Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hypoglycemia;happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. Low blood sugar can be caused by many things including the two different types of diabetes, certain medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, pregnancy , and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:;;
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Tingling lips;;
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or other glucose monitoring device.;
If you dont have access to these tools and start to feel the symptoms of low blood sugar, consume 15 grams of carbs or take a quick dissolve glucose tablet to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Once your blood sugar is back in its target range, you can have a snack or meal to make sure it doesnt drop again.;;;;
Here are some other lifestyle and medicinal treatments that can help treat hypoglycemia:
- Eat a healthy diet full of whole foods that are minimally processed.;
- Take prediabetes or diabetes medications as recommended by your healthcare provider.;;
- Use a glucagon kit in emergencies. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels quickly.;;
What Drinks And Foods Raise Blood Sugar Fast
- 4 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 can of regular soda or juice
Many people like the idea of treating low blood sugar with dietary treats such as cake, cookies, and brownies. However, sugar in the form of complex carbohydrates or sugar combined with fat and protein are much too slowly absorbed to be useful in acute treatment.
Once the acute episode has been treated, a healthy, long-acting carbohydrate to maintain blood sugars in the appropriate range should be consumed. Half a sandwich is a reasonable option.
If the hypoglycemic episode has progressed to the point at which the patient cannot or will not take anything by mouth, more drastic measures will be needed. In many cases, a family member or roommate can be trained in the use of glucagon. Glucagon is a hormone that causes a rapid release of glucose stores from the liver. It is an injection given intramuscularly to an individual who cannot take glucose by mouth. A response is usually seen in minutes and lasts for about 90 minutes. Again, a long-acting source of glucose should thereafter be consumed to maintain blood sugar levels in the safe range. If glucagon is not available and the patient is not able to take anything by mouth, emergency services should be called immediately. An intravenous route of glucose administration should be established as soon as possible.
Also Check: Average Lifespan Of A Diabetic
Symptoms Treatments And Prevention
Hyperglycemia means;high glucose in the blood . Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabeteswhen the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn’t properly using or doesn’t make the hormone insulin.
Eating too many processed foods may cause your blood sugar to rise.
Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, but the biggest changes happen around mealtimes. Before eating, a healthy; sugar level is between 3.9-5.5mmol/L. Around 1-2 hours after eating, expect blood sugar to rise to 5-10mmol/L.
If your blood sugar doesn’t stick within these ranges, the body may have stopped regulating blood sugar effectively which can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.;;
Read Also: Diabetics And Cheese
A Low Blood Sugar Level And Driving
You may still be allowed to drive if you have diabetes or you’re at risk of a low blood sugar level for another reason, but you’ll need to do things to reduce the chance of this happening while you’re driving.
You also need to tell the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency and your car insurance company about your condition.
For more information, see:
A Low Blood Sugar Level Without Diabetes
A low blood sugar level is uncommon in people who do not have diabetes.
Possible causes include:
- a gastric bypass
- other medical conditions, such as problems with your hormone levels, pancreas, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands or heart
- some;medicines, including quinine
See a GP if you think you keep;getting symptoms of a low blood sugar level. They can arrange some simple tests to check if your blood sugar level is low and try to find out what’s causing it.
You May Like: What Is Type 1 Diabetes Caused By
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.;;
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.;;;;;;;;
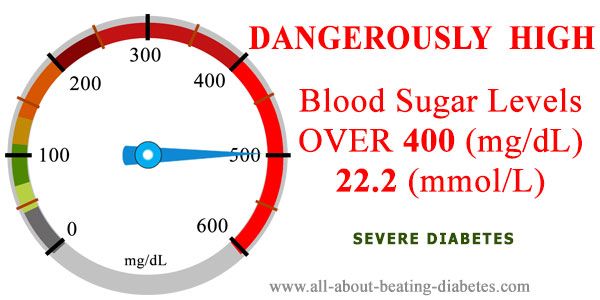
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.;;;;;;;;;
Change Your Life Today And Reduce Your Risk Of Diabetes
Diabetes can be a massive burden on both your health and your wallet. But, maintaining normal blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and staying physically active are great ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.;
If you are looking to improve your health and monitor your risk factors for disease, getting covered is a great way to relieve the financial pressures of looking after yourself.;
Why not contact us today at Insurdinary for a free, personalized, no-obligation quote from some of the best health care providers in Canada!
Also Check: What Happens If A Diabetic Eats Sugar
High Blood Sugar Facts
- Low high blood sugar;;is abnormally high blood levels of insulin in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes, and diabetes is the most common cause of it. Severely elevated glucose levels can result in a medical emergency like diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome .
- The primary symptom of hyperglycemia is excessive amounts of sugar in the urine. Other symptoms and signs of high blood sugar levels in the blood are blurred vision, hunger , and headaches.
- Other conditions that can cause high blood sugar are pancreatitis, Cushing’s syndrome, unusual hormone-secreting tumors, pancreatic cancer, certain medications, and severe illnesses.
