Who Could Get The Treatment
Peter Senior, MBBS, PhD, director at the Alberta Diabetes Institute, told Verywell that most stem cell-based treatments have been focused on people with severe forms of type 1 diabetes because they are the most at-risk for serious, detrimental health outcomes, and have often experienced dangerous blood sugar levels.
According to Senior, these patients have “problems with erratic blood sugars, but that’s not their only problemthey’ve got eye problems and kidney problems and other things like that.”
Stem cell-derived treatment in humans is new, which means that its going to take time to prove long-term benefits. However, the potential for short-term successas in Sheltons caseis being seen already.
If stem cell-derived therapies prove effective over time and researchers can find a way to deliver the treatments without the need for immunosuppressants, Senior said that the candidate pool would open up.
Effectively curing someone of type 1 diabetes before the disease has progressed and caused serious health complications will help improve patients’ overall quality of life.
If I was a parent with a child with type 1 diabetes, I would want a treatment that meant they never had to worry about diabetes, Senior said. But it may take 40 years for us to be able to show those long-term benefits.
What Are The Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
Insulin helps budge sugar or glucose into the cells of the body for use as a fuel. Damage to the beta cells due to too much sugar disturbs this process of producing receiving energy for various purposes. Rather, sugar pools up in the blood and weakens the blood vessels of the body. There is a bucket full of conditions that be caused by type 1 diabetes, such as:
Small cuts on the bottom of feet, which are hard to be seen can become life-threatening infections, such as ulcers. This is way too harmful if blood sugar is not controlled. Hence, its important to diagnose your feet if you have diabetes.
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes
- Family history of diabetes
- ever had diabetes during pregnancy
- have given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- have polycystic ovary syndrome
Type 1 Diabetes Treatments
People with type 1 diabetes can live long, happy lives with proper care and disease management. Advancements in medication types and delivery methods give people the freedom to choose which treatment options work best with their particular circumstance. T1D prognoses can be greatly improved with a combination of treatments and lifestyle choices.
Don’t Miss: Do I Need To Check Blood Sugar While Taking Metformin
Managing And Treating Type 1 And Type 2
Managing and treating your diabetes is so important. This is because itll help you avoid serious health complications. And itll play a big part in your daily life regardless of if you have type 1 or type 2.
If you have type 1 diabetes, youll need to take insulin to control your blood sugar levels. Youll also need to test your blood glucose levels regularly. And count how many carbs you eat and drink. Counting carbs will help you work out how much insulin you should take when you inject with your meals.
And generally you should be trying to have a healthy lifestyle. That includes regular physical activity and a healthy balanced diet. These will help you reduce your risk of diabetes complications.
If you have type 2 diabetes, you also need to eat a healthy diet and be active. These things will help you manage your weight and diabetes.
But quite often people with type 2 also need to take medication. Such as tablets and insulin, or other treatments too. Whether you need to test your blood glucose level like someone with type 1, depends on the treatment you take. Your GP can tell you what you should do at home.
How Common Is Type 1 Diabetes
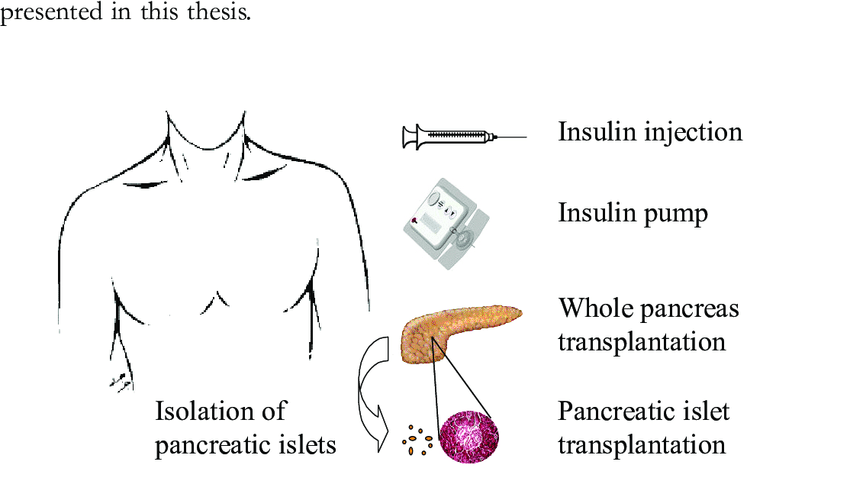
Type 1 diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases in children. About one in every 400 children in the United States develops type 1 diabetes.
People at any age, from toddlers to adults, can be diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. However, most children with type 1 diabetes are diagnosed between the ages of 4 to 6 or during puberty, between the ages of 10 and 14.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not known. Infections or environmental factors may trigger the immune system to destroy the beta cells. Family history may also contribute to the risk of developing diabetes.
