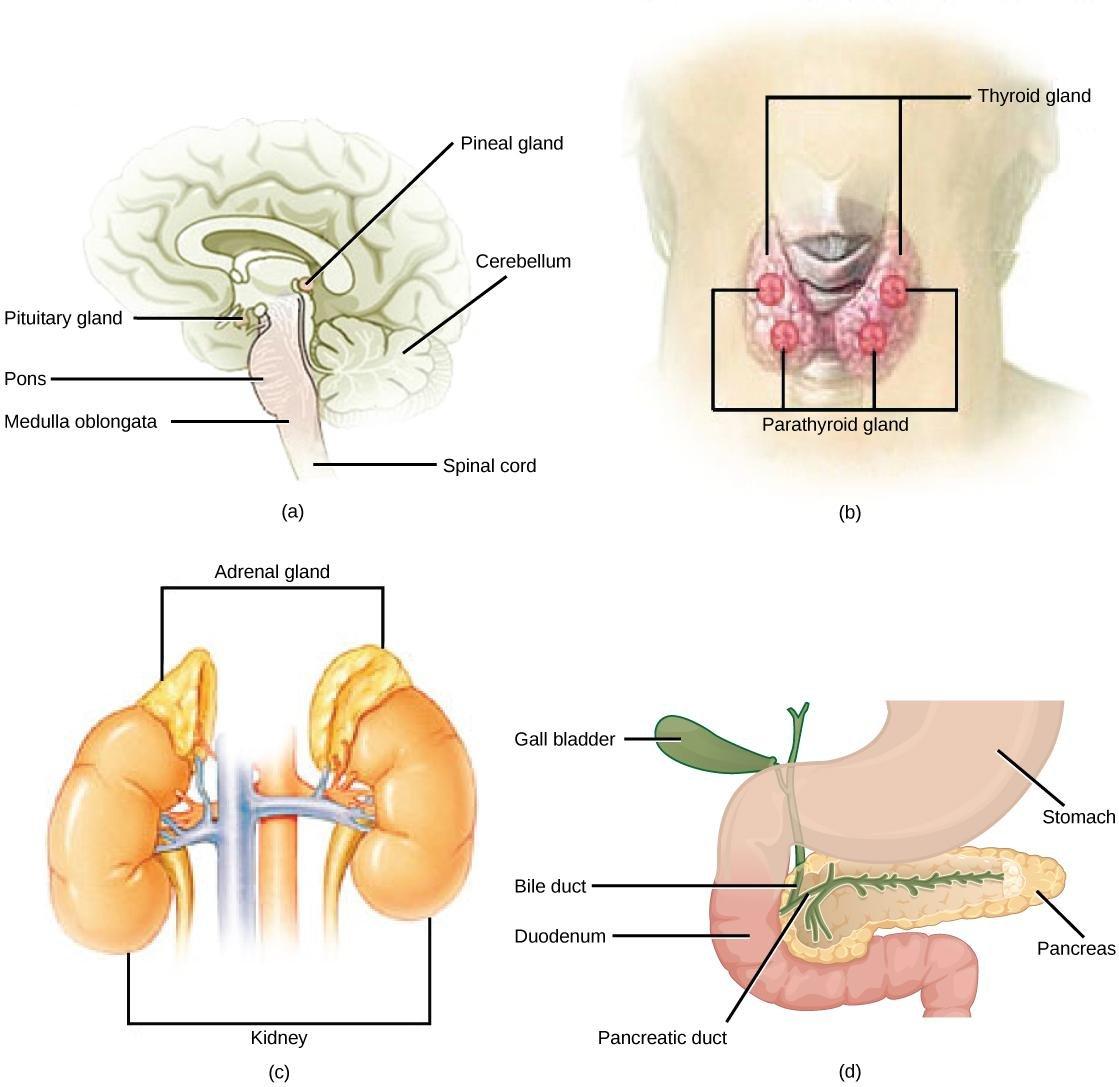
How Is The Pancreas Linked With Diabetes
Diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar. This results from insufficient insulin production or function, which can be one effect of problems with the pancreas.
