How Long Does Alcohol Affect Your Blood Sugar
Alcohol affects your blood sugar for as long as it is in your body. The effects of alcohol on your blood sugar will initially increase as the sugar from alcohol enters your blood, then peak once the maximum amount of sugar in the alcohol has been absorbed. This often occurs in about 12 hours.
Once your body has absorbed all the sugar it can from alcohol, it will start to use up the sugar, decreasing your blood sugar levels. As the liver inhibits the release of more sugar, your blood sugar levels will lower. This makes your blood sugar artificially low as long as the alcohol keeps impacting your livers normal function. Once enough alcohol has been eliminated, your liver will regain the ability to release sugar. This often takes about 12 hours.
Why Does Alcohol Make Blood Sugar Levels Drop
Alcohol makes your blood sugar levels drop by inhibiting the livers ability to release glucose. Alcohol also creates an initial sugar spike that makes your body process sugar at a higher rate, causing the spike in sugar to be quickly metabolized below what is normal. When these two factors are combined, it makes your blood sugar levels drop after the initial spike in sugar.
The Insulin Secretion Signaling Pathway
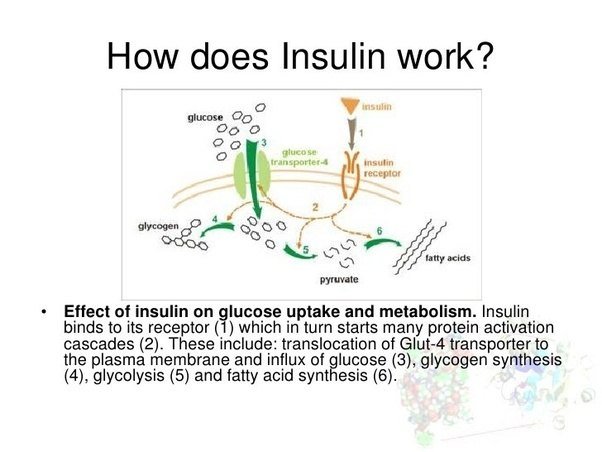
Endocrine cells secrete their respective hormones in response to external signals, such as nutrient intake or stress, via humoral, neural or hormonal signaling pathways. The underlying molecular process that translates the stimulus into the actual hormone release is called stimulus-secretion coupling which is known as the stimulus-dependent exocytosis of a particular substance, such as glucose-stimulated -cell insulin release.
Glucose-stimulated insulin release from a pancreatic -cell. Exogenous glucose is taken up by GLUT2 and undergoes glycolysis inside the cell. Elevated adenosine triphosphate levels alter the ATP/ADP ratio, which in turn leads to the closure of ATP-sensitive K+-channels. The subsequent membrane depolarization opens voltage-dependent Ca2+-channels in response to increasing intracellular calcium levels, which eventually trigger insulin secretion following vesicle fusion with the membrane.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin, glucose stays in the blood and can’t get into the body’s cells to be used for energy. This can happen, for example, when someone skips doses of insulin or when the need for insulin suddenly increases and the doses are not adjusted.
When the body can’t use glucose for fuel, it starts to use fat. When this happens, chemicals called ketones are released into the blood. Some of these ketones, like extra glucose, pass out of the body through the urine.
High levels of ketones in the blood can be a problem because they cause the blood to become acidic. Too much acid in the blood throws off the body’s chemical balance and causes the symptoms listed below. In people with diabetes, this problem is called diabetic , or DKA. DKA is a very serious condition that can lead to coma or death if it’s not treated. The good news, though, is that it’s preventable and can be treated.
DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but can sometimes also happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
Genes To Regulate Blood Glucose Levels
Genetics is identifying a whole new set of genes, proteins and pathways that are related to diabetes and blood sugar control. Till now, scientist have identified a genetic disorder in MafA . Surprisingly, this genetic defect was present in an unrelated family along with diabetic and insulinoma family members. The link of this gene with a defect was detected for the first time and a stable resultant mutant protein was found with a longer life in the cell, and found to be significantly more abundant in -cells than its normal version .
Gene on chromosome-2 is linked with fasting glucose levels and is primarily expressed in pancreatic -cells to convert glucose-6-phosphate back to glucose. Its genetic variation may be responsible for reduction in insulin secretion that increases glucose concentration. Chronically elevated levels of glucose may be a precursor for type 2 diabetes .
13 new genetic variants has been discovered by an international research consortium and these variants can manipulate blood glucose regulation, insulin resistance and function of insulin-secreting -cells in European descent populations, in which 05 of the following newly discovered variants raised the risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
SNPs in the region of ADCY5 which influence fasting and postprandial glucose levels.
FADS1 which is linked with fasting glucose as well as lipid traits.
Only one variant, near IGF1 which is associated with insulin resistance
You May Like: What Happens If A Diabetic Eats Too Much Sugar
The Important Roles Of Insulin And Glucagon: Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
The human body wants blood glucose maintained in a very narrow range. Insulin and glucagon are the hormones which make this happen. Both insulin and glucagon are secreted from the pancreas, and thus are referred to as pancreatic endocrine hormones. The picture on the left shows the intimate relationship both insulin and glucagon have to each other. Note that the pancreas serves as the central player in this scheme.; It is the production of insulin and glucagon by the pancreas which ultimately determines if a patient has diabetes, hypoglycemia, or some other sugar problem.
Type 2 Diabetes And Insulin
Getting Started
When most people find out they have Type 2 diabetes, they are first instructed to make changes in their diet and lifestyle. These changes, which are likely to include routine exercise, more nutritious food choices, and often a lower calorie intake, are crucial to managing diabetes and may successfully lower blood glucose levels to an acceptable level. If they do not, a drug such as glyburide, glipizide, or metformin is often prescribed. But lifestyle changes and oral drugs for Type 2 diabetes are unlikely to be permanent solutions. This is because over time, the pancreas tends to produce less and less insulin until eventually it cannot meet the bodys needs. Ultimately, insulin is the most effective treatment for Type 2 diabetes.
There are many barriers to starting insulin therapy: Often they are psychological; sometimes they are physical or financial. But if insulin is begun early enough and is used appropriately, people who use it have a marked decrease in complications related to diabetes such as retinopathy , nephropathy , and neuropathy . The need for insulin should not be viewed as a personal failure, but rather as a largely inevitable part of the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. This article offers some practical guidance on starting insulin for people with Type 2 diabetes.
Also Check: Can Type 2 Diabetics Donate Blood
Exercise And Blood Sugar
Exercise can have a big effect on your blood sugar levels because blood sugar is used for energy. When you use your muscles, your cells absorb sugar from the blood for energy.
Depending on the intensity or duration of exercise, physical activity can help lower your blood sugar for many hours after you stop moving.
If you exercise regularly, the cells in your body may be more sensitive to insulin. This will help keep blood sugar levels within normal ranges.
Measurement Of Insulin And Insulin Resistance
There are a variety of approaches to the laboratory assessment of insulin resistance. Over the years the limited specificity of older radio-immunoassays that cross-react with proinsulin have reduced the credibility of measuring insulin resistance in clinical settings. Current assays have improved specificity and precision. A comprehensive review of insulin assays is beyond the scope of this review and the reader is encouraged to consult Sapin in this regard. Insulin resistance may be measured by looking directly at insulin mediated glucose uptake in the basal or post-stimulated state, by inference from the relative concentrations of glucose and insulin, or by looking at surrogate markers of insulin action.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
What Will Insulin Be Like In The Future
Pharmaceutical companies are working on very long-acting versions of insulin that could last for a week. There is also an ultra-fast version of insulin under development that will act in less than 15 minutes.
Another group of researchers is looking at glucose responsive insulin , which would react to the needs of your body in real time. It would have nanosensors bound to the insulin so that when insulin is needed, it releases, and when it isnt, it stops, according to Dr. Hirsch.
Alcohol And Blood Sugar When You Have Diabetes
The livers functionality is an important part of understanding how alcohol affects blood sugar. Your liver is a key component when it comes to regulating your blood sugar levels throughout the day. When you drink, it impacts the liver and, more specifically, its ability to release glucose into your bloodstream as its supposed to. Alcohol impairs liver function and can keep your liver from releasing enough glycogen to keep your blood glucose levels from going too low. So, if you have diabetes, drink alcohol and take insulin as a medicine, you may experience hypoglycemia.
With alcohol and blood sugar, blood sugar can increase, then decrease to a dangerous point. This occurs because alcohol is high in sugar, causing an initial spike. Your body releases insulin to bring this high sugar level down and inhibits the release of more sugar from the liver. This causes your blood sugar to initially spike, then to decrease. This can be especially dangerous if you are using insulin or other diabetes medications because it can lead to hypoglycemia.
Also Check: Early Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus
How Are High Blood Sugar Levels Treated
Treating high blood sugar levels involves fixing what caused them in the first place. Your diabetes health care team will give you specific advice on how to keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. But here are some ways to manage the common causes of high blood sugar levels:
| Reason for High Blood Sugar Level | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Not getting enough insulin or other diabetes medicine |
|
| Not following the meal plan |
|
| Not getting enough exercise |
|
| Illness or stress |
|
| Use of other medicines that can increase blood sugar |
|
page 3
Why Is My Cats Blood Sugar So High
Cat Diabetes and Glucose Fluctuations. But even if that is not the cause of your cats high readings, sometimes giving too much insulin can cause these spikes as well. What happens in this case is that your cats glucose actually gets too low, and it causes rebound effect, creating a skyrocketing blood glucose level later in the day.
Also Check: Can You Be Skinny And Have Diabetes
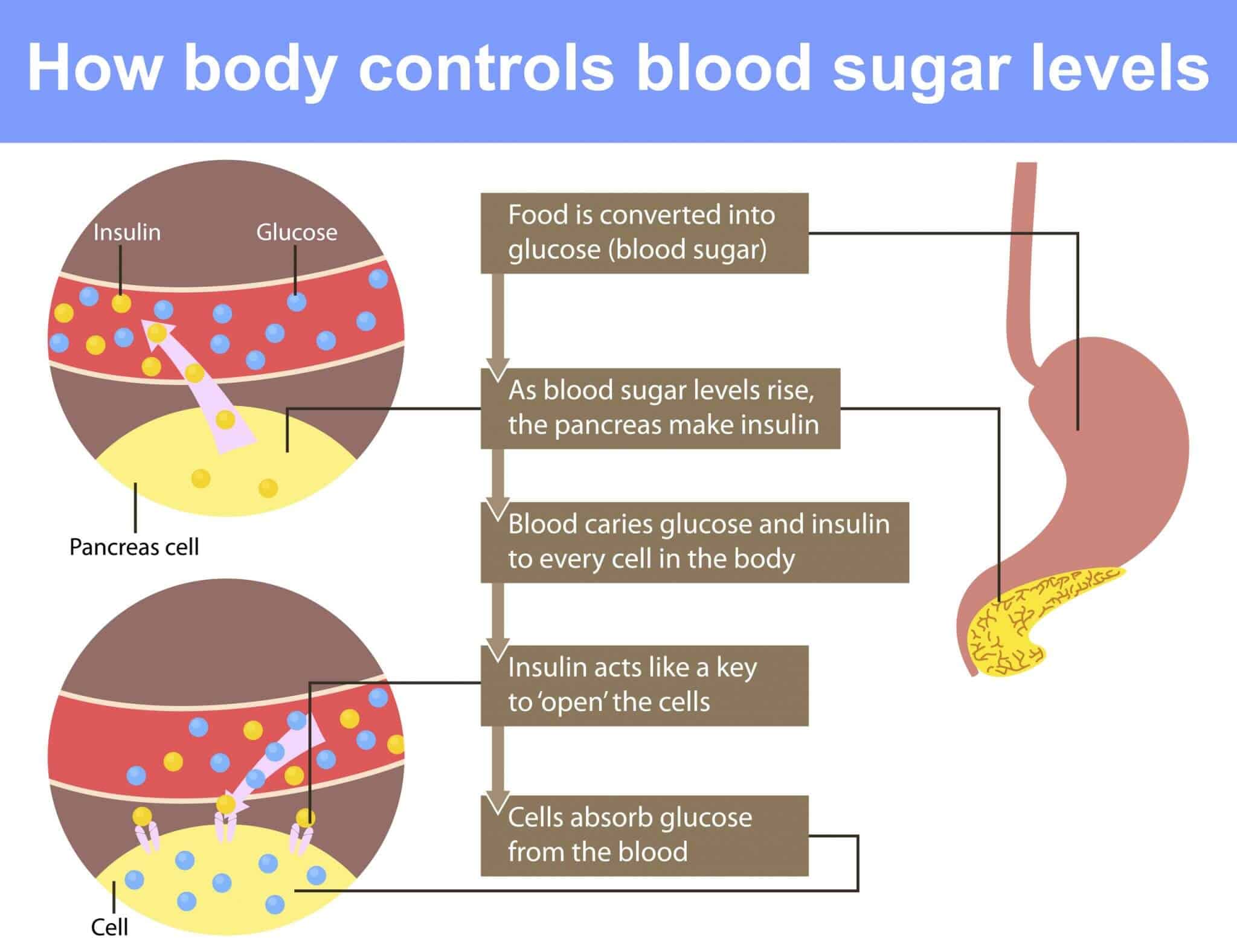
Insulin And Blood Sugar
Insulin is an important hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar levels. The pancreas makes insulin. It helps control your blood sugar levels by assisting the cells that absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body doesnt make insulin. This means you have to inject insulin every day.
If diet and exercise arent enough to manage blood sugar, those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications to help keep blood sugar levels within target ranges.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body produces insulin, but may not use it properly or produce enough of it. Your cells dont respond to insulin, so more sugar keeps circulating in the blood.
Exercise can help the cells respond better and be more sensitive to insulin. The proper diet can also help you avoid spikes in blood sugar. This can help keep your pancreas functioning well since high blood sugar levels decrease pancreatic function.
Insulin And The Bloodbrain Barrier
Insulin levels in cerebrospinal fluid are much lower than plasma insulin levels, but are highly correlated with them , which suggests that brain insulin originates predominantly from circulating pancreatic insulin that crosses the bloodbrain barrier . The cerebral BBB is established by tight junctions between endothelial cells and serves to protect the brain from diffusion of neuroactive nutrients , infectious agents, inflammatory molecules, and other substances in the systemic circulation. The BBB allows passive diffusion of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and highly lipid-soluble molecules, whereas glucose, amino acids, hormones such as insulin, and most other peptide, free fatty acids, and carbohydrate entities cross via selective transporters. Insulin crosses the BBB primarily via selective receptor-mediated transport . Insulin binding receptors located on capillary endothelial cells are presumed to be the same as those involved in canonical insulin signaling, but whether the insulin-binding transporter is the same gene product or an isoform remains to be established.
N.B. Panda, … A. Swain, in, 2017
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Modulating Insulin Secretion As A Means Of Diabetes Therapy
Due to the worldwide, still spreading epidemic of T2DM, there is an urgent need for anti-diabetic drugs and therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Currently, the most commonly used drugs can be classified into agents that enhance insulin secretion and incretin mimetics), sensitize the target organs of insulin , or reduce glucose absorption from the gastrointestinal tract . Different therapies address different problems and stages of T2DM and may be prescribed in combination to exert synergistic effects.
The Discovery Of Insulin
In 1889 German scientists Minkowski and von Mering noted, from their experimental work with animals, that total pancreatectomy led to the development of severe diabetes. They hypothesised that a substance secreted by the pancreas was responsible for metabolic control. Others later refined this hypothesis, noting diabetes to be associated with destruction of the islets of Langerhans. While Minkowski, as well as Zuelzer in Germany and Scott in the USA attempted, with inconsistent results, to isolate and administer the missing pancreatic islet substance, Belgian investigator de Meyer in 1909 proposed the name insuline, as did British researcher Schaefer in 1916.
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Soda Raise Insulin Levels
What Causes Someone To Be Prescribed Insulin
If your body doesnt make insulin or doesnt make enough, you are eventually diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. It used to be called juvenile diabetes, but new estimates show that as many as half of people with type 1 diabetes are not diagnosed until adulthood. On the other hand, if your body doesnt use insulin properly, you have type 2 diabetes.
While people with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin to survive, many people with type 2 are able to stave off insulin use or even avoid it altogether by exercising, losing weight, adapting healthier eating habits, or using other prescription medications.
What Is High Blood Sugar
The is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat, and it’s also formed and stored inside the body. It’s the main source of energy for the cells of our body, and it’s carried to each cell through the bloodstream.
Hyperglycemia is the medical word for high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels happen when the body either can’t make insulin or can’t respond to insulin properly . The body needs insulin so glucose in the blood can enter the cells of the body where it can be used for energy. In people who have developed diabetes, glucose builds up in the blood, resulting in hyperglycemia.
Having too much sugar in the blood for long periods of time can cause serious health problems if it’s not treated. Hyperglycemia can damage the vessels that supply blood to vital organs, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems. These problems don’t usually show up in kids or teens who have had the disease for only a few years. But they can happen in adulthood in some people with diabetes, particularly if they haven’t managed or controlled their diabetes well.
Blood sugar levels are considered high when they’re above your target range. Your diabetes health care team will let you know what your target blood sugar levels are.
page 1
Don’t Miss: How Much Vitamin B12 Should A Diabetic Take
Learn More About Treatment Approaches>>
Large studies of people with Type 2 diabetes have shown that only about 30% of people taking two oral medicines have an HbA1c level of less than 7% after three years. Insulin is usually recommended as the initial therapy for diabetes if a persons HbA1c level at diagnosis is greater than 10% or if someones fasting blood glucose level is consistently above 250 mg/dl.
Studies have shown that many doctors wait until someones HbA1c level is higher than 9% to start insulin therapy, which often results in months or years of high blood glucose and an increased risk of developing complications later on. One unfortunate reality is that many busy medical practices are not set up to address the needs of people who take insulin. Starting insulin requires education and easy access to health-care providers who are knowledgeable about insulin therapy, including diabetes nurse educators, pharmacists, and doctors.

