Is Sugar Bad For You
If you love sweets, don’t despair. You don’t have to give them up forever. Sugar will raise your blood sugar levels more quickly than other carbs, but diabetes experts now say the total amount of carbs is most important. So keep your serving sizes small and take into account the total carbs and calories.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia
Many symptoms can happen when a person experiences hypoglycemia. The sudden drop in blood sugar can cause both mild and severe symptoms. Most people will experience a few mild symptoms.
Appropriate action can then be taken to counter the hypoglycemia. There are also cases where patients experience more serious symptoms. In rare scenarios, these symptoms become life-threatening. When this happens, the patient needs urgent medical care.
Dont Drive When You Have Low Blood Sugar
It’s dangerous. If you’re driving and you have hypoglycemia symptoms, pull off the road, check your blood sugar, and eat a sugary food. Wait at least 15 minutes, check your blood sugar, and repeat these steps if needed. Eat a protein and carbohydrate source before you drive on. Be prepared. Keep a sugar source, such as glucose tablets, in your car at all times for emergencies.
Allina Health: âNon-diabetic Hypoglycemia.”
Endotext: “Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia.”
UW Health: âNutrition Management of Low Blood Sugar without Diabetes .â
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: âHow to Give an Emergency Glucagon Injection to Treat Low Blood Sugar.â
American Diabetes Association: âHypoglycemia .â
Joslin Diabetes Center: âDriving with Diabetes,â âHow To Treat A Low Blood Glucose,â âIs Low Blood Glucose Dangerous?â âOral Diabetes Medications Summary Chart,â âPrandin âOral Hypoglycemic Agent.â”
Journal of the American Medical Association: âFactitious Hypoglycemia Due to Chlorpropamide: Report of a Case, with Clinical Similarity to an Islet Cell Tumor of the Pancreas.â
AMN Healthcare: âAdvances in Diabetes, Part II: Oral Medications.â
Physiciansâ Desk Reference: âAllopurinol,â âCoumadin,â âProbenecid.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âLow Blood Glucose .â
Hormone Health Network: âNon Diabetic Hypoglycemia.â
University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics: âHypoglycemia .â
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
How Can I Be Better Prepared For Hypoglycemia
You can take some steps to be ready for hypoglycemia:
- Be aware of the symptoms and treat them early.
- Carry some fast-acting carbs with you all the time.
- Check your glucose levels frequently, especially around meals and exercise.
- Inform family, friends and co-workers so they know what do if you need help.
- Talk to your healthcare provider regularly to make and update your plan.
- Wear a medical bracelet that lets people know you have diabetes. Carry a card in your purse or wallet with instructions for hypoglycemia.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hypoglycemia is quite common in people with diabetes. If not treated, it can cause troubling symptoms, and even serious health problems. Fortunately, you can avoid hypoglycemic episodes by monitoring your blood sugar. You can also make small adjustments to eating and exercising routines.
Hypoglycemia Tests And Diagnosis

To diagnose nondiabetic hypoglycemia, your doctor will do a physical exam and ask questions about any medicines you take. Theyâll want to know all about your health and any history of diseases or stomach surgery.
Theyâll check your blood glucose level, especially when you are having symptoms. Theyâll also check to see if you feel better when your sugar goes back to a normal level.
If your doctor suspects hypoglycemia, you may have to fast until you start to have symptoms. Theyâll test your blood glucose level at different times throughout the fast.
To check for reactive hypoglycemia, you may have to take a test called a mixed-meal tolerance test . For this, you take a special drink that raises your blood glucose. The doctor will check your blood glucose levels over the next few hours.
Read Also: How To Test For Diabetes Insipidus
Tips For Keeping Blood Sugar Steady
The best way to address your personal concerns and needs is to discuss your diet, medication, and lifestyle with your healthcare team. They can diagnose any underlying conditions, adjust or change your medications, and advise you on the best ways to prevent hypoglycemia.
Tips that apply across the board to keep blood sugar stable include:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Planning meals
- Getting adequate sleep
People with diabetes may face more challenges when managing blood sugar levels, but it is possible to stay healthy.
Preventing A Low Blood Sugar Level
If you have diabetes, you can reduce your chance of getting a low blood sugar level if you:
- Check your blood sugar level regularly and be aware of the;symptoms of a;low blood sugar level so you can treat it quickly.
- Always carry a sugary snack or drink with you, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice or some sweets. If you have a glucagon injection kit, always keep it with you.
- Do not skip meals.
- Be careful when drinking;alcohol. Do not drink large amounts, check your blood sugar level regularly, and eat a carbohydrate snack afterwards.
- Be careful when exercising; eating a carbohydrate snack before exercise can help to reduce the risk of a hypo. If you take some types of diabetes medicine, your doctor may recommend you take a lower dose before or after doing intense exercise.