People with diabetes experience high or low blood sugar levels at different times, depending on what they eat, how much they exercise, and whether they take insulin or diabetes medication.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both involve the pancreas.
Body Can Regain The Ability To Produce Insulin
Researchers have discovered that patients with type 1 diabetes can regain the ability to produce insulin. They showed that insulin-producing cells can recover outside the body.
Hand-picked beta cells from the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Photo: Oskar Skog, Uppsala University.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious disease that affects many children and adolescents. The disease causes the pancreas to stop producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
When blood sugar levels are too high, the smallest blood vessels in the body eventually become damaged. This can lead to serious health problems further down the line, including heart attacks, stroke, blindness, kidney failure and foot amputations.
Professor Knut Dahl-Jørgensen and doctoral student Lars Krogvold are leading a research project, , in which they want to ascertain among other things whether a virus in the pancreas might cause type 1 diabetes.
They have previously discovered viruses in hormone-producing cells, the so-called islets of Langerhans, in the pancreas. Now their research has generated some new and surprising results.
Lars Krogvold, doctoral student at the University of Oslo and paediatrician at Oslo University Hospital. Photo: Private
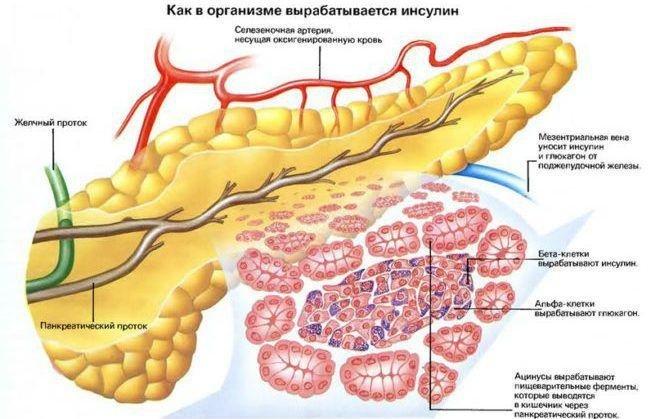
How Insulin Is Synthesized In The Pancreas
A group of cells located in the pancreas synthesize a precursor peptide called preproinsulin. As this precursor polypeptide is released from the cell, the amino acids are cleaved from the peptide end and the middle of the chain. This interruption results in an insulin molecule containing two polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bonds. Diabetics can not produce enough insulin and take insulin as medicine. Insulin taken as medicine is produced in bacteria.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Safe Dose Range
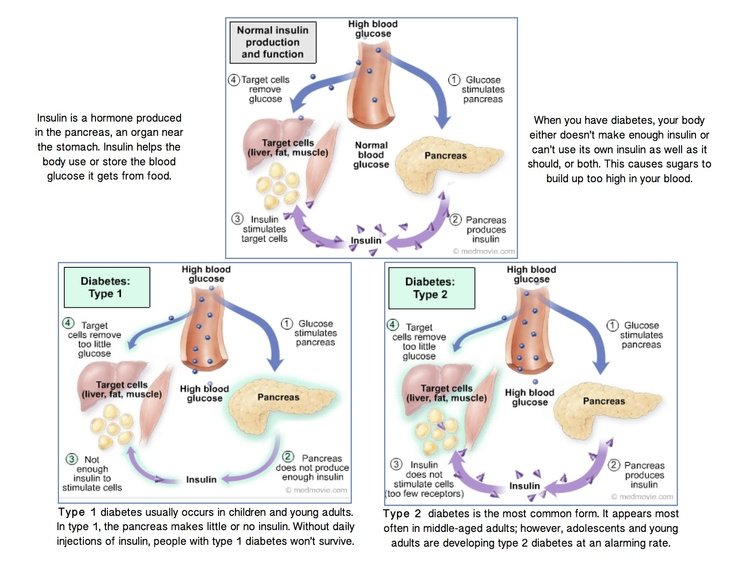
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by the body not responding effectively to insulin. This is termed insulin resistance. As a result the body is less able to take up glucose from the blood. In the earlier stages of type 2 diabetes, the body responds by producing more insulin than it would normally need to.
