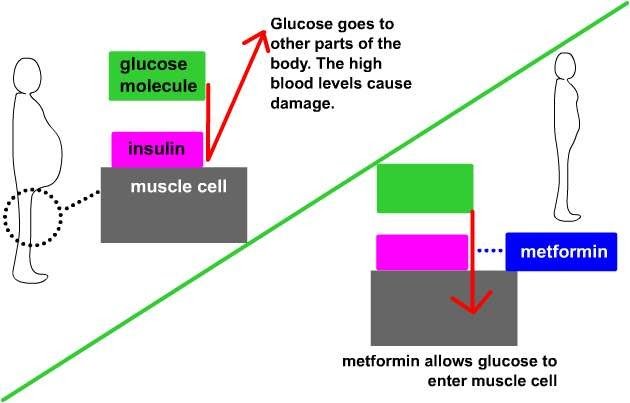
How Does Metformin Work
The medicine does not increase insulin levels in the body, but instead lessens the amount of sugar the body produces and absorbs. As it lowers glucose production in the liver, metformin also lowers blood sugar by increasing the bodys sensitivity to insulin. It also decreases the amount of glucose that our bodies absorb from the foods we eat.
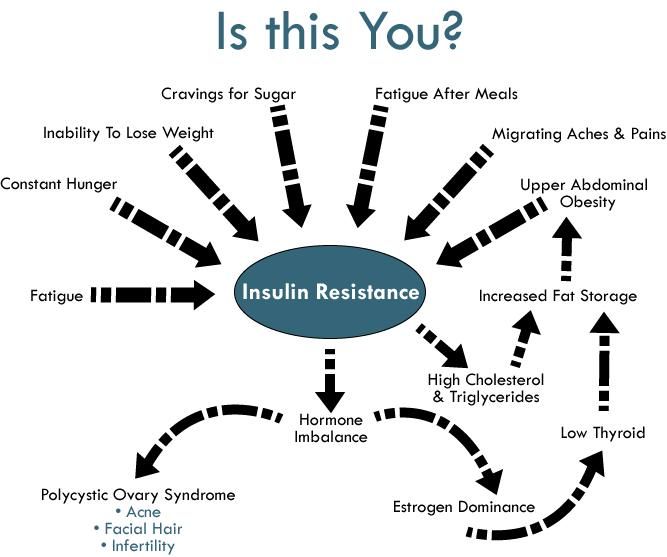
Options For Treating Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance affects as many as 70% of women with PCOS and is believed to be a main contributing factor to metabolic complications like high blood pressure, abdominal weight gain, and type 2 diabetes. The three best ways to improve insulin resistance are with diet, exercise, and medications and/or nutrition supplements.
Metformin And Exercise On Brain Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin impacts the central nervous system by regulating hepatic glucose production, food intake and adipose metabolism, vasodilation/vasoconstriction of blood vessels as well as pancreatic insulin secretion and skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity . Although these effects of insulin are clearly important for systemic glucose control, more recent work highlights that insulin also impacts memory, mood, and cognition . Interestingly, Williams et al. demonstrated direct effects of insulin on memory using intravenous insulin administration via a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp in 12 healthy older adults. In particular, this improvement in memory was related to increased blood oxygen level-dependent signaling as measured by functional MRI during the clamp . Furthermore, improved memory was best in those individuals with the highest systemic insulin sensitivity. This suggests that declines in insulin sensitivity may contribute to brain pathology in the hypothalamus . Not surprisingly, this may relate to cognitive decline , cerebral atrophy as well as low brain blood flow and metabolism across aging . Additionally, this altered brain insulin action may be a key pathological factor in regulating glycemic control in individuals with obesity, T2D, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease .
Read Also: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Take Medications As Prescribed
Doctors typically prescribe metformin as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes and also recommend changes to diet and activity levels. Metformin does not lower blood sugar levels instantly like insulin injections. It may take a few weeks or months for a doctor to be able to tell whether metformin is working.
Certain medications, including insulin and a group of drugs called sulfonylureas, can reduce blood sugar levels much more rapidly. However, a common side effect of sulfonylureas is low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia.A doctor will provide clear instructions about how to take medication to maximize the benefits and minimize the risk of side effects. Taking medication in any other way can be extremely dangerous.
