Identifying The Why Of Blood Sugar Control
Thus, when considering goals for blood glucose in older adults, it is important to ask why we are managing diabetes. As the reason to tightly control diabetes is to prevent complications in the future, tighter control of diabetes could be a goal in an older adults who are in good health and have few risk factors for hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia risk factors include previous history of severe hypoglycemia that required hospital or emergency department visits, memory problems, physical frailty, vision problems, and severe medical conditions such as heart, lung, or kidney diseases.
In older individuals with multiple risk factors for hypoglycemia, the goal should not be tight control. Instead, the goal should be the best control that can be achieved without putting the individual at risk for hypoglycemia.
Lastly, it is important to remember that health status is not always stable as we get older, and the need or the ability to keep tight glucose control may change over time in older adults. Goals for all chronic disease, not just blood sugar control, need to be individualized to adapt to the changing circumstances associated with aging.
The Best Healthcare Options To Prevent Diabetes
Health care is expensive.; Canada spent an estimated $253.5 billion in 2018, and as the cost of health care increases, so does the cost to you. Pre-existing medical conditions, family history, and BMI are all factors that increase the cost of health care. These factors also increase your risk of diabetes, so;you must be covered.;
Of course, as a Canadian, you are entitled to some free and subsidized health care, which is great. But many people opt for private healthcare and for diabetes prevention this can be very useful. If you’re shopping around for private healthcare, it’s important to choose the right package.;
Basic health insurance will usually cover health care, medical services, and prescriptions, but they tend to lack customizations.;If you opt for a premium/guaranteed health insurance you have the bonus of a custom plan based on your needs; if you are worried about your risk of diabetes this is like gold dust.;
Private healthcare plans can cover the cost of many expenses related to diabetes such as blood tests, blood sugar monitors, specialist referrals, hospital stays, and much more! The most important thing to note about private health care is that it covers costs for preventative care, not just treatment for diseases.;
There are many different options available, so make sure you search for the best quotes.
Special Concerns In The Elderly Population
A concern with blood sugar levels and elderly people is that some of the symptoms can be overlooked or mistaken for other common changes that develop with age. For instance, the normal decrease in thirst that the elderly commonly experience could mask the symptom of increased thirst usually found in diabetes.
There are normal aging process symptoms, such as mental confusion, incontinence and changes in eyesight that may otherwise be viewed as the normal aging process, when in fact in some patients may be the presenting symptoms of diabetes. Depression is a major concern because studies have shown that elderly people who suffer from depression are 60 percent more likely to develop diabetes
The rising cost that it takes for each individual to properly maintain their blood sugar levels may be beyond the means of elderly people on a limited income, forcing them to forego some treatments or receive inadequate care.
Since the elderly are also at risk for illnesses like dementia or Alzheimerâs disease, there is the real possibility that they may forget to monitor their blood sugar level, take their medication or adhere to special diets that would otherwise help them to maintain their nutritional needs. The sedentary lifestyles of the elderly can also prevent them from getting the adequate exercise that a diabetic patient needs to maintain their blood sugar levels.
Also Check: Bananas Bad For Diabetics
Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
- Eat a healthy breakfast containing fiber and protein within an hour of waking up to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Always eat healthy fats, protein, and fiber with each meal, as this slows the digestive process and the number of carbohydrates released into the bloodstream, keeping blood sugar levels stable.
- Exercise regularly to burn off extra blood sugar.
- Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary drinks, such as soda, sports drinks, and juice, as these quickly raise blood sugar levels.
- Keep a supply of hard candy, juice boxes, or glucose tablets on hand in case of low blood sugar crashes. If your loved one has hypoglycemia, he or she should consume a sugary snack or drink as soon as possible and then recheck his or her levels.
How To Stay In Target
Eating healthy, exercising and taking medication, if necessary, will help you keep your blood sugar levels within their target range. Target ranges for blood sugar can vary depending on your age, medical condition and other risk factors.