If type 2 diabetes develops over a number of years, the extra demands on the pancreas to produce insulin can lead to a loss of insulin producing cells as they wear out.
Depending on their level of insulin resistance, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
Types Of Insulin Treatments
All types of insulin produce the same effect. They are used to mimic the natural increases and decreases of insulin levels in the body during the day. The makeup of different types of insulin affects how fast and how long they work.
The type of insulin youll be prescribed will vary depending on things like:
- your age
- how long it takes your body to absorb insulin
- how long insulin stays active in your system
| Insulin type | ||
|---|---|---|
| varied peaks | 10 to 16 hours | Taken twice a day, commonly 10 to 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner. This type is a combination of intermediate- and short-acting insulin. |
Talk with a doctor about the right insulin for you and your lifestyle.
Read Also: Metformin Initial Dose
Insulin And Fatty Acids
Insulin helps synthesize fatty acids in the liver cells. If the glycogen levels make up at least 5 percent of the mass of the liver, the glycogen synthesis is suppressed and fatty acids are instead made by the liver to be used to make the lipid layer of the cells of the body. The fatty acids are then taken out of the liver and are transferred to lipoproteins, which allow for the transportation of the fatty acids to make cells or to be stored inside fat cells as fat.
Can I Have A Negative Reaction To Insulin
One complication facing people with diabetes who use insulin is the potential for severe hypoglycemia, also known as insulin shock, which involves using too much insulin and causing your blood sugar to drop extremely low. This can cause coma, seizures, and heart attacks, says Dr. Powers. It requires treatment in a hospital but thankfully is highly treatable once you are there.
Recommended Reading: Which Blood Glucose-lowering Hormone Is Produced By The Pancreatic Islet Cells
The Primary Hormones That Are Produced By The Pancreas Include:
- Insulin this hormone works by allowing the bodys cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it as energy. This in turn helps to reduce high blood sugar levels.
- Gastrin gastrin hormone stimulates specific cells in the stomach that aids in digestion.
- Glucagon this hormone helps insulin to maintain a normal blood sugar level by stimulating the cells to release glucose when it is too low.
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide vasoactive intestinal peptide helps to control absorption and secretion of water from the intestines.
- Somatostatin in case other hormones such as glucagon and insulin are too high, the hormone somatostatin will be released to help maintain blood sugar.
Foods That Can Produce Insulin Naturally N Body To Fight Diabetes
These days diabetes is a lifestyle disease and once it is dictated in someone, then there is the only chance that it can be controlled. Hardly you have heard that someone actually got cured of diabetes. So, lets not put anyone in the confusion that, this article is not written for the purpose of curing diabetes, rather it is written to make you aware of the issues and you can have control over your insulin so that everything is in control.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps your blood sugar level from getting too high or too low .
Rose of Pancreas
We hardly think of the pancreas as an important endocrine organ unless it starts to create a problem. The pancreas has two important roles to play Make insulin for blood sugar control. Create enzymes for the metabolism of fats and proteins.
Malfunction of the pancreas could result in a variety of problems the most common being diabetes. Fortunately, nature has given us some foods that boost the beta cells of the pancreas to produce insulin and help alleviate diabetes, of course, coupled with the right lifestyle changes.
Foods Help Growing Insulin
1. Red Cabbage
Cabbage, especially red, is a boon for cancer and diabetes patients. The natural red pigments of red cabbage, betalains, helps lower blood sugar levels and boosts insulin production.
4. Fenugreek Seeds
Don’t Miss: Symptom Of Type 1 Diabetes
Problems With The Pancreas
If there is a problem with the pancreas, it can affect the entire body. This can affect the amount of digestive enzymes that are produced by the pancreas. In case there is not enough digestive enzymes being produced, food will not be properly absorbed. This may lead to health complications such as diarrhea and weight loss. The pancreatic islets are responsible for producing the hormone insulin. People with type 1 diabetes do not produce any insulin. This is because the insulin producing beta cells are mistakenly attacked by the immune system. When we eat carbohydrates, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream tends to rise. Glucose is a form of sugar which is one of the biggest sources of fuel for the body.