- Have a carbohydrate snack,;such as toast,;if your blood sugar level drops too low while you’re asleep
If you keep getting a low blood sugar level, talk to your diabetes care team about things you can do to help prevent it.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Tips To Prevent Blood Sugar From Dropping At Night
Sulay Shah, M.D. contributes to topics such as Diabetes.
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar or low blood glucose, occurs when blood glucose levels drop below normalwhich is typically below a level of 70 milligrams per deciliter . With levels more commonly dipping at nighttime, otherwise referred to as nighttime hypoglycemia, this condition affects mostly patients with diabetes.
Slurred Speech And Clumsiness
Your sugar-starved brain may change the way you sound. Slurred speech is a common symptom associated with blood sugar levels that drop below 40 mg/dL, according to University of Michigan Health Systems. Combined with clumsiness another sign of low blood sugar ;you may seem as though you’ve had a few too many cocktails, even if you haven’t touched a drop, according to the National Health Service.
For more on managing low blood sugar, check out Diabetes Daily’s article “How to Treat Lows Without Sabotaging Your Diet!“
Also Check: What Produces Insulin And Glucagon
What Are The Complications Of Low Blood Glucose
Mild-to-moderate low blood glucose can be easily treated. But severely low blood glucose can cause serious complications, including passing out, coma, or death.
Repeated episodes of low blood glucose can lead to
- high blood glucose levels, if worry or fear of low blood glucose keeps you from taking the medicines you need to manage your diabetes8
- hypoglycemia unawareness, a condition in which you dont notice any symptoms of low blood glucose until your blood glucose level has dropped very low
How Do I Treat Low Blood Glucose
If you begin to feel one or more symptoms of low blood glucose, check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose level is below your target or less than 70 mg/dL, follow these steps
You May Like: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
Understanding Your Blood Sugar
The best way to understand how your blood sugar changes day-to-day is to regularly use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar level. If youre newly diagnosed, its also helpful to keep a food journal in addition to a blood sugar log, as well as tracking any physical activity.
Your blood sugar patterns are unique to you. Over time youll have a better understanding of which foods raise your blood sugars the most, as well as how your blood sugar responds to different types of exercise.
Some people with diabetes choose to use a continuous glucose monitor to monitor their blood sugar trends.;
A continuous glucose monitor;is a device with a sensor worn under the skin which measures blood sugar levels every 5-15 minutes. This is useful for identifying trends in blood sugar levels and can help predict and identify hypoglycemia sooner.
Using a CGM can reduce the amount of finger prick glucose tests needed each day, which is an added benefit.
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemia
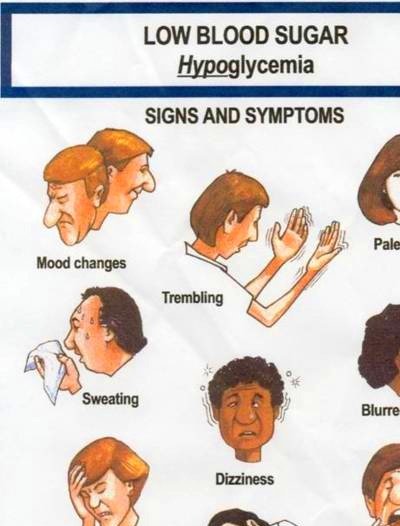
You may need to change what and when you eat to prevent low blood sugar levels. Follow the meal plan that you and the dietitian have planned. The following guidelines may help you keep your blood sugar levels under control.
- Eat 5 to 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large meals. Eat the same amount of carbohydrate at meals and snacks each day. Most people need about 3 to 4 servings of carbohydrate at meals and 1 to 2 servings for snacks. Do not skip meals. Carbohydrate counting can be used plan your meals. Ask your healthcare provider or dietitian for information about carbohydrate counting.
- Limit refined carbohydrates. Examples are white bread, pastries , regular sodas, syrups, and candy.
- Do not have drinks or foods that contain caffeine. Examples are coffee, tea, and certain types of sodas. Caffeine may cause you to have the same symptoms as hypoglycemia, and may cause you to feel worse.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol. Women should limit alcohol to 1 drink a day. Men should limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor. Do not drink alcohol on an empty stomach. Drink alcohol with meals to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Include protein foods and vegetables in your meals. Some foods that are high in protein include beef, pork, fish, poultry , beans, and nuts. Eat a variety of vegetables with your meals.
You May Like: How To Mix Nph And Regular Insulin
If A Person Is Unconscious
If a person loses consciousness;because of;severe hypoglycaemia, they need to be put into the;recovery position and given an injection of the hormone glucagon;. The injection will raise their blood glucose level.
The injection should be carried out by a friend or family member who knows what they’re doing, or by a trained healthcare professional.
You should dial 999 to request an ambulance if:
- a glucagon injection kit isn’t available
- there’s nobody available who’s trained to give the injection
- the injection is ineffective after 10 minutes
Never try to put food or drink into the mouth of someone who’s unconscious as;they could choke.
