How Managing Blood Sugar Helps Now
Keeping your blood sugar levels on target can help you avoid serious health problems like heart disease and nerve damage down the road. But did you know avoiding ups and downs in blood sugar can help you feel better right away?
Steady blood sugar levels can help you have more energy, better sleep, an easier-to-manage appetite, better focus, and stable moods. If youre having trouble meeting your target, talk to your doctor or diabetes educator about making changes to your treatment plan so you can stay in range longer and feel better.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask about your familys health history. He or she will give your child a physical exam. Your child may also have blood tests, such as:;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
- Fasting plasma glucose.;The blood is tested after at least 8 hours of not eating.
- Random plasma glucose.;The blood is tested when there are symptoms of increased thirst, urination, and hunger.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes causes can be any kind of illness, including the common cold. That said, here are the most common causes:
- Viral infection.;Researchers believe that type 1 diabetes can be triggered by a virus, such as the common flu or cold. Frequently, type 1 diabetes comes on in the weeks following a viral infection, such as mumps, rubella, cytomegalovirus, measles, influenza, encephalitis, polio, or Epstein-Barr.
- Injury to or removal of the pancreas.;Very rarely, type 1 diabetes can be triggered by an injury or trauma to the pancreas. Whenever the pancreas is surgically removed, the body also loses the ability to produce insulin, which then causes type;
These are some common causes of Type 1 Diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
How Does Type 1 Diabetes Affect Your Weight
The above symptoms tend to develop quite quickly, over a few days or weeks. After treatment is started, the symptoms soon settle and go. However, without treatment, the blood sugar level becomes very high and acids form in the bloodstream . If this persists you will become lacking in fluid in the body and are likely to lapse into a coma and die.
Less Common T1d Tests

Because each case can be as unique as the individual, some doctors may employ the following tests to find markers of T1D to ensure the optimal treatment plan:
- C-PeptideWhile most tests check for antibodies, this test measures how much C-peptide is in a persons blood. Peptide levels typically mirror insulin levels in the body. Low levels of C-peptide and insulin;can point to T1D.
- Insulin Autoantibodies This tests looks for the antibodies targeting insulin.
- Insulinoma-Associated-2 Autoantibodies This test looks for antibodies mounted against a specific enzyme in beta cells. Both the IA-2A and GADA tests are common T1D antibody tests.
- Zinc Transporter 8 This test looks at antibodies targeting an enzyme that is specific to beta cells.
- Islet Cell Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies Islet cells are clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce hormones, including insulin.;This test identifies a type of islet cell antibodies present in up to 80 percent of people with T1D.
- Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Autoantibodies This test looks for antibodies built against a specific enzyme in the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells.
Also Check: Can You Take Too Much Insulin
Can Symptoms Appear Suddenly
In people with type 1 diabetes, the onset of symptoms can be very sudden, while in type 2 diabetes, they tend to come about more gradually, and sometimes there are no signs at all.;
Symptoms sometimes occur after a viral illness. In some cases, a person may reach the point of diabetic ketoacidosis before a type 1 diagnosis is made. DKA occurs when blood glucose is dangerously high and the body can’t get nutrients into the cells because of the absence of insulin. The body then breaks down muscle and fat for energy, causing an accumulation of ketones in the blood and urine. Symptoms of DKA include a fruity odor on the breath, heavy, taxed breathing and vomiting. If left untreated, DKA can result in stupor, unconsciousness, and even death.
People who have symptomsof type 1 or of DKAshould contact their health care provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis. Keep in mind that these symptoms could signal other problems, too.
Some people with type 1 have a “honeymoon” period, a brief remission of symptoms while the pancreas is still secreting some insulin. The honeymoon phase usually occurs after someone has started taking insulin. A honeymoon can last as little as a week or even up to a year. But its important to know that the absence of symptoms doesn’t mean the diabetes is gone. The pancreas will eventually be unable to secrete insulin, and, if untreated, the symptoms will return.
Type 1 Diabetes And Pregnancy
Pregnant women with type 1 diabetes need to be extra careful to maintain good blood sugar control. If blood sugar runs too high during pregnancy, there is an increased risk of complications including having a very large baby, having the baby too early, and having preeclampsia, a condition that can be life threatening to the mother and baby. You can minimize the risk for complications by paying close attention to blood sugar, eating a low-glycemic diet, and staying regularly active.
Read Also: Diabetic Mac And Cheese
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Lada
The main difference between type 1 diabetes and type 1.5 diabetes is the speed and strength of the autoimmune condition.
Type 1 diabetes is a fast-progressing, strong autoimmune condition which results in a near complete loss of insulin production between 12-18 months on average. Patients with type 1 diabetes often test positive for multiple antibodies to beta cell proteins.
Type 1.5 diabetes is a slow-progressing, weaker autoimmune condition which results in a decline in insulin production that may take years to develop. Patients with type 1.5 diabetes often test positive for a single antibody to beta cell proteins.