An increase in blood sugar will stimulate the pancreas to release the hormone insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels. As a result of beta cells dying, the pancreas in people with type 1 diabetes will struggle to secrete enough insulin. This leads to a build up of blood sugar levels which, if not treated, can lead to serious health problems like nerve and kidney damage. To prevent this risk, people with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to keep their blood sugar levels normal.
How Should I Store My Insulin
Like food, insulin doesnt have a forever shelf life. Its recommended that you store any insulin youre not using in the fridge.
However, injecting cold insulin may make the injection feel more painful. Because of this, a best practice is to keep the bottle of insulin youre currently using in a safe place, away from direct heat and sunlight. Insulin kept at room temperature can last about a month.
Do not store insulin in the freezer, and always check the expiration date before using it.
Side effects from injecting or receiving insulin are rare, but can occur in certain cases. The symptoms of mild allergic reactions are swelling, itching, or redness around the injection area. More severe insulin allergies may include nausea and vomiting.
In either case, talk with your doctor if you notice any of these signs.
Hypoglycemia, or blood glucose levels that are too low, can sometimes occur when you take insulin.
Its important to balance the insulin that you give yourself with food or calories. If you exercise longer or harder than usual or dont eat the right amount of calories or carbs, your glucose level can drop too low and trigger low blood sugar. Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
Recommended Reading: Does Type One Diabetes Shorten Your Life
Pharmacological Influences On Insulin Action And Insulin Resistance
A wide range of pharmacological agents have been associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Antihypertensive agents such as diuretics and ?-blockers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, nicotinic acid and antipsychotic agents have been reported to impair glucose tolerance, as have the anti-retroviral protease inhibitors used to treat human immunodeficiency virus infection. The mechanisms vary ?-blockers impair insulin secretion from the pancreas by blockade of ?-adrenoceptors, thiazide diuretics are thought to act by depleting potassium levels, corticosteroids and oral contraceptives have counter-regulatory hormonal activity, and the HIV-1 protease inhibitors result in partial lipodystrophy with loss of peripheral subcutaneous fat and accumulation of truncal adipose tissue leading to insulin resistance.
Common Conditions Associated With Insulin Resistance
Type 2 Diabetes
Following pioneering work by Bornstein and the Nobel Prize-winning work of Yalow and Berson, the first insulin assays became widely available in the late 1960s it was subsequently confirmed that diabetic patients with so-called or maturity onset or type 2 diabetes had normal or increased plasma insulin levels. Insulin resistance was reported to be a characteristic feature of T2DM in the early 1970s. A progressive inability of the ? cells to compensate for the prevailing insulin resistance by sufficient hyperinsulinaemia, heralds the clinical onset of this disorder. While twin studies and linkage analyses are consistent with a strong genetic component in the development of type 2 diabetes, several decades of research have failed to identify a predominant genetic abnormality in the majority of cases. The aetiology of T2DM is thought to be polygenic, with environmental factors being superimposed upon this basic predisposition.
Insulin resistance typically predates the development of diabetes and is commonly found in unaffected first-degree relatives. The morbidity of the disorder relates both to the severity of hyperglycaemia and the metabolic consequences of insulin resistance itself. The primary defects in insulin action appear to be in muscle cells and adipocytes, with impaired GLUT 4 translocation resulting in impaired insulin-mediated glucose transport.
Metabolic Syndrome
Read Also: Which Type Of Cell Secretes Glucagon And Promotes Gluconeogenesis
Insulin And The Circulatory System
Insulin is secreted into the bloodstream and helps the cells of the body make use of glucose. It is the responsibility of the circulatory system to provide the insulin for all the cells of the body. As long as enough insulin is produced by the body, the glucose is able to be used and the cells of the body thrive.
If there isnt enough insulin in the circulatory system, glucose levels go up and there can be complications, such as diabetic nephropathy , diabetic retinopathy , diabetic neuropathy , and heart disease.