- Insulin is the treatment for people with type 1 diabetes, and life-threatening increases in glucose levels. People with type 2 diabetes may be managed with a combination of different oral and injectable medications. Hyperglycemia due to medical conditions other than diabetes is generally treated by treating the underlying condition responsible for the elevated glucose.
When To Get Urgent Medical Attention
Contact;your diabetes care team immediately;if you have a high blood sugar level and experience the following symptoms:
- feeling or being sick
- a fever for more than 24 hours
- signs of;dehydration, such as a headache, dry skin and a weak, rapid heartbeat
- difficulty staying awake
These symptoms;could be a sign of a more serious complication of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital.
You May Like: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
How Is High Blood Sugar Diagnosed
There are different kinds of blood tests that can diagnose hyperglycemia. These include:
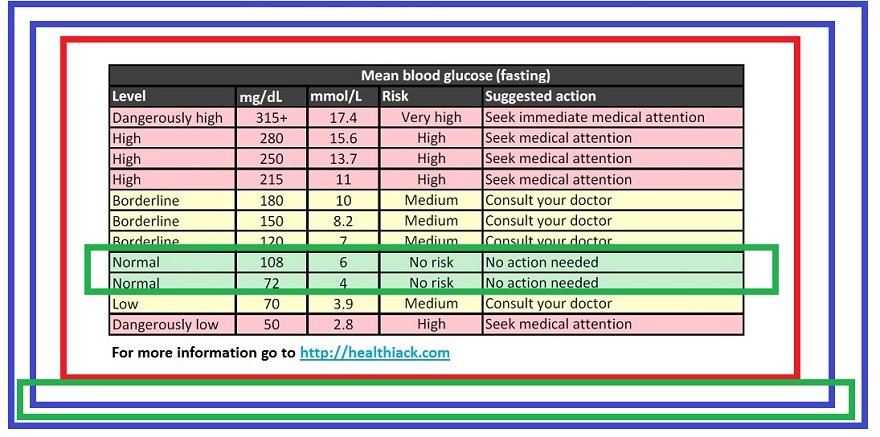
Random blood glucose: this test reflects the blood sugar level at a given point in time. Normal values are generally between 70 and 125 mg/dL, as discussed earlier.
Fasting blood glucose: this is a measurement of blood sugar level taken in the early morning prior to eating or drinking anything since the night before. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are less than 100 mg/dL. Levels above 100 mg/dL up to 125 mg/dL suggest prediabetes, while levels of 126 mg/dL or above are diagnostic of diabetes.
Oral glucose tolerance test: this is a test that measures blood glucose levels at given time points after a dose of sugar is consumed. This test is most commonly used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
Glycohemoglobin A1c: is a measurement of glucose that is bound to red blood cells and provides an indication about blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
How Do You Treat Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar levels happen when theres too little glucose left in the bloodstream to continue supplying fuel to your organs, muscles, and tissues. It most often occurs when you dont eat enough food, especially carb-containing foods, given your blood-sugar-lowering medications and physical activity levels, ONeill says. Levels can decrease gradually or suddenly.
When the amount of glucose in the bloodstream drops to too-low levels, the body reacts by releasing epinephrine, also called adrenaline or the fight or flight hormone. Epinephrine revs your heart rate and can cause sweating, shaking, anxiety, and irritability. If not enough glucose is able to reach the brain, the result may be difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, and slurred speech. In extreme cases, a lack of glucose within the brain can lead to seizures, coma, and even death, she says.
People with low glucose levels can use the ADAs 15-15 Rule, which advises people consume 15 g of carbs, wait 15 minutes, and check their levels again. If the number is still low, repeat until reaching at least 70 mg/dL.
You can find 15 g of carbs in:
- 1 slice of bread
- 1 small piece of fresh fruit
- cup of yogurt
- Three to four hard candies
- Glucose tablets as indicated on the label
- Glucose gel as indicated on the label
Once your glucose levels are back to normal, the ADA suggests going ahead and eating your next scheduled meal or snack, which will help prevent levels from dropping again.
Read Also: What Is A Unit Of Insulin
When To Go To The Er
High blood sugar can be very concerning because your body can start burning fat for energy instead of blood glucose.
This can cause conditions such as DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome . These conditions are medical emergencies and can be fatal if left untreated.
DKA is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes. Its rare in people with type 2 diabetes, but can occur.
Symptoms that can indicate you should go to the emergency room include:
- ketones in your urine, as diagnosed using a urine dipstick test
- confusion
- stomach pain
- vomiting
High blood sugar levels can cause a fluid imbalance in the body and can cause the blood to become acidic in a manner that doesnt support life.
Medical treatments for these conditions include administering intravenous insulin on a continuous basis and IV fluids to correct dehydration.
Summary
High blood sugar can become a medical emergency. Go to the ER if you suspect DKA or HHS.