As we mentioned above, identifying these conditions through the onset of their symptoms can be difficult. However, both adult-onset type 1 diabetes and LADA/type 1.5 diabetes can be effectively identified with two decisive tests: the C-peptide test, and a diabetes antibody panel.
Distinguishing Which Type Of Diabetes You Have
To fully determine which type of diabetes you have, we strongly recommend taking a c-peptide test, which determines the ability of your beta cells to produce insulin.
If your c-peptide value is medium or high, this indicates that your ability to manufacture and secrete insulin is enough to control your blood glucose well.
If your c-peptide value is low, this indicates that your beta cells are compromised in their ability to secrete insulin, resulting in either insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes, or type 1 diabetes.
The final test that we recommend is a diabetes antibody panel, which identifies whether you test positive for any of several autoantibodies. If you test positive for one or more antibodies, this suggests that you have autoimmune type 1 or type 1.5 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Live A Long Life With Diabetes
Further Information And Support
For further information and support contact your doctor, practice nurse, or:;Diabetes New Zealand;Freephone: 0800 DIABETES ;Email: admin@diabetes.org.nz;Website: www.diabetes.org.nz;Diabetes New Zealand provides education and support resources specifically for young New Zealanders with type 1 diabetes and many of its branches around the country host Type 1 youth support groups.;
Kids Health;Website: www.kidsheatlh.org.nz;
Is Type 1 Diabetes An Autoimmune Disease
When type 1 diabetes is triggered by a virus, someone predisposed to autoimmune conditions may develop an autoimmune response. This means that their bodys immune system will start attacking its own cells. In type 1 diabetes, the body attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin.
Don’t Miss: How To Increase Blood Flow To Feet For Diabetics
Is Type 1 Diabetes Genetic
If one family member has type 1 diabetes, other relatives have an increased chance of developing the condition. One study of more than 1,400 children with type 1 diabetes showed that 12% had a first-degree relative who also had type 1in other words, a parent or sibling.
The same study also showed that children with type 1 diabetes had a slightly higher chance of having a father diagnosed with type 1 rather than a mother, brother, or sister. In some cases, family members of people with type 1 diabetes also have a history of autoimmune conditions such as celiac disease or lupus.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by lifestyle and other factors, while type 1 is either;genetic;or acquired after the onset of an illness.
You Are Entitled To Free Diabetes Checks Every Year Also Known As The 15 Health Care Essentials

When you have diabetes, youre entitled to certain checks, tests and services every year such as eye screening and foot checks. These will help you manage your diabetes and theyre all free read about the diabetes checks you should get, or take this handy 15 healthcare essentials check list to your GP.
When you are eligible for diabetic eye screening, you will recieve an invitation by letter with a list of screening locations close to your postcode so you can choose where the screening will be carried out. You can also see this list online, and read more about your eye screening appointment.
Recommended Reading: Can You Lose Weight With Diabetes
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
The major process that happens in type 1 diabetes is that the pancreas can no longer produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is more a result of insulin resistance , that is, it takes a large amount of insulin to move glucose out of the blood and into the cells. Over time, people with type 2 diabetes also may experience decreased insulin production in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, over time, the body can also develop insulin resistance — especially in people who gain a lot of weight while using insulin. This means there is some overlap in treatment and diet for people who have had diabetes of either type for a long time.
Increase In Type 1 Diabetes
The number of type 1 diabetes cases is increasing worldwide, with estimates of children and adolescents under 20 with type 1 growing to over 1 million cases, according to IDF’s 2017 Diabetes Atlas. Here’s more info from several sources:
- The overall annual increase in type 1 diabetesis estimated to be around 3%, according to IDF’s 2017 Diabetes Atlas.
- While the incidence is increasing worldwide,there’s variations by country and region, with some locations having far higherincidences than others. This could be due to genetic and environmental factorsthat we don’t yet fully understand.
- 5 million people in the U.S. are expected tohave type 1 diabetes by 2050, according to JDRF.
- Nearly 600,000 youth/children in the U.S. areexpected to have type 1 diabetes by 2050, according to JDRF.
- There’s no effective intervention to prevent type1 diabetes so reducing the rising case load isn’t yet feasible, the IDF’s 2017 Diabetes Atlas reports.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
About Type 1 Diabetes Statistics
First, let’s talk about how reporting the incidence of all type 1 diabetes cases is challenging. There are two main reasons for this: age and diabetes type. Here’s why:
- Peak age of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes isaround 13 or 14, according to the CDC. According to the International DiabetesFederation ‘s 2019 Diabetes Atlas, type 1diabetes is likely the major cause of diabetes in children.
- This young age at diagnosis is likely what contributes to type 1 diabetes statistics in adults being”very limited,” according to the August 2018 book Diabetes in America from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and KidneyDiseases .
- Most studies and databases like SEARCH, the largest,most comprehensive surveillance study of diabetes in younger people in the U.S.to date, launched by the CDC and NIDDK in 2000 break out some statistics by type 1 or type 2 diabetes, but oftencombine the two diabetes types into overarching diabetes stats. This makes itdifficult to define some diabetes statistics by type.