Targets are different for pregnant women, older adults and children 12 years of age and under.
You May Like: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
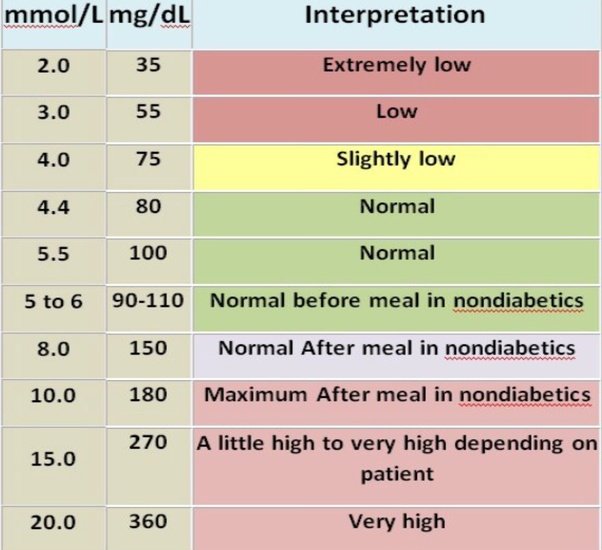
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
What Causes Blood Sugar Levels To Rise In Seniors
High blood sugar is referred to as hyperglycemia. In addition to age-related changes, it could be caused by undiagnosed or improperly managed diabetes, or even certain medications. Excess weight, poor eating habits, and lack of regular exercise are additional contributing factors. Seniors with consistently high blood sugar levels may experience: Confusion and disorientation
You May Like: Insulin Resistance And Glucose Intolerance
How Do I Check My Blood Sugar
You use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar. This device uses a small drop of blood from your finger to measure your blood sugar level. You can get the meter and supplies in a drug store or by mail.
Read the directions that come with your meter to learn how to check your blood sugar. Your health care team also can show you how to use your meter. Write the date, time, and result of the test in your blood sugar record. Take your blood sugar record and meter to each visit and talk about your results with your health care team.
What Are Considered Normal Blood Sugar Levels
You might not have diabetes now, but do you know the risk factors?
In 2015, 22% of Canadian adults were pre-diabetic and the number of Canadians suffering from diabetes has increased by 44% in the last 10 years. As the leading cause of blindness, kidney problems, and non-trauma amputations, it is important to protect ourselves against diabetes.
But its not all bad news, diabetes is often a preventable disease. Knowing whether you have normal blood sugar levels is one of the best indicators of risk. If your blood sugar levels are high, mindful eating and lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Read on for all the hottest tips on how to manage your blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes.
You May Like: How To Mix Nph And Regular Insulin
Why Do I Need To Know My Blood Sugar Numbers
Your blood sugar numbers show how well your diabetes is managed. And managing your diabetes means that you have less chance of having serious health problems, such as kidney disease and vision loss.
As you check your blood sugar, you can see what makes your numbers go up and down. For example, you may see that when you are stressed or eat certain foods, your numbers go up. And, you may see that when you take your medicine and are active, your numbers go down. This information lets you know what is working for you and what needs to change.
How To Measure Blood Sugar Levels
There are two main ways to check your blood sugar levels:;
Type 1 diabetics, along with some type 2 diabetics, who require insulin medication, must check their blood sugar at least four times per day, says Mathioudakis. Typically, this should be done before a meal, one to two hours after a meal, and at bedtime.;
The timing of these measurements can help determine how much insulin to use. For example, it can be important to use more insulin after a high-sugar meal, or to avoid falling into hypoglycemia while you’re sleeping.;
To check your blood sugar at home, you should use blood glucose tests, such as a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor . Both devices measure blood sugar with the unit mg/dL, which means a milligram of sugar per deciliter of blood.;
If you don’t have diabetes, but you may be at risk, your doctor might have you take an A1C test during a yearly check-up. This test reports results as a percentage; the higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar has been in the past three months. Those with diabetes should get an A1C test at least twice a year and sometimes every three months.;
You May Like: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
How Can An Elderly Person Control Blood Sugar Levels
The relationship between blood sugar levels and elderly people is an important topic that has been addressed by physicians and caregivers because of the affects that it has on them. There are several ways that an elderly person can control blood sugar levels, although assistance may be needed by caregivers or loved ones:
- Providing someone to help the elderly in taking their medications ensures that they are taking their medications properly.
- The caregiver or loved one can remind the patient to use the blood glucose meters to make sure that their blood sugar levels stay within normal range. It it also important to keep diabetes testing strips nearby in case of emergencies.
- Monitoring the daily health of the elderly patient for symptoms that might be related with low or high blood sugar is important. Assuring that the patient gets enough of exercise recommended by their physician and within doctorâs orders.
- Maintaining proper nutrition is important for the patient. Assistance in preparing meals may be necessary to assure that their nutritional needs are met. There are programs such as meals on wheels that may be available in the area to assist with delivery of meals to them.
- Family members can read and understand the insurance policies in regards to diabetic care. Doing this may help them to save money as much as possible.
So What Can You Do If You Are Elderly And You Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
Its no fun to get the diagnosis of diabetes when you are already getting older, and have other health issues and concerns already. Your health care provider may prescribe a combination of diet, exercise, and medications to help you manage your new diagnosis of diabetes. Your health care team should look at all of your health issues, and help tailor a plan that is individualized for you. You should see a certified diabetes educator to learn about all the aspects of self-management that you will need to know in order to decrease your risks for the complications of diabetes.
You will need to learn to self-manage your diabetes by:
In addition, keep the following regular appointments for your diabetes care:
Don’t Miss: How Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
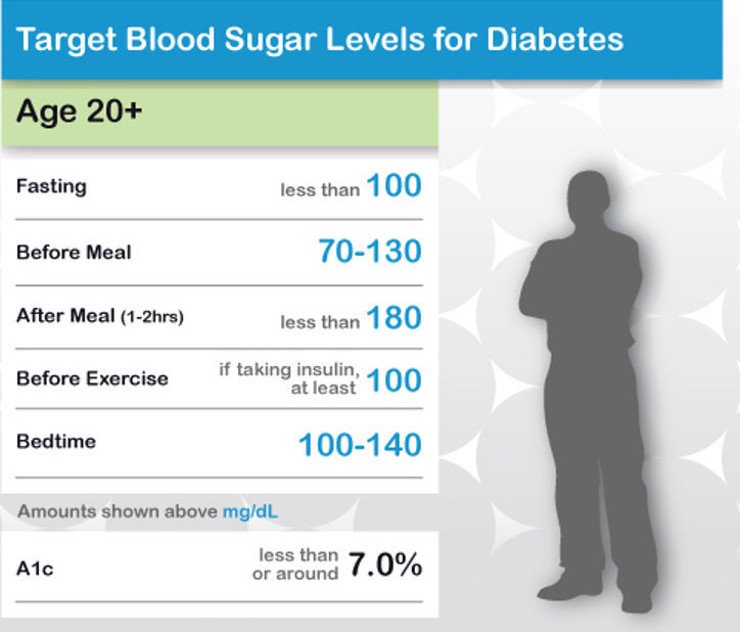
What Is Normal Blood Sugar 60 Year Old
Normal ranges of blood sugar levels are between 70 and 130 mg/dL before eating meals. The American Diabetes Association recommends seniors have blood glucose levels of less than 180 mg/dL two hours after eating. Not every senior has the same care needs, which means they dont all need the same type of at-home care.
Check Your Blood Sugar Often
Checking your blood sugar levels often and writing down, or using an app to track the results will tell you how well you are managing your diabetes. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about how often you should check your blood sugar.
- Not everyone with diabetes needs to check their blood sugar every day. But some people may need to check it many times a day.
- If you have type 1 diabetes, check your blood sugar at least 4 times a day.
Usually, you will test your blood sugar before meals and at bedtime. You may also check your blood sugar:
- After you eat out, particularly if you have eaten foods you don’t normally eat
- If you feel sick
- Before and after you exercise
- If you have a lot of stress
- If you eat too much
- If you are taking new medicines that can affect your blood sugar
Keep a record for yourself and your provider. This will be a big help if you are having problems managing your diabetes. It will also tell you what works and what doesn’t work, to keep your blood sugar under control. Write down:
- The time of day
- The amount of carbohydrates or sugar you ate
- The type and dose of your diabetes medicines or insulin
- The type of exercise you do and for how long
- Any unusual events, such as feeling stressed, eating different foods, or being sick
Many glucose meters let you store this information.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Other Severe Symptoms Of Hyperglycaemia Include:
- Nerve damage
- Kidney damage
- Blood vessel damage
Mild hyperglycaemia, depending on the cause, will not typically require medical treatment. Most people with this condition can lower their blood sugar levels sufficiently through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Those with type 1 diabetes will require the administration of insulin , while those with type 2 diabetes will often use a combination of injectable and oral medications , although some may also require insulin.
Diabetes In Older Adults: A Growing Population With Special Challenges
The population of elderly patients with diabetes is rapidly growing, with significant impact on population health and economics . Currently in the United States, older adults make up >25% of the total population with diabetes . Even if the diabetes incidence rates were to level off, the prevalence of diabetes will double in the next 20 years as the population ages .
You May Like: Jonas Brother Diabetes
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes may include feeling tired, increased hunger or thirst, losing weight without trying, urinating often, or having trouble with blurred vision. You may also get skin infections or heal slowly from cuts and bruises. Some people with type 2 diabetes may not realize they have it because symptoms often develop slowly and go unnoticed. Sometimes older adults dismiss these symptoms as getting old, but they can be signs of a serious problem. Talk with your doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
Current Guidelines For Diabetes Management In Community
Several organizations have published guidelines regarding diabetes management in older adults. Most of these guidelines stress the importance of considering patients overall health, comorbidities, cognitive and physical status, hypoglycemia risk, and life expectancy to guide glycemic goal-setting. The details vary by guideline, and these differences are summarized below.
The European Diabetes Working Party for Older People in 2011 published clinical guidelines for treating older adults with diabetes who are 70 years of age . With regard to glycemic targets, these guidelines divide older adults into two categories. For those without other major comorbidities, an A1C goal of 77.5% and a fasting glucose target range of 6.57.5 mmol/L are recommended, whereas for frail older adults and those with multisystem disease, an A1C goal of 7.68.5% and a fasting glucose target range of 7.69.0 mmol/L are recommended to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia and metabolic decompensation.
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Soda Affect Blood Sugar
What Are Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are related to high blood sugar levels . Symptoms may not be present at first because type 2 diabetes can develop gradually over time. High blood sugar levels can result in symptoms including thirst, frequent urination, tiredness, listlessness, nausea, and dizziness. If the blood sugar levels are extremely high, symptoms may escalate to confusion, drowsiness, and even loss of consciousness .
Teaching Tools For The Elderly With Diabetes
Instruction by diabetes educators should be provided, presenting one concept at a time, making sure that the patient can hear instructions. Write instructions down in large print, and provide aids such as a magnaguide for drawing up of insulin doses. Decide between teaching carbohydrate counting and a food group planning curriculum, as some older adults may prefer the later.
Refer to appropriate community resources
The elderly with diabetes should be referred to the appropriate community resources in their communities, including the Area Agency on Aging, local senior centers , diabetes support groups, exercise and walking groups, meals-on-wheels, or other social services.3
You May Like: Side Effects Of Stopping Insulin