A lack of insulin in the bloodstream results in starvation of the cells. As the cells cant make use of glucose, they start to break down fat to be used as cellular fuel. If glucose in the bloodstream becomes extremely high, ketones can build up in the body. Ketones are the metabolic byproduct of other sources of fuel the body is using. When ketones build up, there can be obvious symptoms, such as a dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, and a sweetness in the breath. When this happens, it is called diabetic ketoacidosis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance And Prediabetes
Insulin resistance and prediabetes usually have no symptoms. Some people with prediabetes may have darkened skin in the armpit or on the back and sides of the neck, a condition called acanthosis nigricans. Many small skin growths called skin tags often appear in these same areas.
Even though blood glucose levels are not high enough to cause symptoms for most people, a few research studies have shown that some people with prediabetes may already have early changes in their eyes that can lead to retinopathy. This problem more often occurs in people with diabetes.
You May Like: Max Metformin Dose
Factors Influencing Insulin Biosynthesis And Release
Insulin secretion may be influenced by alterations in synthesis at the level of gene transcription, translation, and post-translational modification in the Golgi as well as by factors influencing insulin release from secretory granules. Longer-term modification may occur via influences on ? cell mass and differentiation. Given insulins pivotal role in glucose utilisation and metabolism, it is not surprising that glucose has multiple influences on insulin biosynthesis and secretion. However, other factors such as amino acids, fatty acids, acetylcholine, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide , glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide , glucagon-like peptide-1 , and several other agonists, together in combination, also influence these processes.
How To Choose The Right Method For Injecting Insulin
Both syringes and insulin pens use a small needle to inject insulin into your body. There are pros and cons to each, and which one you ultimately end up with will depend on your lifestyle and your doctors advice.
Things to know about insulin syringes:
- They come in a few different sizes.
- Your doctor will tell you how much insulin you need per dose.
- You will usually draw the insulin into the syringe when you need it.
- Theyre not as discreet as an insulin pen.
Things to know about insulin pens:
- Some pens use cartridges that are manually inserted into the pen.
- Other pens are prefilled and thrown away after all the insulin is used.
- Needles in pens are often smaller than those in syringes.
- Not all types of insulin can be used with a pen.
- Pens can be more expensive than syringes and are sometimes not covered by insurance.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Most Common Side Effects
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can say for sure if a person has diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. Even if someone doesn’t have any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, doctors may order blood tests to check for it if the person has certain risk factors .
Some kids and teens with diabetes may go to a pediatric endocrinologist â a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating children and teens living with diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes and growth problems.
p
Insulin Blood Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. This vital hormoneyou cant survive without itregulates blood sugar in the body, a very complicated process. Here are the high points:
- The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar.
- Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps blood sugar enter the bodys cells so it can be used for energy.
- Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use.
- Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too.
- Lower insulin levels alert the liver to release stored blood sugar so energy is always available, even if you havent eaten for a while.
Thats when everything works smoothly. But this finely tuned system can quickly get out of whack, as follows:
- A lot of blood sugar enters the bloodstream.
- The pancreas pumps out more insulin to get blood sugar into cells.
- Over time, cells stop responding to all that insulintheyve become insulin resistant.
- The pancreas keeps making more insulin to try to make cells respond.
- Eventually, the pancreas cant keep up, and blood sugar keeps rising.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects If You Stop Taking Metformin
What Is The Function Of The Pancreas
A pancreas that is functioning normally produces chemicals which are responsible for digesting food that we eat. The pancreas plays a role in two different systems, that is the exocrine system and the endocrine system. The exocrine tissue in the pancreas secretes an alkaline fluid that consists of several enzymes. These enzymes work by breaking down the food we eat into small particles that can be absorbed by the intestines.
Overweight Obesity And Physical Inactivity
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are not physically active and are overweight or obese. Extra weight sometimes causes insulin resistance and is common in people with type 2 diabetes. The location of body fat also makes a difference. Extra belly fat is linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart and blood vessel disease. To see if your weight puts you at risk for type 2 diabetes, check out these Body Mass Index charts.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Take Glipizide And Don T Eat