Also Check: Diabetic Orthostatic Hypotension
Try To Lose Weight If You Are Overweight Or Obese
Excess weight is also a risk factor for heart and blood vessel disease. Getting to a perfect weight is often unrealistic. However, if you are overweight, losing some weight will help.
Some of these lifestyle issues may not seem to be relevant at first to young children who are diagnosed as having diabetes. However, as children grow, a healthy lifestyle should be greatly encouraged for the long-term benefits. See the separate leaflet called Cardiovascular Disease .
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Also Check: Normal A1c Levels Non Diabetics
A Cure For Type 1 Diabetes For One Man It Seems To Have Worked
A new treatment using stem cells that produce insulin has surprised experts and given them hope for the 1.5 million Americans living with the disease.
- Read in app
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this article
- Read in app
Brian Sheltons life was ruled by Type 1 diabetes.
When his blood sugar plummeted, he would lose consciousness without warning. He crashed his motorcycle into a wall. He passed out in a customers yard while delivering mail. Following that episode, his supervisor told him to retire, after a quarter century in the Postal Service. He was 57.
His ex-wife, Cindy Shelton, took him into her home in Elyria, Ohio. I was afraid to leave him alone all day, she said.
Early this year, she spotted a call for people with Type 1 diabetes to participate in a clinical trial by Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The company was testing a treatment developed over decades by a scientist who vowed to find a cure after his baby son and then his teenage daughter got the devastating disease.
Mr. Shelton was the first patient. On June 29, he got an infusion of cells, grown from stem cells but just like the insulin-producing pancreas cells his body lacked.
Now his body automatically controls its insulin and blood sugar levels.
Its a whole new life, Mr. Shelton said. Its like a miracle.
But, he said, bottom line, it is an amazing result.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
In general, the treatment methodology for type 1 diabetes centers around monitoring blood glucose levels using a blood glucose monitor. Based on your blood glucose levels, the typical treatment model then prescribes a specific insulin dose, which is injected by an insulin pump, syringe, or pen.
Think of these insulin injections as a supplement to the insulin produced by your body , in order to maintain your blood glucose within range.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Thing On Stomach
Be Open To Additional Therapies To Improve Your Glucose Control
Therefore, it is always good to have a conversation with your healthcare professional about the benefits of using such medications and also inquiring about what the cost of taking a recommended medication may mean to you.
Your healthcare provider will choose the insulin will depend upon many things including the expiration date for insulin once the vial or pen is used for the first time as well as their onset , the peak and duration .
Of course, your level of physical activity level, the presence of a fever, and stress level as well as your usual meals and snacks , will also be considered when planning for your insulin needs.
Diabetes Sick Day Rules
If you need to take insulin to control your diabetes, you should have received instructions about looking after yourself when you’re ill known as your “sick day rules”.
Contact your diabetes care team or GP for advice if you haven’t received these.
The advice you’re given will be specific to you, but some general measures that your sick day rules may include could be to:
- keep taking your insulin it’s very important not to stop treatment when you’re ill your treatment plan may state whether you need to temporarily increase your dose
- test your blood glucose level more often than usual most people are advised to check the level at least four times a day
- keep yourself well hydrated make sure you drink plenty of sugar-free drinks
- keep eating eat solid food if you feel well enough to, or liquid carbohydrates such as milk, soup and yoghurt if this is easier
- check your ketone levels if your blood glucose level is high
Seek advice from your diabetes care team or GP if your blood glucose or ketone level remains high after taking insulin, if:
- you’re not sure whether to make any changes to your treatment
- you develop symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
- you have any other concerns
Read more about sick day rules
Recommended Reading: Is Hyperglycemia The Same As Diabetes
Do Some Physical Activity Regularly
Regular physical activity also reduces the risk of some complications such as heart and blood vessel disease. If you are able, a minimum of 30 minutes’ brisk walking at least five times a week is advised. Anything more vigorous is even better – for example, swimming, cycling, jogging, dancing. Ideally you should do an activity that gets you at least mildly out of breath and mildly sweaty. You can spread the activity over the day .
Red Light Green Light Yellow Light Foods
The diet guidelines for managing your blood glucose levels while living with type 1 diabetes are actually very simple, following a clear green light, yellow light, red light, categorization for foods.
Green light foods include all fruits , starchy and non-starchy vegetables, all legumes , intact whole grains , and herbs and spices.
Green light foods are foods that you can eat as much as you want, as these are unrefined whole foods low in fat with a high nutrient density that have been demonstrated to reverse insulin resistance.
Yellow light foods include whole grain or bean pastas, whole grain cereals, refined grains, whole grain bread and tortillas, avocados, nuts, seeds, coconut meat, soybeans, and soy products.
Yellow light foods are foods okay to include in small quantities, because they are slightly processed or have higher fat content. They shouldnt be daily staples, but are still considered a healthy choice.
Red light foods include all red meats, all white meats, all seafood, eggs, dairy products, refined oils, and refined sugars .
Red light foods are foods that we recommend removing from your cabinet, your fridge, and your plate.
These foods are documented by evidence-based research to cause insulin resistance, increase your blood glucose , and promote chronic diseases in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Read Also: Why Does Diabetes Happen
Checking Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood sugar levels is the only way to see how well your insulin injections and meal plan are working. Most kids with type 1 diabetes should test blood sugar levels with a blood glucose meter. Kids with type 1 diabetes usually need to test about four times a day. Some kids test their blood sugar levels even more often. The meter works by taking a very small blood sample. When you test, you’ll feel a quick pinch.
Your parents and diabetes care team may want you to use a continuous glucose monitor . A CGM is a wearable device that can measure your blood sugar every few minutes around the clock. Getting more blood sugar readings with a CGM can help you and the care team do an even better job of controlling your blood sugar levels.
What Oral Medicines Treat Type 2 Diabetes
You may need medicines along with healthy eating and physical activity habits to manage your type 2 diabetes. You can take many diabetes medicines by mouth. These medicines are called oral medicines.
Most people with type 2 diabetes start medical treatment with metformin pills. Metformin also comes as a liquid. Metformin lowers the amount of glucose that your liver makes and helps your body use insulin better. This drug may help you lose a small amount of weight.
Other oral medicines act in different ways to lower blood glucose levels. You may need to add another diabetes medicine after a while or use a combination treatment. Combining two or three kinds of diabetes medicines can lower blood glucose levels more than taking just one.
Read about different kinds of diabetes medicines from the Food and Drug Administration .
Also Check: How To Lower Blood Sugar Fast
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Diabetes
When medicines and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage your diabetes, a less common treatment may be an option. Other treatments include bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and an “artificial pancreas” and pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes.
Initiation And Dosing Of Sglt Inhibitors
As discussed, blood ketone levels should be < 0.6 mmol/L prior to initiating SGLT inhibitor therapy. If blood ketones are 0.6 mmol/L, additional baseline blood ketone values should be obtained to determine whether the elevated ketones are normal for the patient or an indication of chronic inadequate insulin coverage in the fasting state.
We recommend that SGLT inhibitor therapy be initiated at the lowest dose available. Some suggest even splitting tablets for the currently marketed SGLT2 inhibitors to get to lower-than-marketed doses. Patients who have a good experience with low-dose SGLT inhibitor therapy could be considered for dose escalation based on clinical response.
As observed in clinical trials, lower doses of SGLT inhibitors are associated with reasonable efficacy and lower risks of DKA . Specifically, the EASE program included a lower dose , which is not currently available, in addition to the doses approved for use in patients with type 2 diabetes . The ketoacidosis rate was comparable between empagliflozin 2.5 mg and placebo but increased with doses of 10 mg and 25 mg. These data suggest that SGLT2 inhibitor dose selection itself is an important factor in terms of DKA risk mitigation.
Read Also: How Long Can A Person Live With Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
People who have type 1 diabetes can live long, healthy lives. Youâll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you a range that the numbers should stay within. Adjust your insulin, food, and activities as necessary.
Everyone with type 1 diabetes needs to use insulin shots to control their blood sugar.
When your doctor talks about insulin, theyâll mention three main things:
- “Onset” is how long it takes to reach your bloodstream and begin lowering your blood sugar.
- “Peak time” is when insulin is doing the most work in terms of lowering your blood sugar.
- “Duration” is how long it keeps working after onset.
Several types of insulin are available.
- Rapid-acting starts to work in about 15 minutes. It peaks about 1 hour after you take it and continues to work for 2 to 4 hours.
- Regular or short-acting gets to work in about 30 minutes. It peaks between 2 and 3 hours and keeps working for 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting wonât get into your bloodstream for 2 to 4 hours after your shot. It peaks from 4 to 12 hours and works for 12 to 18 hours.
- Long-acting takes several hours to get into your system and lasts about 24 hours.
Your doctor may start you out with two injections a day of two types of insulin. Later, you might need more shots.
The Typical Treatment Model
Recently, many doctors have begun to follow a treatment methodology utilizing strategic lifestyle changes to improve blood glucose control.
Some of these recommendations, like increased physical activity, and reducing or eliminating refined sugars and other refined ingredients, can dramatically improve blood glucose control and reduce your risk for long-term complications.
However, there are also some major problems with this treatment model, which often focuses on carbohydrate counting, and high-fat, low carbohydrate diets.
Though these diets can provide short-term results, over time they can actually result in increased insulin use, increased oral medication use, and increased A1c over time.
This may sound very different from what youve heard, and we know that can be surprising! Keep reading and well explain why high-fat, low-carbohydrate diets are not ideal for people living with type 1 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: How Long To Lower Blood Sugar