Complications From Chronic High Blood Sugar
Over time, high blood sugar damages the arteries and vessels of the body. When these vessels are damaged, complications can occur.
- Heart disease: people with diabetes are;two to four times more likely;to die from cardiovascular disease than those without diabetes. People with diabetes are also more likely to have;high blood pressure, which is another risk factor for heart disease.
- Stroke: Diabetes increases the risk of stroke, as well as;increases mortality;when a stroke occurs.
- Kidney disease and failure: High blood sugar damages the kidneys and can lead to kidney disease. About;one in four people;with diabetes have kidney disease.
- Poor wound healing leading to amputations: High blood sugar inhibits proper wound healing. Diabetes is thought to be the;leading cause of leg amputations;worldwide.
- Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves, which can cause painful symptoms like numb and tingling legs and feet, as well as delayed stomach emptying from damage to the stomachs nerves.
- Retinopathy and blindness: Damage to the nerves in the eyes is called;retinopathy, which can lead to blindness if not treated.
Don’t Miss: Does Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Blood Sugar
What Blood Sugar Level Is Considered Normal
Note: the definition of “normal” blood sugar is hard to define because it depends on the person and whether or not you’re diabetic. We’ll be focusing mostly on nondiabetics.
As Dr. Adimoolam told POPSUGAR, “For those people with diabetes, each individual has different goals for their blood sugar values . . . so there is no one perfect number for everyone.” She gave us the following parameters for nondiabetics: “Normal blood sugar is considered below 200 mg/dL after meals and below 100 mg/dL when fasting.” Dangerous levels of blood sugar would be less than 70 mg/dL and more than 200 mg/dL persistently, she said, stressing that we “need to differentiate between what’s dangerous for someone who has diabetes and someone who does not have diabetes.”
Dr. Ahn gave us a similar range. “If you’re someone walking off the street and you’re otherwise healthy, and a doctor takes your blood sugar and it’s 150 mg/dL,” then he’d say you needed further medical attention. In the range between 150-250 mg/dL, “you’ll walk around feeling fine, but it’s still not safe and I’d consider it high-risk.” For people who are nondiabetic, “Your body usually is very, very good at regulating your sugar levels. Within an hour or two of having a big meal, it will come down to the 90-130 mg/dL range.”
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Despite advances in the treatment of diabetes, low blood sugar episodes occur as a side effect of many treatments for diabetes. In fact, these episodes are often the limiting factor in achieving optimal blood sugar control, because many medications that are effective in treating diabetes carry the risk of lowering the blood sugar level too much, causing symptoms. In large scale studies looking at tight control in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, low blood sugars occurred more often in the patients who were managed most intensively. This is important for patients and physicians to recognize, especially as the goal for treating patients with diabetes becomes tighter control of blood sugar.
While people who do not have any metabolic problems can complain of symptoms that resemble low blood sugar, true hypoglycemia usually occurs in people with diabetes mellitus . People with pre-diabetes or insulin resistance also can have low blood sugars on occasion if their high circulating insulin levels are further challenged by a prolonged period of fasting. There are other rare causes for the condition, such as insulin-producing tumors and certain medications.
These uncommon causes of hypoglycemia will not be discussed in this article, which will primarily focus on the condition occurring with type 1 or 2 diabetes and its treatment.
Also Check: Are Pickled Beets Good For Diabetics
Then What If The Blood Sugar Is Too Low
Too low blood sugar or hypoglycemia can occur when your blood sugar levels are below 70 mg/dL. Low blood sugar levels are at risk of causing various organs of the body to malfunction, especially in parts of the brain.
Because the brain is a very sensitive organ to low blood sugar levels because glucose is the main source of energy for the brain.
When you experience hypoglycemia, you will feel symptoms of dizziness, confusion, tired and weak body, headache, inability to concentrate, heart palpitations, cold sweats, vision impairment, seizures, to loss of consciousness up to coma.
If not treated immediately, hypoglycemia can also cause permanent brain damage. Usually, symptoms of severe hypoglycemia are often experienced by diabetics with the following habits:
- The use of diabetes medications is not offset by proper carbohydrate intake.
- Heavy physical activity but not balanced with the intake of foods that meet the needs of carbohydrates.
- Fasting with improper nutrition management.
However, you who are able-bodied also need to be careful. Because hypoglycemia can also attack if you undergo long-term fasting without proper nutritional preparation. In addition, long-term food supply shortages in an area are also prone to hunger or starvation, resulting in a drastic drop in blood sugar.
How Do I Check My Blood Sugar
You use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar. This device uses a small drop of blood from your finger to measure your blood sugar level. You can get the meter and supplies in a drug store or by mail.
Read the directions that come with your meter to learn how to check your blood sugar. Your health care team also can show you how to use your meter. Write the date, time, and result of the test in your blood sugar record. Take your blood sugar record and meter to each visit and talk about your results with your health care team.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night

