What Types Of Healthcare Professionals Might Be Part Of My Diabetes Treatment Team
Most people with diabetes see their primary healthcare provider first. Your provider might refer you to an endocrinologist/pediatric endocrinologist, a physician who specializes in diabetes care. Other members of your healthcare team may include an ophthalmologist , nephrologist , cardiologist , podiatrist , neurologist , gastroenterologist , registered dietician, nurse practitioners/physician assistants, diabetes educator, pharmacist, personal trainer, social worker, mental health professional, transplant team and others.
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Advancements in technology have given us another way to monitor glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring uses a tiny sensor inserted under your skin. You don’t need to prick your finger. Instead, the sensor measures your glucose and can display results anytime during the day or night. Ask your healthcare provider about continuous glucose monitors to see if this is an option for you.
Also Check: Average Lifespan Of Type 1 Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
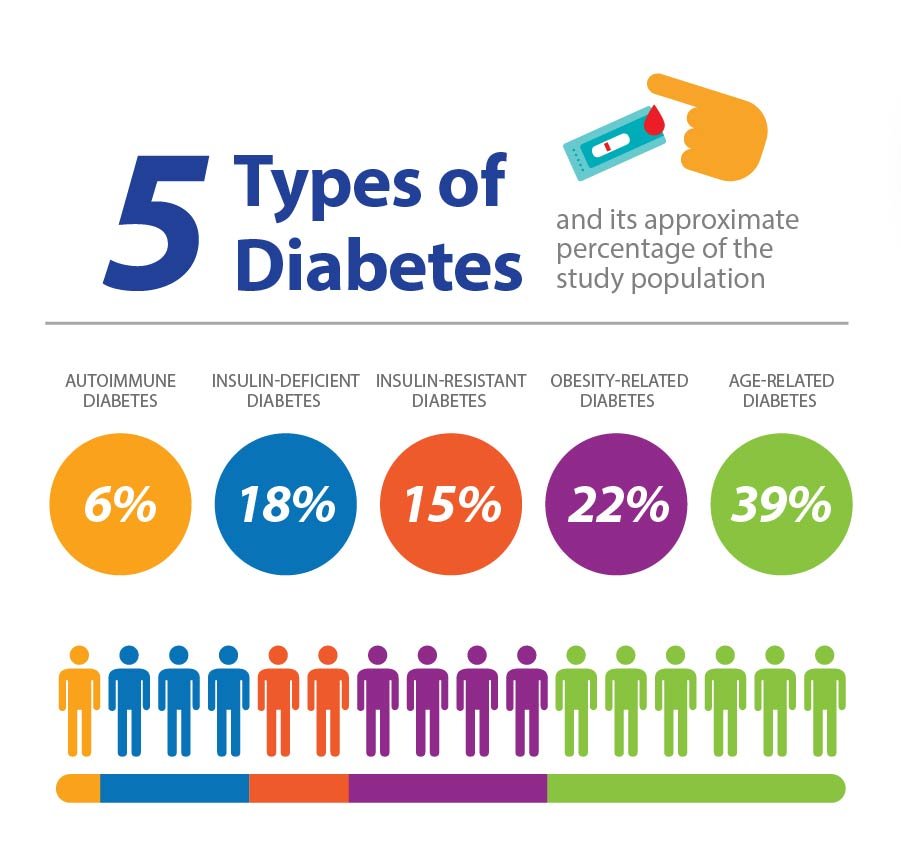
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
You May Like: Non Diabetic A1c Levels
Why Is My Blood Glucose Level High How Does This Happen
The process of digestion includes breaking down the food you eat into various different nutrient sources. When you eat carbohydrates , your body breaks this down into sugar . When glucose is in your bloodstream, it needs help a “key” to get into its final destination where it’s used, which is inside your body’s cells . This help or “key” is insulin.
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas, an organ located behind your stomach. Your pancreas releases insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks the cell wall door, which allows glucose to enter your bodys cells. Glucose provides the fuel or energy tissues and organs need to properly function.
If you have diabetes:
- Your pancreas doesnt make any insulin or enough insulin.
- Your pancreas makes insulin but your bodys cells dont respond to it and cant use it as it normally should.
If glucose cant get into your bodys cells, it stays in your bloodstream and your blood glucose level rises.
Which Type Of Diabetes Do I Have
In some cases, it may not be clear which type of diabetes you have. If your doctor cannot be sure which type of diabetes you have, they may run one or more tests to help determine your diabetes type
Learn about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
There are a number of different types of diabetes. In this video we look at 5 of the most common types of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes amongst adults about 85% of people with diabetes in the UK have type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the second most common approximately 15% of people with diabetes in the UK have type 1. There are also other less common types of diabetes including gestational diabetes, LADA and MODY.
The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, meaning that most people who develop type 2 diabetes are usually middle aged or older. However, type 2 diabetes can develop earlier in adulthood or even childhood. Diabetes UK reports that obesity accounts for over 80% of the overall risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Other risk factors include having a close family member with type 2 diabetes, being of African/Caribbea, South Asian or Middle Eastern descent, or having high blood pressure and/or cholesterol. Type 2 diabetes can be treated with diet and exercise alone, or with tablets, insulin or other injectable medication.
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes come on slowly and may take months or years to appear.
You May Like: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
What Are The Treatment Options
If youre living with diabetes, treatment is needed to live a full, healthy life. You need to keep your blood glucose levels and blood pressure as close to normal as possible3.
The treatment options are fairly similar for each type of diabetes, but should be discussed specifically with your doctor prior to moving forward. Treatment begins with monitoring your blood glucose levels with an at-home device. The American Diabetes Association recommends that most people with diabetes aim for the following treatment goals3:
- The target blood sugar goal before a meal is 80 mg/dl130 mg/dl3.
- When using a meter that gives plasma glucose levels, the target goal before a meal is between 90 mg/dl and 130 mg/dl3.
Almost every diabetic will take insulin, but Type 2 diabetes severity can be reduced with some major lifestyle changes.
If youve been diagnosed with diabetes and are looking for a way to safely and affordably purchase your diabetes supplies, learn more about our diabetes solutions today. today. We offer patients the ability to conveniently secure insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors, blood glucose test strips, and more. Our one source, total solution for diabetes care also offers a number of resources, educational updates, and great customer service.
Types Of Diabetes: Type 1 Diabetes
Results from the bodys failure to produce insulin, the hormone that unlocks the cells of the body, allowing glucose to enter and fuel them. It is estimated that 5-10% of Americans who are diagnosed with diabetes have type 1 diabetes. Most treatment is administered with insulin pumps.
Having type 1 diabetes increases your risk for many serious complications. Some complications of type 1 diabetes include heart disease , blindness , nerve damage , and kidney damage .
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Are The Lesser
Only about 2% of people have other types of diabetes worldwide. These include different types of monogenic diabetes, cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, and diabetes caused by rare conditions.
Certain medications like steroids and antipsychotics can lead to other types of diabetes.
People with these types of diabetes can face challenges getting a correct diagnosis, and sometimes wait months or years for answers to their medical questions.
The 3 Types Of Diabetes
It is estimated that over 200,000 people in Utah have diabetes and an astonishing 619,000 Utahns have prediabetes. Diabetes affects nearly 30 Million Americans and is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States.
November is diabetes awareness month, and while diabetes is a common word, many people are unable to distinguish between the three common types. Below are the main variations of type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
You May Like: Drawing Up Regular And Nph Insulin
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes
To diagnose type 1 diabetes you’ll need to get blood tests done, one of which is called an A1C screening. A1C screenings measure your blood sugar levels from the past two to three months and can be used to diagnose type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Life Line Screening also offers an A1C screening from the privacy of you own home through our home tests. You can learn more here.
How Are Different Types Of Diabetes Treated
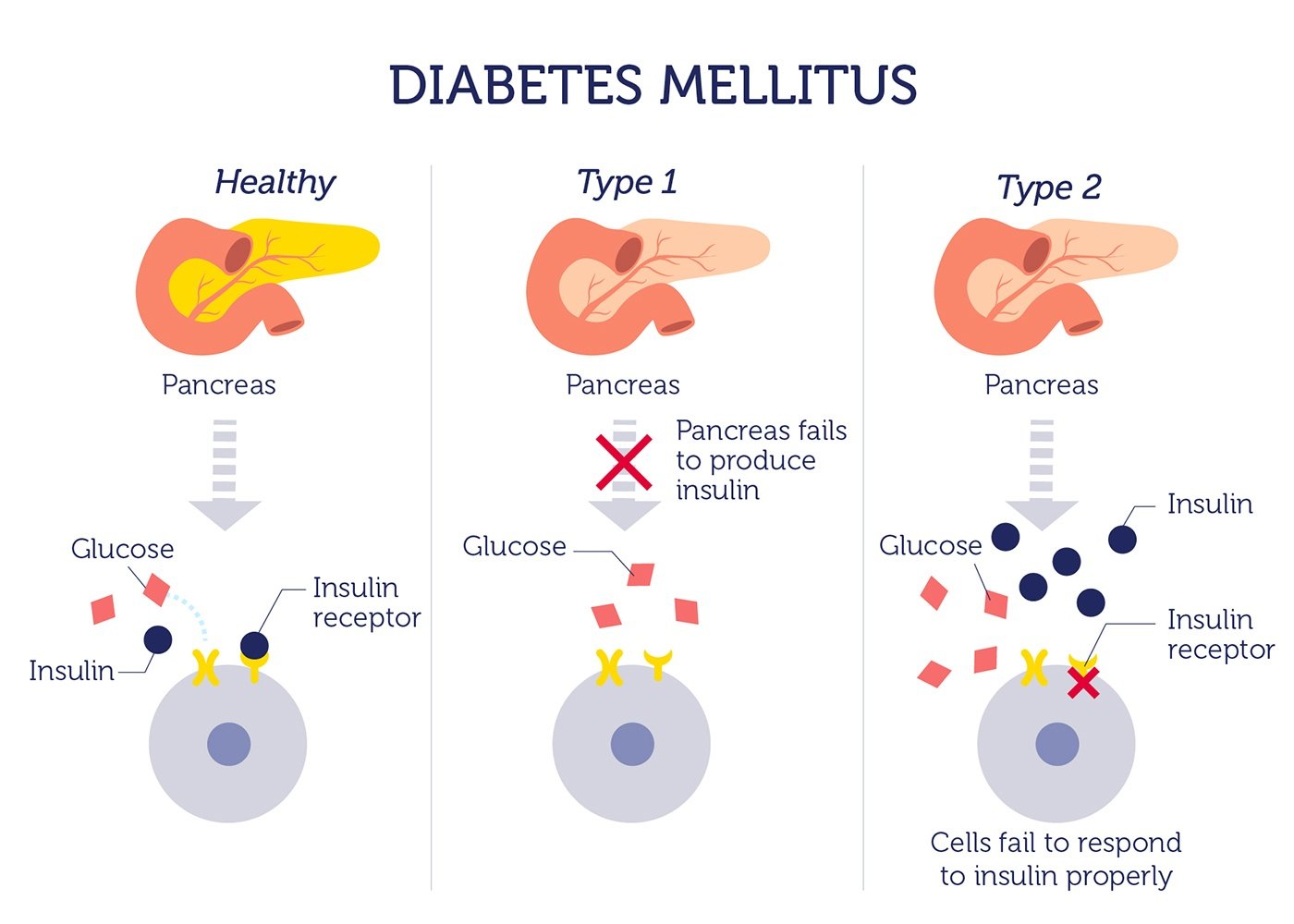
No matter what type of diabetes you have, youll need to work closely with your doctor to keep it under control.
The main goal is to keep blood glucose levels within your target range. Your doctor will let you know what your target range should be. Targets vary with the type of diabetes, age, and presence of complications.
If you have gestational diabetes, your blood sugar targets will be lower than people with other types of diabetes.
Physical activity is an important part of diabetes management. Ask your doctor how many minutes per week you should devote to aerobic exercise. Diet is also crucial to good control. Youll also need to monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol.
Also Check: Bananas Bad For Diabetics
The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2
30.3 million people have diabetes , in one type or another. 84.1 million adults aged 18 years or older have prediabetes (33.9% of the adult US population. But what exactly is Diabetes? There are a lot of myths and misunderstandings surrounding the disease, particularly when it comes to type 1 versus type 2.
So lets start with the basics.
The two main types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. In type 1 diabetes , the body completely stops making insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take daily insulin injections to survive. This form of diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but can occur at any age.In type 2 diabetes the body produces insulin, but the cells dont respond to insulin the way they should. This is called insulin resistance. In response to this insulin resistance, the pancreas should make more insulin, but in the case of type 2 diabetes, this does not happen. Because of these two problems, insulin resistance and trouble making extra insulin, there is not enough of an insulin effect to move the glucose from the blood into the cells. Type 2 diabetes is more likely to occur in people who are over the age of 40, overweight, and have a family history of diabetes, although more and more younger people, including adolescents, are developing type 2 diabetes.
Its important to know a few things about how your body works before you can take the best care of your diabetes.
Topics featured in this article
Maturity Onset Diabetes Of The Young
MODY is a rare form of diabetes which is different from both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and runs strongly in families. MODY is caused by a mutation in a single gene. If a parent has this gene mutation, any child they have, has a 50 per cent chance of inheriting it from them. If a child does inherit the mutation they will generally go on to develop MODY before theyre 25, whatever their weight, lifestyle, ethnic group etc.
Also Check: High Blood Sugar In Diabetics
Less Common Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes mentioned below affect far fewer people than the conditions outlined above, but they are just as important to know about.
Monogenic
Under the umbrella of monogenic diabetes syndromes there are two main categories: neonatal diabetes mellitus and maturity-onset diabetes of the young . Neonatal diabetes appears before a baby turns a year old while MODY emerges in adolescence or young adulthood. In those diabetes, there’s a single mutation that causes the disease, says Dr. Redondo.
She says researchers have identified some genes that can be affected, but there are many more potential variants to be discovered. It is really important because in some of those, the molecular defect is known and you can treat it with a specific treatment for that, explains Dr. Redondo. For example, people with a particular type of MODY used to be treated with insulin, thinking that they have type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes, but since this has been discovered, the molecular mechanism was known and then people realized that they respond better with sulfonylurea which is a type of oral medication. If youve been told your diabetes is atypical , Dr. Redondo recommends checking out the Rare and Atypical Diabetes Network and signing up to see if youre a fit for any research studies. The organization is trying to define lesser-known types of diabetes, advance testing, and identify proper treatments.
Chemical-induced
Cystic fibrosis-related
What They Have In Common
All types of diabetes are characterized by changes in the function of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to move glucose from the blood into cells, where it’s used for fuel.
Depending on the type of diabetes, either the pancreas does not produce insulin or the body is unable to use it as it should. Either way, without ample insulin or a healthy response to it, the sugar circulating in the blood cannot get into cells.
Early symptoms of diabetes, whatever the type, include fatigue, extreme thirst, and frequent urination.
If the disease progresses, a number of complications are possible, including vision changes or loss , diabetic neuropathy , increased risk of heart disease, kidney damage, and more.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
An absolute lack of insulin, usually due to destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, is the main problem in type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes was formerly referred to as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus . Its causes are different from type II diabetes, as will be reviewed in this article.
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.