High And Low Blood Sugar
Blood sugar levels change often during the day. Youll need to notice if your blood sugar drops too low and be prepared to treat it right away.
If your blood sugar spikes very high and your insulin is low, you can develop diabetic ketoacidosis , a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. Youll need medical care immediately if you develop DKA.
Your health care team will let you know how to identify and treat high and low blood sugar and related health problems. Be sure to get in touch with your doctor or diabetes educator if you have any questions.
Don’t Miss: Night Blood Sugar Levels
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible.;If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast ;acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing artificial pancreas technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Complications Are Associated With Type 1 Diabetes
Having type 1 diabetes increases a persons risk of developing long-term health complications. Over time, the high blood sugar levels that are associated with diabetes can damage the body, affecting the nervous system, blood vessels, eyes, heart, and kidneys. Careful management, and maintaining stable blood glucose levels, can reduce a persons risk for complications. To read more about complications, click here.;
In the short term, type 1 diabetes can cause hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia , as well as diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.;
How Else Can I Manage Type 1 Diabetes
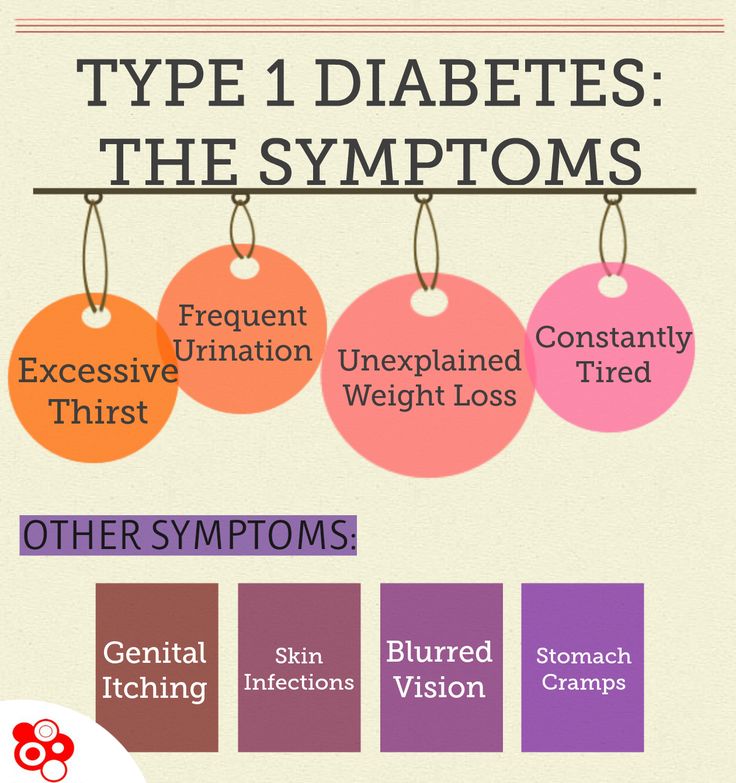
Along with insulin and any other medicines you use, you can manage your diabetes by taking care of yourself each day. Following your diabetes meal plan, being physically active, and checking your blood glucose often are some of the ways you can take care of yourself. Work with your health care team to come up with a diabetes care plan that works for you. If you are planning a pregnancy with diabetes, try to get your blood glucose levels in your target range before you get pregnant.
You May Like: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Get The Support You Need
Diabetes Canada is here to help provide information and support so that you can live a healthy life. A positive and realistic attitude toward your diabetes can help you manage it. Talking to other people with;diabetes is a great way to learn, and to feel less alone.
Your health-care team is there to help you. Depending on your needs and the resources available in your community, your team may include a family doctor, diabetes educator , endocrinologist, pharmacist, social worker, exercise physiologist, psychologist, foot-care specialist, eye-care specialist. They can answer your questions about how to manage diabetes and work with you to adjust your food plan, activity and medications.
Treating High Blood Glucose
Hyperglycaemia can occur when your blood glucose levels become too high. It can happen for several reasons, such as eating too much, being unwell or not taking enough insulin.
If you develop hyperglycaemia, you may need to adjust your diet or your insulin dose to keep your glucose levels normal. Your diabetes care team can advise you about the best way to do this.
If hyperglycaemia isn’t treated, it can lead to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis, where the body begins to break down fats for energy instead of glucose, resulting in a build-up of ketones in your blood.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is very serious and, if not addressed quickly, it can lead to unconsciousness and, eventually, death.
The signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- frequently passing urine
Read more about the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
Your healthcare team will educate you on how to decrease your risk of ketoacidosis by testing your own blood for ketones using blood ketone sticks if you’re unwell.
If you develop diabetic ketoacidosis, you’ll need urgent hospital treatment. You’ll be given insulin directly into a vein . You may also need other fluids given by a drip if you’re dehydrated, including salt solution and potassium.
Don’t Miss: Donate Blood Diabetic