What Does It Mean For Your Health
Insulin resistance comes in degrees. The more insulin resistant a person with type 2 is, the harder it will be to manage their diabetes because more medication is needed to get enough insulin in the body to achieve target blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance isn’t a cause of type 1 diabetes, but people with type 1 who are insulin resistant will need higher insulin doses to keep their blood sugar under control than those who are more sensitive to insulin. As with type 2, people with type 1 may be genetically predisposed to become insulin resistant, or they may develop resistance due to being overweight. Some research indicates that insulin resistance is a factor in cardiovascular disease and other complications in people with type 1.
Recommended Reading: What Makes Insulin In The Body
Reduce The Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates contribute to raising blood sugar. However, not all carbohydrates are bad for people with diabetes.
Foods that rank high on the glycemic index cause blood sugar levels to rise quickly, while foods that rank low have less drastic and immediate effects.
Diabetes Canada provide the following examples of carbohydrate-rich foods that rank low, medium, and high on the glycemic index.
| Low glycemic index foods |
Response From Mary Anne Dumas Phd Rn Cfnp Faanp
In order to understand the role of metformin in insulin resistance and obesity, it is essential to understand the pathophysiology of both clinical problems and the pharmacologic mechanisms of metformin. Insulin resistance occurs when there is an impairment of insulin transport at either the prereceptor, receptor, or postreceptor sites. Insulin resistance occurs in obese individuals, usually at the postreceptor site, where there is an apparent failure to activate the postreceptor tyrosine kinase. Failure of the cellular transport of insulin results in hyperglycemia, requiring greater amounts of insulin to maintain euglycemia . Euglycemia may be maintained for a long period by hyperinsulinemia; however, insulin levels are not able to sustain control glucose levels, and hyperglycemia results.
Metformin is a biguanide that has been demonstrated to decrease hepatic glucose production and improve peripheral insulin sensitivity. Metformin benefits individuals with diabetes by:
Reducing lipid levels ;
Facilitating postreceptor transport of insulin; and
Facilitating weight loss.
Each of these benefits of metformin leads to a physiological environment in which peripheral insulin sensitivity is improved, and insulin resistance is reduced.
Practice guidelines for metformin use:
Population:
Obese individuals with impaired glucose
Individuals with type II diabetes, as primary or secondary agent
Metformin dosing:
Maximum dose 2550 mg in divided doses, lower for elderly patients
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know When Your Blood Sugar Is Low
What Are The Common Side Effects Of Metformin
Another great thing about metformin is that, compared to other diabetes medications, it typically causes mild side effects. The most common side effects of metformin are related to stomach discomfort, like gas, upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea, or cramping.
You can limit these side effects by:
- Starting with a low dose of metformin and gradually increasing the dose. This gives your body time to get used to the new medication.
- Taking metformin with food. Taking the medication with food will help you feel less sick or nauseous.
- Taking an extended-release version of metformin. Instead of all the medication being released into your body and absorbed at once, metformin ER is released and absorbed over an extended period of time. This makes it easier on your digestive system.
What Is The Average Weight Loss With Metformin
About 4 or 5 pounds, says Dr. Apovian, who prescribes metformin along with one of the approved drugs for obesity for people who have diabetes and obesity or prediabetes and obesity to help with bigger weight loss. If someone has obesity, you always need another agent aside from metformin. The heavier a person is, the better they are likely to drop a few pounds on metformin, and research shows that the weight loss in people with diabetes who stay on the the drug lasts.
Recommended Reading: How Many Nuts Can A Diabetic Eat
What Are The Most Common Side Effects Of Metformin
Metformin does cause side effects in some people, but many of these are mild, and are associated with taking the medicine for the first time. Nausea and gastric distress such as stomach pain, gas, bloating, and diarrhea are somewhat common among people starting up on metformin.
For some people, taking large doses of metformin right away causes gastric distress, so its common for doctors to start small and build the dosage up over time. Many people start with a small metformin dose 500 milligrams once a day and build up over a few weeks until the dosage reaches least 1,500 milligrams daily. This means theres less chance of getting an upset stomach from the medicine, but also means it may take a bit longer to experience the full benefit when getting started on metformin.
I experienced some mild side effects when I started taking metformin, and I found that the symptoms correlated with how many carbs I had in my diet. Once I dropped my carbs to 30-50 grams per day something that took me weeks to do any symptoms of gastric upset went away.
Asking your doctor for the extended-release version of metformin can keep these symptoms at bay, and so can tracking your diet.
Does Metformin Have Any Side Effects
In general, healthy young people dont experience many side effects. About a third of people who take Metformin have stomach upset such as nausea, diarrhea, gas, and loss of appetite. Some people may complain of a metallic taste. If the side effects are a problem for you, its important to talk with your health care provider. You may be able to lower your dose for a few days and slowly build back up to your regular dose.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Metformin To Treat Obesity In Children With Insulin Resistance
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : May 22, 2000Results First Posted : April 7, 2011Last Update Posted : May 8, 2015 |
- Study Details
This study will examine the safety and effectiveness of the medicine metformin to help overweight children control their food intake, weight, insulin, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Obesity and high insulin levels can lead to high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels and heart disease. Metformin-approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus-helps lower insulin levels and may control weight gain in adults.
Participants will be hospitalized for 2-3 days for the following procedures: history and physical examination; fasting blood test; several urine collections; X-ray studies to determine bone age and amount of body fat and muscle; magnetic resonance imaging scan to measure body fat; “hyperglycemic clamp study” to evaluate insulin resistance; food intake testing; nutrition consultation; resting metabolic rate; and a “doubly labeled water” test.
| Drug: Metformin HCLDrug: Placebo | Phase 2 |
Pregnancy.
Different Types Of Metformin
When you get your prescription;you might notice that it has a different name. That’s because there are many different brands out there that provide the drug metformin. But the important thing for you to know is that the medication you’ve been given is metformin. Speak to your doctor if you have any questions.;
Metformin comes in the following brands:
- Bolamyn
- Glucophage
- Metabet.
You can also be given metformin in combination with other diabetes medication all in the same tablet. This is because;on its own it doesn’t always work and so needs support from other medicines.;
Diabetes medication often exists in groups or families depending on how they work. Metformin is part of the biguanide family and it’s the only type of diabetes medication in this group.;
Metformin is the most common treatment for type 2 diabetes
Recommended Reading: What Does A Diabetes Rash Look Like
Metformin For Insulin Resistance
Metformin is the most common treatment for type 2 diabetes, the form of the disease most closely related to obesity, according to The British Diabetic Association. It belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides and is available in generic form as well as brand names such as Glucophage, Fortamet, Glumetza and Riomet. Metformin can be used alone or with other medications, depending on each person’s medical needs.
“Everybody with type 2 diabetes goes on metformin as soon as possible because it offers so many advantages,” says Gerald Bernstein, MD, director of the diabetes management program at Friedman Diabetes Institute in New York City. “In terms of diabetes, metformin helps control blood sugar by reducing the amount of glucose absorbed from food and decreasing the levels of glucose produced by the liver.” In addition, it helps the body better use insulin, he says.
These benefits may even start before you develop full-blown type 2 diabetes, he adds. Insulin resistance occurs when your insulin doesn’t work as well as it should and your blood sugar levels rise. This condition is a precursor to diabetes it’s called prediabetes and metformin may help prevent or delay the disease, according to National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
Pcos: Insulin And Metformin
- PCOS is a hormone imbalance that can cause irregular periods, unwanted hair growth, and acne.
- The tiny cysts on the ovaries arent harmful and dont need to be removed.
- The treatment for PCOS is healthy nutrition, exercise, and medications.
Young women with PCOS often have elevated insulin levels and are more likely to develop diabetes. Metformin is a medication often prescribed for women with PCOS to help prevent or treat diabetes. A lifestyle that includes healthy nutrition and daily exercise is an important part of a PCOS treatment plan.
Don’t Miss: Do You Need Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
Metformin Improved Insulin Resistance
|
Figure 1 Metformin improved insulin resistance. The increase of glucose consumption in insulin-resistant cells induced by 1.5 and 2.0 nmol/L metformin with the absence of insulin. In the presence of insulin, 0.52.0 nmol/L metformin increased the glucose consumption of insulin-resistant cells, and the increment was larger than that of the group with metformin alone. ITT results of insulin-resistant rats. GTT results of insulin-resistant rats. *Indicated P<0.05, **Indicated P<0.01, and ***Indicated P<0.001 compared with the model group. |
Should You Take Metformin
These questions will help you decide if metformin can help you:
Do you have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes?
Are you having trouble controlling your blood sugar?
Are you free of liver or kidney disease?
Do you have polycystic ovary syndrome?
If you answered yes to all or most of these questions, you might want to talk to your health care provider about taking metformin.
- Related:
Recommended Reading: How To Instantly Lower Blood Sugar
Influence Of Metformin And Exercise Vasculature Function
Insulin promotes vasodilation in large conduit arteries and resistance arterioles as well as microvasculature perfusion . Conduit and resistance arteries are important for the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to metabolically active tissues, whereas the microvasculature provides a critical role in the exchange of these substances. In turn, adequate insulin-stimulated blood flow and endothelial function are essential for glucose regulation. However, during periods of physical inactivity and/or nutrient excess, hyperinsulinemia develops and has been related to elevated endothelin-1 mediated vasoconstriction. This impaired glucose delivery may not only increase risk for T2D but also contribute to endothelial dysfunction through lower nitric oxide bioavailability. Interestingly, people with insulin resistance have been noted to have normal fasting vascular function, but impaired conduit or microvascular insulin action . This demonstrates that mechanisms underlying disease states may be unique in the fasted vs. insulin-stimulated state.
Are There Any Reasons Not To Take Metformin
People with kidney or liver problems should not take Metformin. Your health care provider will check your blood to make sure that you do not have blood, kidney or liver problems before you start Metformin and then usually once a year after that. If you get sick and throw up or have diarrhea, call your health care provider and stop your Metformin until you feel completely well. Its very important not to be dehydrated while taking Metformin. You should not binge drink alcohol and take Metformin. Also, if youre going to have surgery or a medical or dental procedure where you cant have anything to eat or drink, talk to your health care provider about stopping the Metformin for 48 hours before the procedure. If youre scheduled for an Xray that includes a contrast material , you should talk to your health care provider about stopping your Metformin for up to 48 hours before and after the test. Getting dehydrated, having kidney problems, or having a serious infection can cause the rare condition called lactic acidosis, so its important to talk to your health care provider about any of these problems.
You May Like: What Does Insulin Do In The Body
What You Should Know About Metformin
Side Effects: You might experience abdominal bloating, nausea, or diarrhea when you begin taking metformin. For most people these symptoms go away quickly, but some people are unable to tolerate metformin.
The recommendation is for your health care provider to start off with a low dose .This can help you minimize or avoid symptoms and determine any side effects you might have. It also helps you and your provider to track the impact on your blood sugar levels. If you need a larger dose to further lower your blood sugar, your health care provider can slowly increase the dosage. About 2,000 mg/day is the largest effective dose.
An extremely rare but potentially serious complication of using metformin is lactic acidosis. When you metabolize metformin, lactic acid is produced and can build up to toxic levels. This happens only in people with kidney disease, which is why people with significant kidney problems are not good candidates for metformin.
Another reason for lactic acidosis is excessive alcohol intake or binge drinking. If you take metformin, avoid drinking more than a moderate amount of alcohol. Talk to your provider if you have concerns about the use of metformin and your alcohol intake.
Metformin And Type 1 Diabetes
It will be an exciting development if metformin is helpful in the treatment of cancer or neurodegenerative conditions like Huntingtons. But what if it is found to help people managing type 1 diabetes?
Metformin is not currently approved by US or European regulatory agencies for use in type 1s, but people have been known to take the medication anyway, and many doctors prescribe it if someone with type 1 diabetes is overweight. There are actually several reasons metformin is an attractive option for many type 1s. One, metformin has been found to help reduce glucose production in the liver, which is a problem in type 1 diabetes. Two, people often form resistance to the insulin they take, and metformin can help improve insulin sensitivity.
And, metformin may support weight loss and protection against heart disease. A study published in the Lancet following type 1 participants for three years found that compared to placebo, participants taking metformin lost weight. Particularly because insulin often causes weight gain, healthcare providers prescribe metformin off-label to their type 1 patients. While the study didnt find that metformin definitively protects against heart disease, based on observed trends in the data, the authors concluded that it may have a role in heart disease risk management.
Don’t Miss: Is Whole Wheat Pasta Good For Diabetics