If you’re able to give a glucagon injection and the person regains consciousness, they should;eat some longer-acting carbohydrate food, such as a few biscuits, a cereal bar or a sandwich.
You should continue to monitor the person for signs of recurring symptoms;in case they need to be treated again.
Complications From Spells Of Hypoglycemia
Mildly low blood sugar levels are somewhat common for people with diabetes; however, severely low blood sugar levels can be life threatening. They may lead to seizures and nervous system damage if left untreated long enough. Immediate treatment is critical.
Its important to learn to recognize your symptoms and treat them fast. For people at risk for low blood sugar, having a glucagon kit a medication that raises blood sugar levels is important. Talk with your doctor for more information.
You may also want to talk with friends, family members, exercise partners, and co-workers about how to care for you if your blood sugar drops too low.
Its important for them to learn to recognize low blood sugar symptoms and know how to use the glucagon kit, as well as understand the importance of calling 911 if you lose consciousness.
Wearing a medical identification bracelet is a good idea. It can help emergency responders care for you properly if you need emergency attention.
Treat low blood sugar as soon as possible. Avoid driving if you are experiencing low blood sugar, as it can increase your risk for having an accident.
There are several ways that you can prevent low blood sugar.
You May Like: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Overdose Of Diabetes Medication
A common cause of hypoglycaemia is taking too much insulin for your current needs. Insulin is a medication that helps control your blood glucose levels. It’s commonly used to treat;type 1 diabetes;and is also recommended for some;people with;type 2 diabetes.
A fall in blood;glucose levels can also occur after taking too much oral hypoglycaemia medication, such as sulphonylurea, which causes a release of insulin. This medication is often used;to lower blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Structural Analysis And Synthesis
Purified animal-sourced insulin was initially the only type of insulin available for experiments and diabetics. was the first to produce the crystallised form in 1926. Evidence of the protein nature was first given by , , and Philip A. Shaffer in 1924. It was fully proven when Hans Jensen and Earl A. Evans Jr. isolated the amino acids phenylalanine and proline in 1935.
The amino acid structure of insulin was first characterized in 1951 by , and the first synthetic insulin was produced simultaneously in the labs of at the and at in the mid-1960s. was achieved by Chinese researchers in 1965. The complete 3-dimensional structure of insulin was determined by in ‘s laboratory in 1969.
The first genetically engineered, synthetic “human” insulin was produced using in 1978 by and at the of the in collaboration with at . Genentech, founded by Swanson, Boyer and , went on in 1982 to sell the first commercially available biosynthetic human insulin under the brand name . The vast majority of insulin used worldwide is biosynthetic recombinant “human” insulin or its analogues. Recently, another approach has been used by a pioneering group of Canadian researchers, using an easily grown plant, for the production of much cheaper insulin.
Two other Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on insulin. British molecular biologist , who determined the of insulin in 1955, was awarded the 1958 . received the 1977 Nobel Prize in Medicine for the development of the for insulin.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
Warning Signs Of Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia can cause both short- and long-term complications. Know the signs so that you can treat the condition as soon as you’re aware of it.
As a person living with diabetes, you know how important it is to reduce blood sugar when it is too high, a phenomenon called hyperglycemia. But blood sugar that is too low, or hypoglycemia, is equally critical to avoid.
“Hypoglycemia happens when the amount of blood glucose drops to a level that’s too low to sustain normal functioning,” says;Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, who is based in Sparta, New Jersey. “In most people, this is defined as a blood sugar level at or below 70 milligrams per deciliter .”
Hypoglycemia is common among people with type 2 diabetes, according to a review published in June 2015 in the journal PLoS One. Individuals with the condition had an average of 19 mild or moderate episodes of hypoglycemia per year and nearly one severe episode per year on average, according to the researchers. Low blood sugar was particularly common among those taking insulin.
RELATED: What to Know Before You Use OTC Insulin
This decrease in blood sugar levels can cause both short-term;complications, like confusion and dizziness, as well as more serious issues, including seizures, coma, and, rarely, death, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Hypoglycemia is usually the result of a too-high dose of insulin or a change in diet or exercise habits, according to Harvard Health Publishing.
Prevention Of Low Blood Sugar
Do not skip or delay meals. If your diet plan includes snacks, make sure to take these.
Measure insulin dosage carefully and inject it properly. If you cannot see well, a family member or a visiting nurse can prepare your insulin injections for you.
Take only the prescribed amount of insulin or oral medication for diabetes that your doctor has ordered.
Keep exercise consistent from day to day. Eat a snack or reduce your insulin prior to unusual exercise.
If you are taking insulin, notify your doctor if you have low blood sugars four or more times per week or if you have a severe low blood sugar. Severe low blood sugars are those less than 40 mg., those requiring help from another person, or those which cause you to have a convulsion or become unconscious.
If you are taking oral medication for your diabetes notify your doctor or nurse if blood sugars are running less than 80 mg. or if you have a severe low blood sugar.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic

